You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Change’ category.
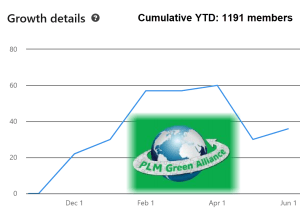 I am happy to see that the number of members of our PLM Green Global Alliance on LinkedIn has been growing fast recently.
I am happy to see that the number of members of our PLM Green Global Alliance on LinkedIn has been growing fast recently.
Early this year, we reached 1000 members; now, as of this post, we have almost 1200 members in our LinkedIn group—a growth of 20 % in less than half a year!
Each member of the #plmgreen alliance has a unique story and reason for joining.
 I’m genuinely interested in learning more about your motivation. To kick off this conversation, I am sharing my journey, and I am eager to hear your thoughts, comments, and suggestions.
I’m genuinely interested in learning more about your motivation. To kick off this conversation, I am sharing my journey, and I am eager to hear your thoughts, comments, and suggestions.
Being aware this is again a long read, but I encourage you to read the article till the end.
Reading a 1500-word post was a 20th-century skill that helped people understand things with their nuances.
Let’s not lose this skill in the 21st century!
How it all started
 Rich McFall reached out to me in late 2019, seeking individuals who shared our vision of establishing a platform for discussion and collaboration on green PLM. He was drawn to my 2015 blog post, ‘PLM and Global Warming,’ which I wrote six months before the famous Paris Agreement.
Rich McFall reached out to me in late 2019, seeking individuals who shared our vision of establishing a platform for discussion and collaboration on green PLM. He was drawn to my 2015 blog post, ‘PLM and Global Warming,’ which I wrote six months before the famous Paris Agreement.
In my 2015 blog post, I drew a parallel between the slow response to digital transformation in the PLM domain and our collective inaction against climate change.
Despite the growing awareness of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions, there needed to be more urgency. This post was a call to action, not just for digital transformation in the PLM domain, but for our planet’s future. The cartoon below illustrates this mindset:

Both Rich and I felt that, when possible, we should use our energy and PLM-related skills to bring together a community of people who would take Climate Change and Sustainability seriously.
 Rich’s focus was primarily on Climate Change and Greenhouse Gas emissions. – a hot topic in the US, where my passion and interest were related to Sustainability and the Circular Economy – two overlapping topics with a different impact, both parts of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) as formulated and adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015.
Rich’s focus was primarily on Climate Change and Greenhouse Gas emissions. – a hot topic in the US, where my passion and interest were related to Sustainability and the Circular Economy – two overlapping topics with a different impact, both parts of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) as formulated and adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015.
“Climate change creates fear and polarization, whereas the Circular Economy is more of a long-term concept, more complex to grasp, or implement, however crucial for the future of the planet.”
The start in 2020
 When we started in early 2020, a few people were interested in contributing to the alliance—their names are at the bottom of this post. After several internal Zoom meetings, we decided to focus on different Green areas.
When we started in early 2020, a few people were interested in contributing to the alliance—their names are at the bottom of this post. After several internal Zoom meetings, we decided to focus on different Green areas.
The themes are available here: PLM Green Themes, i.e., Sustainability, the Circular Economy, Climate Change, Green Energy and Life Cycle Assessment.
 In the beginning, the alliance was a small group of enthusiastic people supported by approximately 100 members in our LinkedIn group. As an organization of volunteers, we struggled with allocating time and resources to get the needed attention. In 2020, climate change and Sustainability were still niche topics in the PLM domain, and our audience was still small.
In the beginning, the alliance was a small group of enthusiastic people supported by approximately 100 members in our LinkedIn group. As an organization of volunteers, we struggled with allocating time and resources to get the needed attention. In 2020, climate change and Sustainability were still niche topics in the PLM domain, and our audience was still small.
Our interactive medium was the LinkedIn group, where comments and likes were easily shared. Our PLM Green Global Alliance website would be the place where we consolidate information—a challenging approach for us with limited skills and budget.
Starting the interviews in 2022
In 2022, we started interviewing PLM-related software vendors. Together with Klaus Brettschneider and, more recently, Mark Reisig, we were happy to discover what the major players in our PLM ecosystem were doing regarding Sustainability.
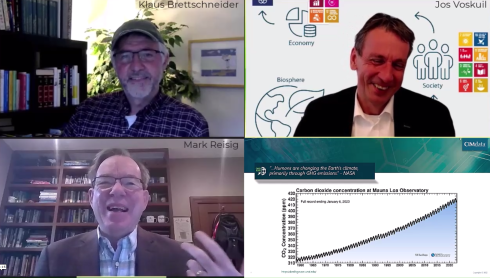
We spoke with SAP (Feb 2022 – Circular Economy), Autodesk (March 2020 – empowering engineers), Dassault Systemes (May 2022 – company targets & Virtual Twin), Sustaira (Sept 2022 – Connecting the dots – ESG reporting) and Aras (Oct 2022 – the need for a digital thread)
2023 – A year of transition
Besides the software vendors, consultancy firms started to address the need for more sustainable product development and understanding of what to do, and we spoke with CIMdata (April 2023 – the importance of sustainable business models) and Transition Technologies PSC (October 2023 – their GreenPLM offering on top of the PTC PLM suite)
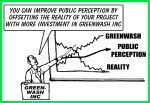 However, as a PLM Green Global Alliance, we discovered that more and more companies were considering moving away from greenwashing and toward implementing actual measures, some of them driven by upcoming regulations and country initiatives.
However, as a PLM Green Global Alliance, we discovered that more and more companies were considering moving away from greenwashing and toward implementing actual measures, some of them driven by upcoming regulations and country initiatives.
It was also a significant year for the PLM Green Global Alliance, as besides receiving increasingly encouraging messages, both CIMdata and CIMPA joined the alliance as moderators.
![]() CIMdata, well known for its PLM consultancy and market analysis, started an additional consultancy practice related to PLM and Sustainability.
CIMdata, well known for its PLM consultancy and market analysis, started an additional consultancy practice related to PLM and Sustainability.
Mark Reisig, their lead consultant, joined us on the themes of Sustainability and Energy, also given his previous work career in that field.
 CIMPA, a European PLM consultancy services company with roots in the aerospace industry, decided to support the alliance on the theme of the circular economy. Patrice Quencez and his team lead and moderate this activity.
CIMPA, a European PLM consultancy services company with roots in the aerospace industry, decided to support the alliance on the theme of the circular economy. Patrice Quencez and his team lead and moderate this activity.
Green in 2024 – what can we do?
Fear or Optimism? Fast and Slow!
 One of the negative characteristics of the human mind is that we only want to act if it is indispensable. The brain’s evolutionary characteristic is to use the maximum amount of energy when there is a dangerous situation that forces us to act.
One of the negative characteristics of the human mind is that we only want to act if it is indispensable. The brain’s evolutionary characteristic is to use the maximum amount of energy when there is a dangerous situation that forces us to act.
There is enough proof for this theory, and it is the main reason why we continue bad habits. The best book to recommend is Thinking Fast and Slow by Daniel Kahneman.
Ask yourself:
- Should you study for the whole year or just before the exams?
- Would you start smoking knowing it is likely killing you in the long term?
- Would you save money for later, as then you might need it?
- Would you spend hours/days mastering a topic, or would you be an expert on social media with some easy facts and statistics?
- Would you act against climate change and overconsumption, knowing the reasons?
All the above questions illustrate that the majority of us (me too – there are no saints anymore) think fast, and media and marketing organizations know our weaknesses.
 The result: we only get attention when there is a message of fear
The result: we only get attention when there is a message of fear
An explanation of why good news channels have no subscribers, whereas bad/fake news and polarising messages create an emotion to act.
In our PLM Green Alliance Group, Rich started with a monthly news digest related to Climate change. In the beginning, it felt like only bad news and the climate changes and disasters were showing us the urgency to handle. Read the last Climate Change Chronicles here.
Bad news and fear might paralyze people. You might think the topic is too big for me to handle; therefore, let’s do nothing. Do you remember the diagram below?
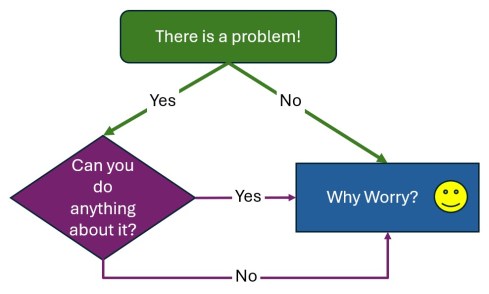
Fortunately, many people believe that something needs to be done.
 A recent UNDP survey shows that 80 percent of people globally want more decisive government climate action. Read the news here, and if you are interested in how your country compares to the rest of the world, check it here.
A recent UNDP survey shows that 80 percent of people globally want more decisive government climate action. Read the news here, and if you are interested in how your country compares to the rest of the world, check it here.
The good news is that the majority supports measures; the bad news is that the minority is the most vocal and influential by having the means and motives not to change the current status quo. And they have been organizing themselves for years.
Therefore, there is some optimism – we need to organize!
Looking back, particularly over the last 1½ years, there are reasons for optimism. Progress might not go as fast as desired, but if you are open to action and your newsfeed algorithm is also switched to positive, you will find encouraging messages.
For example, follow Assaad Razouk; his posts are often encouraging – not creating rage.
Read the monthly ESG Newsletters published by Vincent de la Mar from Sustaira and discover the positive trend. You can find his latest May newsletter here as an example: Sustainability & ESG Insights May ’24: Biden’s carbon market plans & how to get back on track to Paris Targets.
Following the progress within Europe – after the European Green Deal with all its aspects, recently, the Nature Restoration Law was signed, pushing companies to use more generative resources. The Nature Restoration Law and the European Green Deal are regulations pushing for a more circular economy as both the left side (regenerative) and right side (hardware) of the famous butterfly are addressed.
Conclusion
We are making progress, and I hope this post makes you realize that you need to worry about climate change and the Sustainability of our planet. My passion, and the passion of all the people listed below, is to support a movement and not to be silent.
Now, I am asking you to share your story. Which topics do we need to address first? Can you share examples or facts that illustrate—that with 1200 members, we should not be part of the silent majority but become a respected voice?
We’d like to express our exceptional gratitude to all those who supported us or are still supporting us at any stage of our PLM Green Global Alliance. Feel motivated to join this group of the non-silent majority.
In an alfabetical order: Xavier Adam, Zoe Bezpalko, Tom Boudeville, Klaus Brettschneider, Nina Dar, Stephane Declee, Dave Duncan, Stephan Fester, Bjorn Fidjeland, Ryan Flavelle, Matthias Fohrer, Roger L. Franz, Lionel Grealou, Jon den Hartog, Patrick Hilberg, Yousef Hooshmand, Hannes Lindfred, Ilan Madjar, Vincent de la Mar, James Norman, Rich McFall, Frank Popielas, Patrice Quencez, Mark Reisig, Audrey Reyniers, Erik Rieger, Ryan Rochelle, Mark Rushton, Neil D’Souza, Jonathan Thery, Oleg Shilovitsky, Florence Verzelen, Darren West ,Patrick Willemsen, Rafał Witkowski, Morgan Zimmermann.
 Another year passed, and as usual, I took the time to look back. I always feel that things are going so much slower than expected. But that’s reality – there is always friction, and in particular, in the PLM domain, there is so much legacy we cannot leave behind.
Another year passed, and as usual, I took the time to look back. I always feel that things are going so much slower than expected. But that’s reality – there is always friction, and in particular, in the PLM domain, there is so much legacy we cannot leave behind.
It is better to plan what we can do in 2024 to be prepared for the next steps or, if lucky, even implement the next steps in progress.
In this post, I will discuss four significant areas of attention (AI – DATA – PEOPLE – SUSTAINABILITY) in an alphabetic order, not prioritized.
Here are some initial thoughts. In the upcoming weeks I will elaborate further on them and look forward to your input.

AI (Artificial Intelligence)
![]() Where would I be without talking about AI?
Where would I be without talking about AI?
When you look at the image below, the Gartner Hype Cycle for AI in 2023, you see the potential coming on the left, with Generative AI at the peak.
Part of the hype comes from the availability of generative AI tools in the public domain, allowing everyone to play with them or use them. Some barriers are gone, but what does it mean? Many AI tools can make our lives easier, and there is for sure no threat if our job does not depend on standard practices.
AI and People
 When I was teaching physics in high school, it was during the introduction of the pocket calculator, which replaced the slide rule.You need to be skilled to uyse the slide rule, now there was a device that gave immediate answers. Was this bad for the pupils?
When I was teaching physics in high school, it was during the introduction of the pocket calculator, which replaced the slide rule.You need to be skilled to uyse the slide rule, now there was a device that gave immediate answers. Was this bad for the pupils?
If you do not know a slide rule, it was en example of new technology replacing old tools, providing more time for other details. Click on the image or read more about the slide rule here on Wiki.
![]() Or today you would ask the question about the slide rule to ChatGPT? Does generative AI mean the end of Wikipedia? Or does generative AI need the common knowledge of sites like Wikipedia?
Or today you would ask the question about the slide rule to ChatGPT? Does generative AI mean the end of Wikipedia? Or does generative AI need the common knowledge of sites like Wikipedia?
AI can empower people in legacy environments, when working with disconnected systems. AI will be a threat for to people and companies that rely on people and processes to bring information together without adding value. These activities will disappear soon and you must consider using this innovative approach.
 During the recent holiday period, there was an interesting discussion about why companies are reluctant to change and implement better solution concepts. Initially launched by Alex Bruskin here on LinkedIn , the debate spilled over into the topic of TECHNICAL DEBT , well addressed here by Lionel Grealou.
During the recent holiday period, there was an interesting discussion about why companies are reluctant to change and implement better solution concepts. Initially launched by Alex Bruskin here on LinkedIn , the debate spilled over into the topic of TECHNICAL DEBT , well addressed here by Lionel Grealou.
![]() Both articles and the related discussion in the comments are recommended to follow and learn.
Both articles and the related discussion in the comments are recommended to follow and learn.
AI and Sustainability
![]() Similar to the introduction of Bitcoin using blockchain technology, some people are warning about the vast energy consumption required for training and interaction with Large Language Models (LLM), as Sasha Luccioni explains in her interesting TED talk when addressing sustainability.
Similar to the introduction of Bitcoin using blockchain technology, some people are warning about the vast energy consumption required for training and interaction with Large Language Models (LLM), as Sasha Luccioni explains in her interesting TED talk when addressing sustainability.
She proposes that tech companies should be more transparent on this topic, the size and the type of the LLM matters, as the indicative picture below illustrates.

Carbon Emissions of LLMs compared
In addition, I found an interesting article discussing the pros and cons of AI related to Sustainability. The image below from the article Risks and Benefits of Large Language Models for the Environment illustrates nicely that we must start discussing and balancing these topics.
![]() To conclude, in discussing AI related to sustainability, I see the significant advantage of using generative AI for ESG reporting.
To conclude, in discussing AI related to sustainability, I see the significant advantage of using generative AI for ESG reporting.
ESG reporting is currently a very fragmented activity for organizations, based on (marketing) people’s goodwill and currently these reports are not always be evidence-based.
Data
 The transformation from a coordinated, document-driven enterprise towards a hybrid coordinated/connected enterprise using a data-driven approach became increasingly visible in 2023. I expect this transformation to grow faster in 2024 – the momentum is here.
The transformation from a coordinated, document-driven enterprise towards a hybrid coordinated/connected enterprise using a data-driven approach became increasingly visible in 2023. I expect this transformation to grow faster in 2024 – the momentum is here.
 We saw last year that the discussions related to Federated PLM nicely converged at the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference in Paris. I shared most of the topics in this post: The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2023. In addition, there is now the Heliple Federated PLM LinkedIn group with regular discussions planned.
We saw last year that the discussions related to Federated PLM nicely converged at the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference in Paris. I shared most of the topics in this post: The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2023. In addition, there is now the Heliple Federated PLM LinkedIn group with regular discussions planned.
In addition, if you read here Jan Bosch’s reflection on 2023, he mentions (quote):
… 2023 was the year where many of the companies in the center became serious about the use of data. Whether it is historical analysis, high-frequency data collection during R&D, A/B testing or data pipelines, I notice a remarkable shift from a focus on software to a focus on data. The notion of data as a product, for now predominantly for internal use, is increasingly strong in the companies we work with
 I am a big fan of Jan’s posting; coming from the software world, he describes the same issues that we have in the PLM world, except he does not carry the hardware legacy that much and, therefore, acts faster than us in the PLM world.
I am a big fan of Jan’s posting; coming from the software world, he describes the same issues that we have in the PLM world, except he does not carry the hardware legacy that much and, therefore, acts faster than us in the PLM world.
An interesting illustration of the slow pace to a data-driven environment is the revival of the PLM and ERP integration discussion. Prof. Jörg Fischer and Martin Eigner contributed to the broader debate of a modern enterprise infrastructure, not based on systems (PLM, ERP, MES, ….) but more on the flow of data through the lifecycle and an organization.
It is a great restart of the debate, showing we should care more about data semantics and the flow of information.
The articles: The Future of PLM & ERP: Bridging the Gap. An Epic Battle of Opinions! and Is part master in PLM and ERP equal or not) combined with the comments to these posts, are a must read to follow this change towards a more connected flow of information.
While writing this post, Andreas Lindenthal expanded the discussion with his post: PLM and Configuration Management Best Practices: Part Traceability and Revisions. Again thanks to data-driven approaches, there is an extending support for the entire product lifecycle. Product Lifecycle Management, Configuration Management and AIM (Asset Information Management) have come together.
![]() PLM and CM are more and more overlapping as I discussed some time ago with Martijn Dullaart, Maxime Gravel and Lisa Fenwick in the The future of Configuration Management. This topic will be “hot”in 2024.
PLM and CM are more and more overlapping as I discussed some time ago with Martijn Dullaart, Maxime Gravel and Lisa Fenwick in the The future of Configuration Management. This topic will be “hot”in 2024.
People
 From the people’s perspective towards AI, DATA and SUSTAINABILITY, there is a noticeable divide between generations. Of course, for the sake of the article, I am generalizing, assuming most people do not like to change their habits or want to reprogram themselves.
From the people’s perspective towards AI, DATA and SUSTAINABILITY, there is a noticeable divide between generations. Of course, for the sake of the article, I am generalizing, assuming most people do not like to change their habits or want to reprogram themselves.
Unfortunate, we have to adapt our skills as our environment is changing. Most of my generation was brought up with the single source of truth idea, documented and supported by science papers.
In my terminology, information processing takes place in our head by combining all the information we learned or collected through documents/books/newspapers – the coordinated approach.
 For people living in this mindset, AI can become a significant threat, as their brain is no longer needed to make a judgment, and they are not used to differentiate between facts and fake news as they were never trained to do so
For people living in this mindset, AI can become a significant threat, as their brain is no longer needed to make a judgment, and they are not used to differentiate between facts and fake news as they were never trained to do so
The same is valid for practices like the model-based approach, working data-centric, or considering sustainability. It is not in the DNA of the older generations and, therefore, hard to change.
The older generation is mostly part of an organization’s higher management, so we are returning to the technical debt discussion.

Later generations that grew up as digital natives are used to almost real-time interaction, and when applied consistently in a digital enterprise, people will benefit from the information available to them in a rich context – in my terminology – the connected approach.
 AI is a blessing for people living in this mindset as they do not need to use old-fashioned methods to acquire information.
AI is a blessing for people living in this mindset as they do not need to use old-fashioned methods to acquire information.
“Let ChatGPT write my essay.”
However, their challenge could be what I would call “processing time”. Because data is available, it does not necessarily mean it is the correct information. For that reason it remains important to spend time digesting the impact of information you are reading – don’t click “Like”based on the tittle, read the full article and then decide.
Experience is what you get, when you don’t get what you expect.
meaning you only become experienced if you learn from failures.
Sustainability
 Unfortunately, sustainability is not only the last topic in alphabetic order, as when you look at the image below, you see that discussions related to sustainability are in a slight decline at C-level at the moment.
Unfortunately, sustainability is not only the last topic in alphabetic order, as when you look at the image below, you see that discussions related to sustainability are in a slight decline at C-level at the moment.
I share this observation in my engagements when discussing sustainability with the companies I interact with.
 The PLM software and services providers are all on a trajectory of providing tools and an infrastructure to support a transition to a more circular economy and better traceability of materials and carbon emissions.
The PLM software and services providers are all on a trajectory of providing tools and an infrastructure to support a transition to a more circular economy and better traceability of materials and carbon emissions.
In the PLM Global Green Alliance, we talked with Aras, Autodesk, Dassault Systems, PTC, SAP, Sustaira, TTPSC(Green PLM) and more to come in 2024. The solution offerings in the PLM domain are available to start, now the people and processes.
For sure, AI tools will help companies to get a better understanding of their sustainability efforts. As mentioned before AI could help companies in understanding their environmental impact and build more accurate ESG reports.
Next, being DATA-driven will be crucial. As discussed during the latest PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference: The Need for a Governance Digital Thread.
And regarding PEOPLE, the good news is that younger generations want to take care of their future. They are in a position to choose the company to work for or influence companies by their consumer behavior. Unfortunately, climate disasters will remind us continuously in the upcoming decades that we are in a critical phase.
With the PLM Global Green Alliance, we strive to bring people together with a PLM mindset, sharing news and information on how to move forward to a sustainable future.
![]() Mark Reisig (CIMdata – moderator for Sustainability & Energy) and Patrice Quencez (CIMPA – moderator for the Circular Economy) joined the PGGA last year and you will experience their inputs this year.
Mark Reisig (CIMdata – moderator for Sustainability & Energy) and Patrice Quencez (CIMPA – moderator for the Circular Economy) joined the PGGA last year and you will experience their inputs this year.
Conclusion
As you can see from this long post, there is so much to learn. The topics described are all actual, and each topic requires education, experience (success & failures) combined with understanding of the technology concepts. Make sure you consider all of them, as focusing on a single topic will not make move faster forward – they are all related. Please share your experiences this year—Happy New Year of Learning.
 Last week, I have been participating in the biannual NEM network meeting, this time hosted by Vestas in Ringkøbing (Denmark).
Last week, I have been participating in the biannual NEM network meeting, this time hosted by Vestas in Ringkøbing (Denmark).
NEM (North European Modularization) is a network for industrial companies with a shared passion and drive for modular products and solutions.
NEM’s primary goal is to advance modular strategies by fostering collaboration, motivation, and mutual support among its diverse members.
 During this two-day conference, there were approximately 80 attendees from around 15 companies, all with a serious interest and experience in modularity. The conference reminded me of the CIMdata Roadmap/PDT conferences, where most of the time a core group of experts meet to share their experiences and struggles.
During this two-day conference, there were approximately 80 attendees from around 15 companies, all with a serious interest and experience in modularity. The conference reminded me of the CIMdata Roadmap/PDT conferences, where most of the time a core group of experts meet to share their experiences and struggles.
The discussions are so much different compared to a generic PLM or software vendor conference where you only hear (marketing) success stories.
Modularity
 When talking about modularity, many people will have Lego in mind, as with the Lego bricks, you can build all kinds of products without the need for special building blocks. In general, this is the concept of modularity.
When talking about modularity, many people will have Lego in mind, as with the Lego bricks, you can build all kinds of products without the need for special building blocks. In general, this is the concept of modularity.
With modularity, a company tries to reduce the amount of custom-made designs by dividing a product into modules with strict interfaces. Modularity aims to offer a wider variety of products to the customer – but configure these from a narrower assortment of modules to streamline manufacturing, sourcing and service. Modularity allows managing changes and new functionality within the modules without managing a new product.
 From ETO (Engineering To Order) to BTO (Build To Order) or even CTO (Configure to Order) is a statement often heard when companies are investing in a new PLM system. The idea is that with the CTO model, you reduce the engineering costs and risks for new orders.
From ETO (Engineering To Order) to BTO (Build To Order) or even CTO (Configure to Order) is a statement often heard when companies are investing in a new PLM system. The idea is that with the CTO model, you reduce the engineering costs and risks for new orders.
With modularity, you can address more variants and options without investing in additional engineering efforts.
How the PLM system supports modularity is an often-heard question. How do you manage in the best way options and variants? The main issue here is that modularity is often considered an R&D effort – R&D must build the modular architecture. An R&D-only focus is a common mistake in the field similar to PLM. Both
 PLM and Modularity suffer from the framing that it is about R&D and their tools, whereas in reality, PLM and Modularity are strategies concerning all departments in an enterprise, from sales & marketing, engineering, and manufacturing to customer service.
PLM and Modularity suffer from the framing that it is about R&D and their tools, whereas in reality, PLM and Modularity are strategies concerning all departments in an enterprise, from sales & marketing, engineering, and manufacturing to customer service.
PLM and Modularity
 In 2021, I discussed the topic of Modularity with Björn Eriksson & Daniel Strandhammar, who had written during the COVID-19 pandemic their easy-to-read book: The Modular Way. In a blog post, PLM and Modularity, I discussed with Daniel the touchpoints with PLM. A little later, we had a Zoom discussion with Bjorn and Daniel, together with some of the readers of the book. You can find the info still here: The Modular Way – a follow-up discussion.
In 2021, I discussed the topic of Modularity with Björn Eriksson & Daniel Strandhammar, who had written during the COVID-19 pandemic their easy-to-read book: The Modular Way. In a blog post, PLM and Modularity, I discussed with Daniel the touchpoints with PLM. A little later, we had a Zoom discussion with Bjorn and Daniel, together with some of the readers of the book. You can find the info still here: The Modular Way – a follow-up discussion.
What was clear to me at that time is that, in particular, Sweden is a leading country when it comes to Modularity. Companies like Scania, Electrolux are known for their product modularity.
For me it was great to learn the Vestas modularization journey. For sure the Scandinavian region sets the tone. And in addition, there are LEGO and IKEA, also famous Scandinavian companies, but with other modularity concepts.
 The exciting part of the conference was that all the significant modularity players were present. Hosted by Vestas and with a keynote speech from Leif Östling, a former CEO of Scania, all the ingredients were there for an excellent conference.
The exciting part of the conference was that all the significant modularity players were present. Hosted by Vestas and with a keynote speech from Leif Östling, a former CEO of Scania, all the ingredients were there for an excellent conference.
The NEM network
The conference started with Christian Eskildsen, CEO of the NEM organization, who has a long history of leading modularity at Electrolux. The NEM is not only a facilitator for modularity. They also conduct training, certification sessions, and coaching on various levels, as shown below.
Christian mentioned that there are around 400 followers on the NEM LinkedIn group. I can recommend this LinkedIn group as the group shares their activities here.
At this moment, you can find here the results of Workstream 7 – The Cost of Complexity.
Peter Greiner, NEM member, presented the details of this result during the conference on day 2. The conclusion of the workstream team was a preliminary estimate suggesting a minimum cost reduction of 2-5% in terms of the Cost Of Goods Sold (COGS) on top of traditional modularization savings. These estimates are based on real-world cases.
Understanding that the benefits are related to the COGS with a high contribution of the actual material costs, a 2 – 5 % range is significant. There is the intention to dig deeper into this topic.
 Besides these workstreams, there are also other workstreams running or finished. The ones that interest me in the sustainability context are Workstream 1 Modular & Circular and Workstream 10 Modular PLM (Digital Thread).
Besides these workstreams, there are also other workstreams running or finished. The ones that interest me in the sustainability context are Workstream 1 Modular & Circular and Workstream 10 Modular PLM (Digital Thread).
The NEM network has an active group of members, making it an exciting network to follow and contribute as modularity is part of a sustainable future. More on this statement later.
Vestas
![]() The main part of day one was organized by our host, Vestas. Jens Demtröder, Chief Engineer at Vestas for the Modular Turbine Architecture and NEM board member, first introduced the business scope, complexity, and later the future challenges that Vestas is dealing with.
The main part of day one was organized by our host, Vestas. Jens Demtröder, Chief Engineer at Vestas for the Modular Turbine Architecture and NEM board member, first introduced the business scope, complexity, and later the future challenges that Vestas is dealing with.
First, wind energy is the best cost-competitive source for a green energy system, as the image shows when taking the full environmental impact into the equation. As the image below shows
From the outside, wind turbines all look the same; perhaps a difference between on-shore and off-shore? No way! There is a substantial evolution in the size and control of the wind turbine, and even more importantly, as the image shows, each country has its own regulations to certify a wind turbine. Vestas has to comply with 80+ different local regulations, and for that reason, modularity is vital to manage all the different demands efficiently.
A big challenge for the future will be the transport and installation of wind turbines.
 The components become so big that they need to be assembled on-site, requiring new constraints on the structure to be solved.
The components become so big that they need to be assembled on-site, requiring new constraints on the structure to be solved.
As the image to the left, rotor sizes up to 250 m are expected and what about the transport of the nacelle itself?
Click on this link to get an impression.
The audience also participated in a (windy) walk through the manufacturing site to get an impression of the processes & components – an impression below.
Processes, organization and governance
Karl Axel Petursson, Senior Specialist in Architecture and Roadmap, gave insights into the processes, organization and governance needed for the modularity approach at Vestas.
The modularization efforts are always a balance between strategy and execution, where often execution wins. The focus on execution is a claim that I recognize when discussing modularity with the companies I am coaching.
Vestas also created an organization related to the functions it provides, being a follower of Conway’s law, as the image below shows:
With modularity, you will also realize that the modular architecture must rely on stable interfaces between the modules based on clear market needs.
Besides an organizational structure, often more and more a matrix organization, there are also additional roles to set up and maintain a modular approach. As the image below indicates, to integrate all the functions, there are various roles in Vestas, some specialized and some more holistic:
These roles are crucial when implementing and maintaining modularity in your organization. It is not just the job of a clever R&D team.
Just a clever R&D is a misconception I have often discovered in the field. Buying one or more tools that support modularity and then let brilliant engineers do the work. And this is a challenge. Engineers often do not like to be constrained by modular constraints when designing a new capability or feature.
For this reason Vestas has established an Organization Change Management initiative called Modular Minds to make engineers flourish in the organization.
Modular Minds
Madhuri Srinivasan Systems Engineering specialist and Hanh Le Business Transformation leader both at Vestas, presented their approach to the 2020 must-win battle for Modularisation, aiming with various means, like blogs, podcasts, etc., to educate the organization and create Modular Minds for all Vestas employees.
 The team is applying the ADKAR model from Prosci to support this change. As you can see from the (clickable) image to the left, ADKAR is the abbreviation of Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement.
The team is applying the ADKAR model from Prosci to support this change. As you can see from the (clickable) image to the left, ADKAR is the abbreviation of Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement.
The ADKAR model focuses on driving change at the individual level and achieving organizational results. It is great to see such an approach applied to Modularity, and it would also be valuable in the domain of PLM, as I discussed with Share PLM in my network.
Scania
 The 1 ½ hour keynote speech from Leif Östling supported by Karl-Johan Linghede was more of an interactive discussion with the audience than a speech. Leif took us to the origins of Scania, their collaboration in the beginning with learning the Toyota Way. – customer first, respect for people and focus on quality. And initial research and development together with Modular Management resulting in the MFD-methodology.
The 1 ½ hour keynote speech from Leif Östling supported by Karl-Johan Linghede was more of an interactive discussion with the audience than a speech. Leif took us to the origins of Scania, their collaboration in the beginning with learning the Toyota Way. – customer first, respect for people and focus on quality. And initial research and development together with Modular Management resulting in the MFD-methodology.
It led to the understanding that:
- The #1 cost driver is the amount of parts you need to manage,
- The #2 crucial point is to have standardized interfaces and keep the flexibility inside the module
With Ericsson, Scania yearly on partnered to work on the connected vehicle. If you are my age, you will remember connectivity at that time was not easy. The connected vehicle was the first step of what we now would call a digital twin
An interesting topic discussed was that Scania has approximately 25 interfaces at Change Level 1. This is a C-level/Executive discussion to approve potential interface changes. This level shows the commitment of the organization to keep modularity operational.
 Another benefit mentioned was that the move to electrification of the vehicle was not such a significant change as in many automotive companies. Thanks to the modular structure and the well-defined interfaces, creating an electric truck was not a complete change of the truck design.
Another benefit mentioned was that the move to electrification of the vehicle was not such a significant change as in many automotive companies. Thanks to the modular structure and the well-defined interfaces, creating an electric truck was not a complete change of the truck design.
The session with Leif and Karl-Johan could have easily taken longer, giving the interesting question-and-answer dialogue with the curious audience. It was a great learning moment.
Digitization, Sustainability & Modularization
 As a PLM person from the PLM Green Global Alliance, I was allowed to give a speech about the winning combination of Digitization, Sustainability and Modularization. You might have seen my PLM and Sustainability blog post recently; now, a zoom-in on the circular economy and modularity is included.
As a PLM person from the PLM Green Global Alliance, I was allowed to give a speech about the winning combination of Digitization, Sustainability and Modularization. You might have seen my PLM and Sustainability blog post recently; now, a zoom-in on the circular economy and modularity is included.
In this conference, I also focused on Modularity, when implemented based on model-based and data-driven approaches, which is a crucial component of the circular economy (image below) and the lifecycle analysis per module when defined as model-based (Digital Twin).
My entire presentation on SlideShare: Digitization, Sustainability & Modularization.
Conclusion
It was the first time I attended a conference focused on modularity purely, and I realized we are all fighting the same battle. Like the fact that PLM is a strategy and not an engineering system, modularity faces the same challenge. It is a strategy and not an R&D mission. It would be great to see modularity becoming a part of PLM conferences or Circular Economy events as there is so much to learn from each other – and we need them all.
Are you interested in the future of PLM and the meaning of Digital Threads.?
Click on the image to see the agenda and join us for 2 days of discussion & learning.
 During my summer holiday in my “remote” office, I had the chance to digest what I recently read, heard, saw and discussed related to the future of PLM.
During my summer holiday in my “remote” office, I had the chance to digest what I recently read, heard, saw and discussed related to the future of PLM.
I noticed this year/last year that many companies are discussing or working on their future PLM. It is time to make progress after COVID, particularly in digitization.
And as most companies are avoiding the risk of a “big bang”, they are exploring how they can improve their businesses in an evolutionary mode.
PLM is no longer a system
 The most significant change I noticed in my discussions is the growing awareness that PLM is no longer covered by a single system.
The most significant change I noticed in my discussions is the growing awareness that PLM is no longer covered by a single system.
More and more, PLM is considered a strategy, with which I fully agree. Therefore, implementing a PLM strategy requires holistic thinking and an infrastructure of different types of systems, where possible, digitally connected.
This trend is bad news for the PLM vendors as they continuously work on an end-to-end portfolio where every aspect of the PLM lifecycle is covered by one of their systems. The company’s IT department often supports the PLM vendors, as IT does not like a diverse landscape.
 The main question is: “Every PLM Vendor has a rich portfolio on PowerPoint mentioning all phases of the product lifecycle.
The main question is: “Every PLM Vendor has a rich portfolio on PowerPoint mentioning all phases of the product lifecycle.
However, are these capabilities implementable in an economical and user-friendly manner by actual companies or should PLM players need to change their strategy”?
A question I will try to answer in this post
The future of PLM
 I have discussed several observed changes related to the effects of digitization in my recent blog posts, referencing others who have studied these topics in their organizations.
I have discussed several observed changes related to the effects of digitization in my recent blog posts, referencing others who have studied these topics in their organizations.
Some of the posts to refresh your memory are:
- Time to split PLM?
- People, Processes, Data and Tools?
- The rise and the fall of the BOM?
- The new side of PLM? Systems of Engagement!
To summarize what has been discussed in these posts are the following points:
The As Is:
- The traditional PLM systems are examples of a System of Record, not designed to be end-user friendly but designed to have a traceable baseline for manufacturing, service and product compliance.
- The traditional PLM systems are tuned to a mechanical product introduction and release process in a coordinated manner, with a focus on BOM governance.
- The legacy information is stored in BOM structures and related specification files.

System of Record (ENOVIA image 2014)
The To Be:
- We are not talking about a PLM system anymore; a traditional System of Record will be digitally connected to different Systems of Engagement / Domains / Products, which have their own optimized environment for real-time collaboration.
- The BOM structures remain essential for the hardware part; however, overreaching structures are needed to manage software and hardware releases for a product. These structures depend on connected datasets.
- To support digital twins at the various lifecycle stages (design. Manufacturing, operations), product data needs to be based on and consumed by models.
- A future PLM infrastructure is hybrid, based on a Single Source of Change (SSoC) and an Authoritative Source of Truth (ASoT) instead of a Single Source of Truth (SSoT).

Various Systems of Engagement
Related podcasts
I relistened two podcasts before writing this post, and I think they are a must to listen to.
 The Peer Check podcast from Colab episode 17 — The State of PLM in 2022 w/Oleg Shilovitsky. Adam and Oleg have a great discussion about the future of PLM.
The Peer Check podcast from Colab episode 17 — The State of PLM in 2022 w/Oleg Shilovitsky. Adam and Oleg have a great discussion about the future of PLM.
Highlights: From System to Platform – the new norman. A Single Source of Truth doesn’t work anymore – it is about value streams. People in big companies fear making wrong PLM decisions, which is seen as a significant risk for your career.
There is no immediate need to change the current status quo.
 The Share PLM Podcast – Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights from Yousef Hooshmand. Yousef talked with Helena and me about proven ways to migrate an old PLM landscape to a modern PLM/Business landscape.
The Share PLM Podcast – Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights from Yousef Hooshmand. Yousef talked with Helena and me about proven ways to migrate an old PLM landscape to a modern PLM/Business landscape.
Highlights: The term Single Source of Change and the existing concepts of a hybrid PLM infrastructure based on his experiences at Daimler and now at NIO. Yousef stresses the importance of having the vision and the executive support to execute.
![]() The time of “big bangs” is over, and Yousef provided links to relevant content, which you can find here in the comments.
The time of “big bangs” is over, and Yousef provided links to relevant content, which you can find here in the comments.
In addition, I want to point to the experiences provided by Erik Herzog in the Heliple project using OSLC interfaces as the “glue” to connect (in my terminology) the Systems of Engagement and the Systems of Record.
If you are interested in these concepts and want to learn and discuss them with your peers, more can be learned during the upcoming CIMdata PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference.
In particular, look at the agenda for day two if you are interested in this topic.
The future for the PLM vendors
 If you look at the messaging of the current PLM Vendors, none of them is talking about this federated concept.
If you look at the messaging of the current PLM Vendors, none of them is talking about this federated concept.
They are more focused with their messaging on the transition from on-premise to the cloud, providing a SaaS offering with their portfolio.
I was slightly disappointed when I saw this article on Engineering.com provided by Autodesk: 5 PLM Best Practices from the Experiences of Autodesk and Its Customers.
The article is tool-centric, with statements that make sense and could be written by any PLM Vendor. However, Best Practice #1 Central Source of Truth Improves Productivity and Collaboration was the message that struck me. Collaboration comes from connecting people, not from the Single Source of Truth utopia.
I don’t believe PLM Vendors have to be afraid of losing their installed base rapidly with companies using their PLM as a System or Record. There is so much legacy stored in these systems that might still be relevant. The existence of legacy information, often documents, makes a migration or swap to another vendor almost impossible and unaffordable.

The System of Record is incompatible with data-driven PLM capabilities
I would like to see more clear developments of the PLM Vendors, creating a plug-and-play infrastructure for Systems of Engagement. Plug-and-play solutions could be based on a neutral partner collaboration hub like ShareAspace or the Systems of Engagement I discussed recently in my post and interview: The new side of PLM? Systems of Engagement!
 Plug-and-play systems of engagement require interface standards, and PLM Vendors will only move in this direction if customers are pushing for that, and this is the chicken-and-egg discussion. And probably, their initiatives are too fragmented at the moment to come to a standard. However, don’t give up; keep building MVPs to learn and share.
Plug-and-play systems of engagement require interface standards, and PLM Vendors will only move in this direction if customers are pushing for that, and this is the chicken-and-egg discussion. And probably, their initiatives are too fragmented at the moment to come to a standard. However, don’t give up; keep building MVPs to learn and share.
Some people believe AI, with the examples we have seen with ChatGPT, will be the future direction without needing interface standards.
I am curious about your thoughts and experiences in that area and am willing to learn.
Talking about learning?
 Besides reading posts and listening to podcasts, I also read an excellent book this summer. Martijn Dullaart, often participating in PLM and CM discussions, had decided to write a book based on the various discussions related to part (re-)identification (numbering, revisioning).
Besides reading posts and listening to podcasts, I also read an excellent book this summer. Martijn Dullaart, often participating in PLM and CM discussions, had decided to write a book based on the various discussions related to part (re-)identification (numbering, revisioning).
As Martijn starts in the preface:
“I decided to write this book because, in my search for more knowledge on the topics of Part Re-Identification, Interchangeability, and Traceability, I could only find bits and pieces but not a comprehensive work that helps fundamentally understand these topics”.
 I believe the book should become standard literature for engineering schools that deal with PLM and CM, for software vendors and implementers and last but not least companies that want to improve or better clarify their change processes.
I believe the book should become standard literature for engineering schools that deal with PLM and CM, for software vendors and implementers and last but not least companies that want to improve or better clarify their change processes.
Martijn writes in an easily readable style and uses step-by-step examples to discuss the various options. There are even exercises at the end to use in a classroom or for your team to digest the content.
The good news is that the book is not about the past. You might also know Martijn for our joint discussion, The Future of Configuration Management, together with Maxime Gravel and Lisa Fenwick, on the impact of a model-based and data-driven approach to CM.
 I plan to come back with a more dedicated discussion at some point with Martijn soon. Meanwhile, start reading the book. Get your free chapter if needed by following the link at the bottom of this article.
I plan to come back with a more dedicated discussion at some point with Martijn soon. Meanwhile, start reading the book. Get your free chapter if needed by following the link at the bottom of this article.
I recommend buying the book as a paperback so you can navigate easily between the diagrams and the text.
Conclusion
The trend for federated PLM is becoming more and more visible as companies start implementing these concepts. The end of monolithic PLM is a threat and an opportunity for the existing PLM Vendors. Will they work towards an open plug-and-play future, or will they keep their portfolios closed? What do you think?

 Today I read Rhiannon Gallagherer’s LinkedIn post: If Murray Isn’t Happy, No One Is Happy: Value Your Social Nodes. The story reminded me of a complementary blog post I wrote in 2014, although with a small different perspective.
Today I read Rhiannon Gallagherer’s LinkedIn post: If Murray Isn’t Happy, No One Is Happy: Value Your Social Nodes. The story reminded me of a complementary blog post I wrote in 2014, although with a small different perspective.
After reviewing my post, I discovered that nine years later, we are still having the same challenges of how to involve people in a business transformation.
People are the most important assets companies claim, but where do they focus their spending and efforts?
Probably more on building the ideal processes and having the best IT solution.
 Organisational Change Management is not in their comfort zone. People like Rhiannon Gallagher, but also in my direct network, the team from Share PLM, are focusing on this blind spot. Don’t forget this part of your digital transformation efforts.
Organisational Change Management is not in their comfort zone. People like Rhiannon Gallagher, but also in my direct network, the team from Share PLM, are focusing on this blind spot. Don’t forget this part of your digital transformation efforts.
And just for fun, there rest of the post below is the article from 2014. At that time, I was not yet focusing on digital transformation in the PLM domain. That started end of 2014 – the beginning of 2015.
PLM and Blockers
(read it with 2014 in mind – where were you?)
In the past month (April 2014), I had several discussions related to the complexity of PLM.
- Why is PLM conceived as complex?
- Why is it hard to sell PLM internally into an organization?
- Or, to phrase it differently: “What makes PLM so difficult for normal human beings. As conceptually it is not so complex”
(2023 addition: PLM is complex (and we have to accept it?) )
So what makes it complex? What is behind PLM?
 The main concept behind PLM is that people need to share data. It can be around a project, a product, or a plant through the whole lifecycle. In particular, during the early lifecycle phases, there is a lot of information that is not yet 100 percent mature.
The main concept behind PLM is that people need to share data. It can be around a project, a product, or a plant through the whole lifecycle. In particular, during the early lifecycle phases, there is a lot of information that is not yet 100 percent mature.
You could decide to wait till everything is mature before sharing it with others (the classical sequential manner). However, the chances of doing it right the first time are low. Several iterations between disciplines will be required before the data is approved.
The more and more a company works sequentially, the higher the costs of changes and the longer the time to market. Due to the rigidness of this sequential approach, it becomes difficult to respond rapidly to changing customer or market demands.
Therefore, in theory (and it is not only a PLM theory), concurrent engineering should reduce the number of iterations and the total time to market by working in parallel on not yet approved data.
 PLM goes further. It is about the sharing of data, and as it originally started in the early phases of the product lifecycle, the concept of PLM was considered something related to engineering. And to be fair, most of the PLM (CAD-related) vendors have a high focus on the early stages of the lifecycle and have strengthened this idea.
PLM goes further. It is about the sharing of data, and as it originally started in the early phases of the product lifecycle, the concept of PLM was considered something related to engineering. And to be fair, most of the PLM (CAD-related) vendors have a high focus on the early stages of the lifecycle and have strengthened this idea.
However, sharing can go much further, e.g., early involvement of suppliers (still engineering) or downstream support for after-sales/services (the new acronym SLM – Service Lifecycle Management).
In my recent (2014) blog posts, I discussed the concepts of SLM and the required data model for that.
Anticipated sharing
The complexity lies in the word “sharing”. What does sharing mean for an organization, where historically, every person was awarded for their knowledge instead of being awarded for sharing and spreading knowledge. Guarding your knowledge was job protection.
Many so-called PLM implementations have failed to reach the sharing target as the implementation focus was on storing data per discipline and not necessarily storing data to become shareable and used by others. This is a huge difference.
(2023 addition: At that time, all PLM systems were Systems of Record)
 Some famous (ERP) vendors claim if you store everything in their system, you have a “single version of the truth”.
Some famous (ERP) vendors claim if you store everything in their system, you have a “single version of the truth”.
Sounds attractive. However, my garbage bin at home is also a place where everything ends up in a single place, but a garbage bin has not been designed for sharing. Another person has no clue or time to analyze what is inside.
Even data stored in the same system can be hidden from others as the way to find data is not anticipated.
Data sharing instead of document deliverables
The complexity of PLM is that data should be created and shared in a matter not necessarily in the most efficient manner for a single purpose. With some extra effort, you can make the information usable and searchable for others. Typical examples are drawings and document management, where the whole process for a person is focused on delivering a specific document on time. Ok, for that purpose, but this document becomes a legacy for the long term as you need to know (or remember) what is inside the document.
 A logical implication of data sharing is that, instead of managing documents, organizations start to collect and share data elements (a 3D model, functional properties, requirements, physical properties, logistical properties, etc.). Data can be connected and restructured easily through reports and dashboards, therefore, providing specific views for different roles in the organization. Sharing has become possible, and it can be done online. Nobody needed to consolidate and extract data from documents (Excels ?)
A logical implication of data sharing is that, instead of managing documents, organizations start to collect and share data elements (a 3D model, functional properties, requirements, physical properties, logistical properties, etc.). Data can be connected and restructured easily through reports and dashboards, therefore, providing specific views for different roles in the organization. Sharing has become possible, and it can be done online. Nobody needed to consolidate and extract data from documents (Excels ?)
(2023 addition: The data-driven PLM infrastructure talking about datasets)
This does not fit older generations and departmental-managed business units that are rewarded only for their individual efficiency.
 Here is an extract of a LinkedIn discussion from 2014, where the two extremes are visible. Unfortunately (or perhaps good), LinkedIn does not keep everything online. There is already so much “dark data” on the internet.
Here is an extract of a LinkedIn discussion from 2014, where the two extremes are visible. Unfortunately (or perhaps good), LinkedIn does not keep everything online. There is already so much “dark data” on the internet.
Joe stating:
“The sad thing about PLM is that only PLM experts can understand it! It seems to be a very tight knit club with very little influence from any outside sources.
I think PLM should be dumped. It seems to me that computerizing engineering documentation is relatively easy process. I really think it has been over complicated. Of course we need to get the CAD vendors out of the way. Yes it was an obvious solution, but if anyone took the time to look down the road they would see that they were destroying a well established standard that were so cost effective and simple. But it seems that there is no money in simple”
And at the other side, Kais stated:
“If we want to be able to use state-of-the art technology to support the whole enterprise, and not just engineering, and through-life; then product information, in its totality, must be readily accessible and usable at all times and not locked in any perishable CAD, ERP or other systems. The Data Centric Approach that we introduced in the Datamation PLM Model is built on these concepts”
Readers from my blog will understand I am very much aligned with Kais, and PLM guys have a hard time convincing Joe of the benefits of PLM (I did not try).
Making the change happen
 Besides this LinkedIn discussion, I had discussions with several companies where my audience understood the data-centric approach. It was nice to be in the room together, sharing ideas of what would be possible. However, the outside world is hard to convince, and here the challenge is organizational change management. Who will support you and who will work against you?.
Besides this LinkedIn discussion, I had discussions with several companies where my audience understood the data-centric approach. It was nice to be in the room together, sharing ideas of what would be possible. However, the outside world is hard to convince, and here the challenge is organizational change management. Who will support you and who will work against you?.
BLOCKERS: I read an interesting article in IndustryWeek from John Dyer with the title: What Motivates Blockers to Resist Change?
John describes the various types of blockers, and when reading the article combined with my PLM twisted brain, I understood again that this is one of the reasons why PLM is perceived as complex – you need to change, and there are blockers:
Blocker (noun) – Someone who purposefully opposes any change (improvement) to a process for personal reasons
“Blockers” can occupy any position in a company. They can be any age, gender, education level or pay rate. We tend to think of blockers as older, more experienced workers who have been with the company for a long time, and they don’t want to consider any other way to do things. While that may be true in some cases, don’t be surprised to find blockers who are young, well-educated and fairly new to the company.”
The problem with blockers
The combination of business change and the existence of blockers is one of the biggest risks for companies to go through a business transformation. By the way, this is not only related to PLM; it is related to any required change in business.
Some examples:
 A company I worked with was eager to study its path to the future, which required more global collaboration, a competitive business model and a more customer-centric approach. After a long evaluation phase, they decided they needed PLM, which was new for most of the people in the company. Although the project team was enthusiastic, they were not able to pass the blockers for a change – so no PLM. Ironically enough, they lost a significant part of their business to companies that have implemented PLM. Defending the past is not a guarantee for the future.
A company I worked with was eager to study its path to the future, which required more global collaboration, a competitive business model and a more customer-centric approach. After a long evaluation phase, they decided they needed PLM, which was new for most of the people in the company. Although the project team was enthusiastic, they were not able to pass the blockers for a change – so no PLM. Ironically enough, they lost a significant part of their business to companies that have implemented PLM. Defending the past is not a guarantee for the future.
A second example is Nokia. Nokia was famous for the ways they were able to transform their business in the past. How come they did not see the smartphone and touch screens upcoming? Apparently, based on several articles presented recently, it was Nokia´s internal culture and superior feeling that they were dominating the market that made it impossible to switch. The technology was known, and the concepts were there; however, the (middle) management was full of blockers.
Two examples where blockers had a huge impact on the company.
Conclusion:
Staying in business and remaining competitive is crucial for companies. In particular, the changes that currently happen require people to work differently in order to stay competitive. Documents will become reports generated from data. People handling and collecting documents to generate new documents will become obsolete as a modern data-centric approach makes them redundant. Keeping the old processes might destroy a company. This should convince the blockers to give up.

 In the past few weeks, together with Share PLM, we recorded and prepared a few podcasts to be published soon. As you might have noticed, for Season 2, our target is to discuss the human side of PLM and PLM best practices and less the technology side. Meaning:
In the past few weeks, together with Share PLM, we recorded and prepared a few podcasts to be published soon. As you might have noticed, for Season 2, our target is to discuss the human side of PLM and PLM best practices and less the technology side. Meaning:
- How to align and motivate people around a PLM initiative?
- What are the best practices when running a PLM initiative?
- What are the crucial skills you need to have as a PLM lead?
And as there are always many success stories to learn on the internet, we also challenged our guests to share the moments where they got experienced.
As the famous quote says:
Experience is what you get when you don’t get what you expect!
We recently published our with Antonio Casaschi from Assa Abloy, a Swedish company you might have never noticed, although their products and services are a part of your daily life.
It was a discussion to my heart. We discussed the various aspects of PLM. What makes a person a PLM professional? And if you have no time to listen for these 35 minutes, read and scan the recording transcript on the transcription tab.
At 0:24:00, Antonio mentioned the concept of Proof of Concept as he had good experiences with them in the past. The remark triggered me to share some observations that a Proof of Concept (POC) is an old-fashioned way to drive change within organizations. Not discussed in this podcast but based on my experience, companies have been using the Proof Of Concepts to win time, as they were afraid to make a decision.
A POC to gain time?
Company A
 When working with a well-known company in 2014, I learned they were planning approximately ten POC per year to explore new ways of working or new technologies. As it was a POC based on an annual time scheme, the evaluation at the end of the year was often very discouraging.
When working with a well-known company in 2014, I learned they were planning approximately ten POC per year to explore new ways of working or new technologies. As it was a POC based on an annual time scheme, the evaluation at the end of the year was often very discouraging.
Most of the time, the conclusion was: “Interesting, we should explore this further” /“What are the next POCs for the upcoming year?”
There was no commitment to follow-up; it was more of a learning exercise not connected to any follow-up.
Company B
 During one of the PDT events, a company presented that two years POC with the three leading PLM vendors, exploring supplier collaboration. I understood the PLM vendors had invested much time and resources to support this POC, expecting a big deal. However, the team mentioned it was an interesting exercise, and they learned a lot about supplier collaboration.
During one of the PDT events, a company presented that two years POC with the three leading PLM vendors, exploring supplier collaboration. I understood the PLM vendors had invested much time and resources to support this POC, expecting a big deal. However, the team mentioned it was an interesting exercise, and they learned a lot about supplier collaboration.
And nothing happened afterward ………
In 2019
At the 2019 Product Innovation Conference in London, when discussing Digital Transformation within the PLM domain, I shared in my conclusion that the POC was mainly a waste of time as it does not push you to transform; it is an option to win time but is uncommitted.
My main reason for not pushing a POC is that it is more of a limited feasibility study.
- Often to push people and processes into the technical capabilities of the systems used. A focus starting from technology is the opposite of what I have been pushing for longer: First, focus on the value stream – people and processes- and then study which tools and technologies support these demands.
- Second, the POC approach often blocks innovation as the incumbent system providers will claim the desired capabilities will come (soon) within their systems—a safe bet.

The Minimum Viable Product approach (MVP)
With the awareness that we need to work differently and benefit from digital capabilities also came the term Minimum Viable Product or MVP.
The abbreviation MVP is not to be confused with the minimum valuable products or most valuable players.
There are two significant differences with the POC approach:
- You admit the solution does not exist anywhere – so it cannot be purchased or copied.
- You commit to the fact that this new approach will be the right direction to take and agree that a perfect fit solution is not blocking you from starting for real.
These two differences highlight the main challenges of digital transformation in the PLM domain. Digital Transformation is a learning process – it takes time for organizations to acquire and master the needed skills. And secondly, it cannot be a big bang, and I have often referred to the 2017 article from McKinsey: Toward an integrated technology operating model. Image below.
We will soon hear more about digital transformation within the PLM domain during the next episode of our SharePLM podcast. We spoke with Yousef Hooshmand, currently working for NIO, a Chinese multinational automobile manufacturer specializing in designing and developing electric vehicles, as their PLM data lead.
 You might have discovered Yousef earlier when he published his paper: “From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh”. It is highly recommended that to read the paper if you are interested in a potential PLM future infrastructure. I wrote about this whitepaper in 2022: A new PLM paradigm discussing the upcoming Systems of Engagement on top of a Systems or Record infrastructure.
You might have discovered Yousef earlier when he published his paper: “From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh”. It is highly recommended that to read the paper if you are interested in a potential PLM future infrastructure. I wrote about this whitepaper in 2022: A new PLM paradigm discussing the upcoming Systems of Engagement on top of a Systems or Record infrastructure.
To align our terminology with Yousef’s wording, his domains align with the Systems of Engagement definition.
As we discovered and discussed with Yousef, technology is not the blocking issue to start. You must understand the target infrastructure well and where each domain’s activities fit. Yousef mentions that there is enough literature about this topic, and I can refer to the SAAB conference paper: Genesis -an Architectural Pattern for Federated PLM.
 For a less academic impression, read my blog post, The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022, where I share the highlights of Erik Herzog’s presentation: Heterogeneous and Federated PLM – is it feasible?
For a less academic impression, read my blog post, The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022, where I share the highlights of Erik Herzog’s presentation: Heterogeneous and Federated PLM – is it feasible?
There is much to learn and discover which standards will be relevant, as both Yousef and Erik mention the importance of standards.
The podcast with Yousef (soon to be found HERE) was not so much about organizational change management and people.
 However, Yousef mentioned the most crucial success factor for the transformation project he supported at Daimler. It was C-level support, trust and understanding of the approach, knowing it will be many years, an unavoidable journey if you want to remain competitive.
However, Yousef mentioned the most crucial success factor for the transformation project he supported at Daimler. It was C-level support, trust and understanding of the approach, knowing it will be many years, an unavoidable journey if you want to remain competitive.
 And with the journey aspect comes the importance of the Minimal Viable Product. You are starting a journey with an end goal in mind (top-of-the-mountain), and step by step (from base camp to base camp), people will be better covered in their day-to-day activities thanks to digitization.
And with the journey aspect comes the importance of the Minimal Viable Product. You are starting a journey with an end goal in mind (top-of-the-mountain), and step by step (from base camp to base camp), people will be better covered in their day-to-day activities thanks to digitization.
A POC would not help you make the journey; perhaps a small POC would understand what it takes to cross a barrier.
Conclusion
The concept of POCs is outdated in a fast-changing environment where technology is not necessary the blocking issue. Developing practices, new architectures and using the best-fit standards is the future. Embrace the Minimal Viable Product approach. Are you?
 Last week I enjoyed visiting LiveWorx 2023 on behalf of the PLM Global Green Alliance. PTC had invited us to understand their sustainability ambitions and meet with the relevant people from PTC, partners, customers and several of my analyst friends. It felt like a reunion.
Last week I enjoyed visiting LiveWorx 2023 on behalf of the PLM Global Green Alliance. PTC had invited us to understand their sustainability ambitions and meet with the relevant people from PTC, partners, customers and several of my analyst friends. It felt like a reunion.
In addition, I used the opportunity to understand better their Velocity SaaS offering with OnShape and Arena. The almost 4-days event, with approximately 5000 attendees, was massive and well-organized.
So many people were excited that this was again an in-person event after four years.

With PTC’s broad product portfolio, you could easily have a full agenda for the whole event, depending on your interests.
I was personally motivated that I had a relatively full schedule focusing purely on Sustainability, leaving all these other beautiful end-to-end concepts for another time.
Here are some of my observations
Jim Heppelman’s keynote
The primary presentation of such an event is the keynote from PTC’s CEO. This session allows you to understand the company’s key focus areas.
My takeaways:
- Need for Speed: Software-driven innovation, or as Jim said, Software is eating the BOM, reminding me of my recent blog post: The Rise and Fall of the BOM. Here Jim was referring to the integration with ALM (CodeBeamer) and IoT to have full traceability of products. However, including Software also requires agile ways of working.
- Need for Speed: Agile ways of working – the OnShape and Arena offerings are examples of agile working methods. A SaaS solution is easy to extend with suppliers or other stakeholders. PTC calls this their Velocity offering, typical Systems of Engagement, and I spoke later with people working on this topic. More in the future.
- Need for Speed: Model-based digital continuity – a theme I have discussed in my blog post too. Here Jim explains the interaction between Windchill and ServiceMax, both Systems of Record for product definition and Operation.

- Environmental Sustainability: introducing Catherine Kniker, PTC’s Chief Strategy and Sustainability Officer, announcing that PTC has committed to Science Based Targets, pledging near-term emissions reductions and long-term net-zero targets – see image below and more on Sustainability in the next section.

- A further investment in a SaaS architecture, announcing CREO+ as a SaaS solution supporting dynamic multi-user collaboration (a System of Engagement)
- A further investment in the partnership with Ansys fits the needs of a model-based future where modeling and simulation go hand in hand.
You can watch the full session Path to the Future: Products in the Age of Transformation here.
Sustainability
 The PGGA spoke with Dave Duncan and James Norman last year about PTC’s sustainability initiatives. Remember: PLM and Sustainability: talking with PTC. Therefore, Klaus Brettschneider and I were happy to meet Dave and James in person just before the event and align on understanding what’s coming at PTC.
The PGGA spoke with Dave Duncan and James Norman last year about PTC’s sustainability initiatives. Remember: PLM and Sustainability: talking with PTC. Therefore, Klaus Brettschneider and I were happy to meet Dave and James in person just before the event and align on understanding what’s coming at PTC.
We agreed there is no “sustainability super app”; it is more about providing an open, digital infrastructure to connect data sources at any time of the product lifecycle, supporting decision-making and analysis. It is all about reliable data.
Product Sustainability 101
On Tuesday, Dave Duncan gave a great introductory session, Product Sustainability 101, addressing Business Drivers and Technical Opportunities. Dave started by explaining the business context aiming at greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction based on science-based targets, describing the content of Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 emissions.
The image above, which came back in several presentations later that week, nicely describes the mapping of lifecycle decisions and operations in the context of the GHG protocol.
Design for Sustainability (DfS)
On Wednesday, I started with a session moderated by James Norman titled Design for Sustainability: Harnessing Innovation for a Resilient Future. The panel consisted of Neil D’Souza (CEO Makersite), Tim Greiner (MD Pure Strategies), Francois Lamy (SVP Product Management PTC) and Asheen Phansey (Director ESG & Sustainability at PagerDuty). You can find the topic discussed below:
Some of the notes I took:
- No specific PLM modules are needed, LCA needs to become an additional practice for companies, and they rely on a connected infrastructure.
- Where to start? First, understand the current baseline based on data collection – what is your environmental impact? Next, decide where to start
- The importance of Design for Service – many companies design products for easy delivery, not for service. Being able to service products better will extend their lifetime, therefore reducing their environmental impact (manufacturing/decommissioning)
- There Is a value chain for carbon data. In addition, suppliers significantly impact reaching net zero, as many OEMs have an Assembly To Order process, and most of the emissions are done during part manufacturing.
DfS: an example from Cummins
 Next, on Wednesday, I attended the session from David Genter from Cummins, who presented their Design for Sustainability (DfS) project.
Next, on Wednesday, I attended the session from David Genter from Cummins, who presented their Design for Sustainability (DfS) project.
Dave started by sharing their 2030 sustainability goals:
- On Facilities and Operations: A reduction of 50 % of GHG emissions, reducing water usage by 30 %, reducing waste by 25 % and reducing organic compound emissions by 50%
- Reducing Scope 3 emissions for new products by 25%
- In general, reducing Scope 3 emissions by 55M metric tons.
The benefits for products were documented using a standardized scorecard (example below) to ensure the benefits are real and not based on wishful thinking.
Many motivated people wanted to participate in the project, and the ultimate result demonstrated that DfS has both business value for Cummins and the environment.
The project has been very well described in this whitepaper: How Cummins Made Changes to Optimize Product Designs for the Environment – a recommended case study to read.
Tangible Strategies for Improving Product Sustainability
The session was a dialogue between Catherine Kniker and Dave Duncan, discussing the strategies to move forward with Sustainability.
They reiterated the three areas where we as a PLM community can improve: Material choice and usage, Addressing Energy Emissions and Reducing Waste. And it is worth addressing them all, as you can see below – it is not only about carbon reduction.
It was an informative dialogue going through the different aspects of where we, as an engineering/ PLM community, can contribute. You can watch their full dialog here: Tangible Strategies for Improving Product Sustainability.
Conclusion
It was encouraging to see that at such an event as LiveWorx, you could learn about Sustainability and discuss Sustainability with the audience and PTC partners. And as I mentioned before, we need to learn to measure (data-driven / reliable data), and we need to be able to work in a connected infrastructure (digital thread) to allow design, simulation, validation and feedback to go hand in hand. It requires adapting a business strategy, not just a tactical solution. With the PLM Global Green Alliance, we are looking forward to following up on these.
NOTE: PTC covered the expenses associated with my participation in this event but did not in any way influence the content of this post – I made my tour fully independent through the conference and got encouraged by all the conversations I had.
 I am writing this post because one of my PLM peers recently asked me this question: “Is the BOM losing its position? He was in discussion with another colleague who told him:
I am writing this post because one of my PLM peers recently asked me this question: “Is the BOM losing its position? He was in discussion with another colleague who told him:
“If you own the BOM, you own the Product Lifecycle”.
This statement made me think of ä recent post from Jan Bosch recent post: Product Development fallacy #8: the bill of materials has the highest priority.
 Software becomes increasingly an essential part of the final product, and combined with Jan’s expertise in software development, he wrote this article. I recommend reading the full post (4 min read) and next browse through the comments.
Software becomes increasingly an essential part of the final product, and combined with Jan’s expertise in software development, he wrote this article. I recommend reading the full post (4 min read) and next browse through the comments.
If you cannot afford these 10 minutes, here is my favorite quote from the article:
An excessive focus on the bill of materials leads to significant challenges for companies that are undergoing a digital transformation and adopting continuous value delivery. The lack of headroom, high coupling and versioning hell may easily cause an explosion of R&D expenditure over time.
Where did the BOM focus come from? A historical overview related to the rise (and fall) of the BOM.
In the beginning, there was the drawing.
 Before the era of computers, there was “THE drawing”, describing assemblies, subassemblies or parts. And on the drawing, you can find the parts list if relevant. This parts list was the first Bill of Material, describing the parts/materials shown on the drawing.
Before the era of computers, there was “THE drawing”, describing assemblies, subassemblies or parts. And on the drawing, you can find the parts list if relevant. This parts list was the first Bill of Material, describing the parts/materials shown on the drawing.
Next came MRP/ERP
 With the introduction of the MRP system (Material Requirement Planning), it was the first step that by using computers, people could collect the material requirements for one system as data and process.
With the introduction of the MRP system (Material Requirement Planning), it was the first step that by using computers, people could collect the material requirements for one system as data and process.
Entering new materials/parts described on drawings was still a manual process, as well as referring to existing parts on the drawing. Reuse of parts was a manual process based on individual knowledge.
In the nineties, MRP evolved into ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), which included the MRP part and added resource and manufacturing planning and financial reporting.
 The ERP system became the most significant IT system, the execution system of the company. As it was the first enterprise system implemented, it was the first moment we learned about implementation challenges – people change and budget overruns. However, as the ERP system brought visibility to the company’s execution, it became a “must-have” system for management.
The ERP system became the most significant IT system, the execution system of the company. As it was the first enterprise system implemented, it was the first moment we learned about implementation challenges – people change and budget overruns. However, as the ERP system brought visibility to the company’s execution, it became a “must-have” system for management.
The introduction of mainstream 2D CAD did not affect the company’s culture so much. Drawings became electronic drawings, and the methodology of the parts list on the drawing remained.
 Sometimes the interaction with the MRP/ERP system was enhanced by an interface – sending the drawing BOM to ERP. The advantage of the interface: no manual transfer of data reducing typos and BOM errors. The disadvantages at that time: relatively expensive (connectivity between systems was a challenge) and mostly one direction.
Sometimes the interaction with the MRP/ERP system was enhanced by an interface – sending the drawing BOM to ERP. The advantage of the interface: no manual transfer of data reducing typos and BOM errors. The disadvantages at that time: relatively expensive (connectivity between systems was a challenge) and mostly one direction.
And then there was PDM.
 In parallel with the introduction of ERP systems, mainstream 3D CAD systems became affordable, particularly SolidWorks, Solid Edge and Inventor. These 3D CAD systems allow sharing of parts and assemblies in different products, and the PDM database was the first aid to support part reuse, versioning and standardization.
In parallel with the introduction of ERP systems, mainstream 3D CAD systems became affordable, particularly SolidWorks, Solid Edge and Inventor. These 3D CAD systems allow sharing of parts and assemblies in different products, and the PDM database was the first aid to support part reuse, versioning and standardization.
By extracting the parts from the assemblies and subassemblies, it was possible to generate a BOM structure in the PDM system to be transferred or typed into the ERP system. We did not talk about EBOM or MBOM then, as there was only one BOM in the ERP system, and the PDM system was a tool to feed the ERP system.
 Many companies still have based their processes on this approach. ERP (read SAP nowadays) is the central execution system, and PDM is an external system. You might remember the story and image from my previous post about people, processes and tools. The bad practice example: Asking the ERP system to provide a part number when starting to design a part.
Many companies still have based their processes on this approach. ERP (read SAP nowadays) is the central execution system, and PDM is an external system. You might remember the story and image from my previous post about people, processes and tools. The bad practice example: Asking the ERP system to provide a part number when starting to design a part.
And then products started to change.
 In the early 2000s, I worked with SmarTeam to define the E&E (Electronics and Electrical) template. One of the new concepts was to synchronize all design data coming from different disciplines to a single BOM structure.
In the early 2000s, I worked with SmarTeam to define the E&E (Electronics and Electrical) template. One of the new concepts was to synchronize all design data coming from different disciplines to a single BOM structure.
It was the time we started to talk about the EBOM. A type of BOM, as the structure to consolidate all the design data, was based on parts.
The EBOM, most of the time, reflects the design intent in logical groups and sending the relevant parts in the correct order to the ERP system was a favorite expensive customization for service providers. How to transfer an engineering BOM view to an ERP system that only understands the manufacturing view?
Note: not all ERP systems have the data model to differentiate between engineering parts and manufacturing parts
The image below illustrates the challenge and the customer’s perception. 
The automated link between the design side (EBOM) and manufacturing side (MBOM) was a mission impossible – too many exceptions for the (spaghetti) code.
And then came the MBOM.
The identified issues connecting PDM and ERP led to the concept of implementing the MBOM in the PLM system. The MBOM in PLM is one of the characteristics of a PLM implementation compared to a PDM implementation. In a traditional PLM system, there is an interaction and connection between the EBOM and MBOM. EBOM parts should end up as MBOM parts. This interaction can be supported by automation, however, as it is in the same system, still leaving manual changes possible.
 The MBOM structure in PLM could then be the information structure to transfer to the ERP system; however, there is more, as Jörg W. Fischer wrote in his provoking post-Die MBOM muss weg (The MBOM must go). He rightly points out (in German) that the MBOM is not a structure on its own but a combination of different views based on Assembly Drawings, Process Planning and Material Requirements.
The MBOM structure in PLM could then be the information structure to transfer to the ERP system; however, there is more, as Jörg W. Fischer wrote in his provoking post-Die MBOM muss weg (The MBOM must go). He rightly points out (in German) that the MBOM is not a structure on its own but a combination of different views based on Assembly Drawings, Process Planning and Material Requirements.
His conclusion:
Calling these structures, MBOM is trying to squeeze all three structures into one. That usually doesn’t work and then leads to much more emotional discussions in the project. It also costs a lot of money. It is, therefore, better not to use the term MBOM at all.
And indeed, just having an MBOM in your PLM system might help you to prepare some of the manufacturing steps, the needed resources and parts. The MBOM result still has to be localized at the local plant where the manufacturing takes place. And here, the systems used are the ERP system and the MES system.
The main advantage of having the MBOM in the PLM system is the direct relation between specification and manufacturing intent, allowing manufacturing engineering to work collaboratively with engineering in the same environment.
- The first benefit is fewer iterations and a shorter time to production, thanks to early interaction and manufacturing involvement in the engineering process.
- The second benefit is: product knowledge is centralized in a single system. Consolidating your Product Knowledge in ERP does not make sense due to global localization and the missing capabilities to manage the iterative engineering processes on non-existing parts.
And then came the SBOM, the xBOM
 Traditional PLM vendors and implementations kept using xBOM structures as placeholders for related specification data (mechanical designs, electrical, software deliverables, serialized products). Most of the time, related files.
Traditional PLM vendors and implementations kept using xBOM structures as placeholders for related specification data (mechanical designs, electrical, software deliverables, serialized products). Most of the time, related files.
 And with this approach, talking about digital thread, PLM systems also touch on the concepts of Configuration Management.
And with this approach, talking about digital thread, PLM systems also touch on the concepts of Configuration Management.
I will not go into the details here but look at the two images by clicking on them and see a similar mindset.
It is about the traceability of information in structures and systems. These structures work well in a relatively static and linear product development and delivery environment, as illustrated below:
Engineering change and release processes are based on managing the changes in different structures from the left to the right.
And then came software!
 Modern connected products are no longer mechanical products. The product’s functionality no longer depends on the mechanical properties but mainly on embedded electronics and software used. For example, look at the mechanical design of a telecom transmission tower – its behavior merely comes from non-mechanical components, and they can change over time. Still, the Bill of Material contains a lot of concrete and steel parts.
Modern connected products are no longer mechanical products. The product’s functionality no longer depends on the mechanical properties but mainly on embedded electronics and software used. For example, look at the mechanical design of a telecom transmission tower – its behavior merely comes from non-mechanical components, and they can change over time. Still, the Bill of Material contains a lot of concrete and steel parts.
The ultimate example is comparing a Tesla (software on wheels) with a traditional car. For modern connected products, electronics and software need to be part of the solution. Software and electronics allow the product to be upgraded over time. Managing these products in the same manner as mechanical products is impossible, inefficient and therefore threatening your company’s future business.
I requote Jan Bosch:
An excessive focus on the bill of materials leads to significant challenges for companies that are undergoing a digital transformation and adopting continuous value delivery. The lack of headroom, high coupling and versioning hell may easily cause an explosion of R&D expenditure over time.
The model-based, connected enterprise
I will not solve the puzzle of the future in this post. You can read my observations in my series: The road to model-based and connected PLM. We need a new infrastructure with at least two modes. One that still serves as a System of Record, storing information in a traditional manner, like a Bill of Materials for the static parts, as not everyone and everything can be connected.
 In addition, we need various Systems of Engagement that enable close to real-time interaction between products (systems) and relevant stakeholders for the engagement scope(multidisciplinary / consumers).
In addition, we need various Systems of Engagement that enable close to real-time interaction between products (systems) and relevant stakeholders for the engagement scope(multidisciplinary / consumers).
Digital twins are examples of such environments. Currently, these Systems of Engagement often work disconnected from the System of Record due to the lack of understanding of how to connect. (standard connectors? / OSLC?)
Our mission is to explore, as I wrote in my post Time to split PLM and drop our mechanical mindset.
 And while I was finalizing this post, I read a motivating post from Jan Bosch again for all of you working on understanding and pushing the digital transformation in your eco-system.
And while I was finalizing this post, I read a motivating post from Jan Bosch again for all of you working on understanding and pushing the digital transformation in your eco-system.
The title: Be the protagonist of your life: 15 rules A starting point for more to come.
Conclusion
The BOM is no longer the master of the product lifecycle when it comes to managing connected products, where functionality mainly depends on software. BOM structures with related documents are just one of the extracted baselines from a data-driven, connected enterprise. This traditional PLM infrastructure requires other, non-BOM-driven structures to represent the actual status of a virtual or physical product.
The BOM is not dead, but there is more ………
Your thoughts?
 Those who have read my blog posts over the years will have seen the image to the left.
Those who have read my blog posts over the years will have seen the image to the left.
The people, processes and tools slogan points to the best practice of implementing (PLM and CM) systems.
Theoretically, a PLM implementation will move smoothly if the company first agrees on the desired processes and people involved before a system implementation using the right tools.
Too often, companies start from their historical landscape (the tools – starting with a vendor selection) and then try to figure out the optimal usage of their systems. The best example of this approach is the interaction between PDM(PLM) and ERP.
PDM and ERP
 Historically ERP was the first enterprise system that most companies implemented. For product development, there was the PDM system, an engineering tool, and for execution, there was the ERP system. Since ERP focuses on the company’s execution, the system became the management’s favorite.
Historically ERP was the first enterprise system that most companies implemented. For product development, there was the PDM system, an engineering tool, and for execution, there was the ERP system. Since ERP focuses on the company’s execution, the system became the management’s favorite.
The ERP system and its information were needed to run and control the company. Unfortunately, this approach has introduced the idea that the ERP system should also be the source of the part information, as it was often the first enterprise system for a company. The PDM system was often considered an engineering tool only. And when we talk about a PLM system, who really implements PLM as an enterprise system or was it still an engineering tool?
This is an example of Tools, Processes, and People – A BAD PRACTICE.
 Imagine an engineer who wants to introduce a new part needed for a product to deliver. In many companies at the beginning of this century, even before starting the exercise, the engineer had to request a part number from the ERP system. This is implementation complexity #1.
Imagine an engineer who wants to introduce a new part needed for a product to deliver. In many companies at the beginning of this century, even before starting the exercise, the engineer had to request a part number from the ERP system. This is implementation complexity #1.
Next, the engineer starts developing versions of the part based on the requirements. Ultimately the engineer might come to the conclusion this part will never be implemented. The reserved part number in ERP has been wasted – what to do?
It sounds weird, but this was a reality in discussions on this topic until ten years ago.
 Next, as the ERP system could only deal with 7 digits, what about part number reuse? In conclusion, it is a considerable risk that reused part numbers can lead to errors. With the introduction of the PLM systems, there was the opportunity to bridge the gap between engineering and manufacturing. Now it is clear for most companies that the engineer should create the initial part number.
Next, as the ERP system could only deal with 7 digits, what about part number reuse? In conclusion, it is a considerable risk that reused part numbers can lead to errors. With the introduction of the PLM systems, there was the opportunity to bridge the gap between engineering and manufacturing. Now it is clear for most companies that the engineer should create the initial part number.
Only when the conceptual part becomes approved to be used for the realization of the product, an exchange with the ERP system will be needed. Using the same part number or not, we do not care if we can map both identifiers between these environments and have traceability.
It took almost 10 years from PDM to PLM until companies agreed on this approach, and I am curious about your company’s status.
 Meanwhile, in the PLM world, we have evolved on this topic. The part and the BOM are no longer simple entities. Instead, we often differentiate between EBOM and MBOM, and the parts in those BOMs are not necessarily the same.
Meanwhile, in the PLM world, we have evolved on this topic. The part and the BOM are no longer simple entities. Instead, we often differentiate between EBOM and MBOM, and the parts in those BOMs are not necessarily the same.
In this context, I like Prof. Dr. Jörg W. Fischer‘s framing:
EBOM is the specification, and MBOM is the realization.
(Leider schreibt Er viel auf Deutsch).
 An interesting discussion initiated by Jörg last week was again about the interaction between PLM and ERP. The article is an excellent example of how potentially mainstream enterprises are thinking. PLM = Siemens, ERP = SAP – an illustration of the “tools first” mindset before the ideal process is defined.
An interesting discussion initiated by Jörg last week was again about the interaction between PLM and ERP. The article is an excellent example of how potentially mainstream enterprises are thinking. PLM = Siemens, ERP = SAP – an illustration of the “tools first” mindset before the ideal process is defined.
There was nothing wrong with that in the early days, as connectivity between different systems was difficult and expensive. Therefore people with a 20 year of experience might still rely on their systems infrastructure instead of data flow.
But enough about the bad practice – let’s go to people, processes, (data), and Tools
People, Processes, Data and Tools?
I got inspired by this topic, seeing this post two weeks ago from Juha Korpela, claiming:
Okay, so maybe a hot take, maybe not, but: the old “People, Process, Technology” trinity is one of the most harmful thinking patterns you can have. It leaves out a key element: Data.
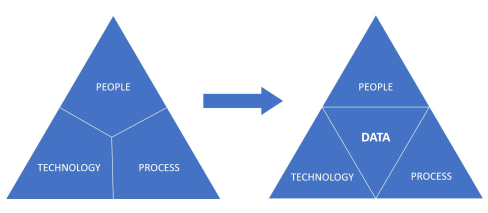
His full post was quite focused on data, and I liked the ” wrapping post” from Dr. Nicolas Figay here, putting things more in perspective from his point of view. The reply made me think about how this discussion fits into the PLM digital transformation discussion. How would it work in the two major themes I use to explain the digital transformation in the PLM landscape?
For incidental readers of my blog, these are the two major themes I am using:
- From Coordinated to Connected, based on the famous diagram from Marc Halpern (image below). The coordinated approach based on documents (files) requires a particular timing (processes) and context (Bills of Information) – it is the traditional and current PLM approach for most companies. On the other hand, the Connected approach is based on connected datasets (here, we talk about data – not files). These connected datasets are available in different contexts, in real-time, to be used by all kinds of applications, particularly modeling applications. Read about it in the series: The road to model-based and connected PLM.
. - The need to split PLM, thinking in System(s) of Record and Systems of Engagement. (example below) The idea behind this split is driven by the observation that companies need various Systems of Record for configuration management, change management, compliance and realization. These activities sound like traditional PLM targets and could still be done in these systems. New in the discussion is the System of Engagement which focuses on a specific value stream in a digitally connected manner. Here data is essential.I discussed the coexistence of these two approaches in my post Time to Split PLM. A post on LinkedIn with many discussions and reshares illustrating the topic is hot. And I am happy to discuss “split PLM architectures” with all of you.
These two concepts discuss the processes and the tools, but what about the people? Here I came to a conclusion to complete the story, we have to imagine three kinds of people. And this will not be new. We have the creators of data, the controllers of data and the consumers of data. Let’s zoom in on their specifics.
A new representation?
 I am looking for a new simplifaction of the people, processes, and tools trinity combined with data; I got inspired by the work Don Farr did at Boeing, where he worked on a new visual representation for the model-based enterprise. You might have seen the image on the left before – click on it to see it in detail.
I am looking for a new simplifaction of the people, processes, and tools trinity combined with data; I got inspired by the work Don Farr did at Boeing, where he worked on a new visual representation for the model-based enterprise. You might have seen the image on the left before – click on it to see it in detail.
I wrote the first time about this new representation in my post: The weekend after CIMdata Roadmap / PDT Europe 2018
 Related to Configuration Management, Martijn Dullaart and Martin Haket have also worked on a diagram with their peers to depict the scope of CM and Impact Analysis. The image leads to the post with my favorite quote: Communication is merely an exchange of information, but connections tell the story.
Related to Configuration Management, Martijn Dullaart and Martin Haket have also worked on a diagram with their peers to depict the scope of CM and Impact Analysis. The image leads to the post with my favorite quote: Communication is merely an exchange of information, but connections tell the story.
Below I share my first attempt to combine the people, process and tools trinity with the concepts of document and data, system(s) of record and system(s) of engagement. Trying to build the story. Look if you recognize the aspects of the discussion above, and feel free to develop enhancements.
I look forward to your suggestions. Like the understanding that we have to split PLM thinking, as it impacts how we look at implementations.
Conclusion
Digital transformation in the PLM domain is forcing us to think differently. There will still be processes based on people collecting, interpreting and combining information. However, there will also be a new domain of connected data interpreted by models and algorithms, not necessarily depending on processes.
Therefore we need to work on new representations that can be used to tell this combined story. What do you think? How can we improve?
 In the last few weeks, I thought I had a writer’s block, as I usually write about PLM-related topics close to my engagements.
In the last few weeks, I thought I had a writer’s block, as I usually write about PLM-related topics close to my engagements.
Where are the always popular discussions related to EBOM or MBOM? Where is the Form-Fit-Function discussion or the traditional “meaningful numbers” discussions?
These topics always create a lot of interaction and discussion, as many of us have mature opinions.
However, last month I spent most of the time discussing the connection between digital PLM strategies and sustainability. With the Russian invasion of Ukraine, leading to high energy prices, combined with several climate disasters this year, people are aware that 2022 is not a year as usual. A year full of events that force us to rethink our current ways of living.
The notion of urgency
 Sustainability for the planet and its people has all the focus currently. COP27 gives you the impression that governments are really serious. Are they? Read this post from Kimberley R. Miner, Climate Scientist at NASA, Polar Explorer& Professor.
Sustainability for the planet and its people has all the focus currently. COP27 gives you the impression that governments are really serious. Are they? Read this post from Kimberley R. Miner, Climate Scientist at NASA, Polar Explorer& Professor.
She doubts if we really grasp the urgency needed to address climate change. Or are we just playing to be on stage? I agree with her doubts.
So what to do with my favorite EBOM-MBOM discussions?
 Last week I attended an event organized by Dassault Systems in the Netherlands for their Dutch/Belgium customers.
Last week I attended an event organized by Dassault Systems in the Netherlands for their Dutch/Belgium customers.
The title of the event was: Sustainable innovation for a digital future. I expected a techy event. Click on the image to see the details.
Asking my grandson, who had just started to his study Aerospace Engineering in Delft (NL), learning to work with CAD and PLM-tools, to join me – he replied:
“Too many software demos”
 It turned out that my grandson was wrong. The keynote speech from Ruud Veltenaar made most of the audience feel uncomfortable. He really pointed to the fact that we are aware of climate change and our impact on the planet, but in a way, we are paralyzed. Nothing new, but confronting and unexpected when going to a customer event.
It turned out that my grandson was wrong. The keynote speech from Ruud Veltenaar made most of the audience feel uncomfortable. He really pointed to the fact that we are aware of climate change and our impact on the planet, but in a way, we are paralyzed. Nothing new, but confronting and unexpected when going to a customer event.
Ruud’s message: Accept that we are at the end of an existing world order, and we should prepare for a new world order with the right moral leadership. It starts within yourself. Reflect on who you really are, where you are in your life path, and finally, what you want.
It sounds simple, and I can see it helps to step aside and reflect on these points.
Otherwise, you might feel we are in a rat race as shown below (recommend to watch).
The keynote was the foundation for a day of group and panel discussions on sustainability. Learning from their customers their sustainability plans and experiences.
 It showed Dassault Systems, with its 2012 purpose (click on the link to see its history), Harmonizing Products, Nature and Life is ahead of the curve (at least they were for me).
It showed Dassault Systems, with its 2012 purpose (click on the link to see its history), Harmonizing Products, Nature and Life is ahead of the curve (at least they were for me).
The event was energizing, and my grandson was wrong:
“No software – next time?”
The impact of legacies – data, processes & people
 For those who haven’t read my previous post, The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022, I wrote about the importance of Heterogeneous and federated PLM, one of the discussions related to data-driven PLM.
For those who haven’t read my previous post, The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022, I wrote about the importance of Heterogeneous and federated PLM, one of the discussions related to data-driven PLM.
Looking back, I have been writing about data-driven PLM since 2014, and few companies have made progress here. Understandable, first of all, due to legacy data, which is not in the right format or quality to support data-driven processes.
However, also here, legacy processes and legacy people are blocking the change. There is no blame here; it is difficult to change. You might have a visionary management team, but then it comes down to the execution of the strategy. The organizational structure and the existing people skills are creating more resistance than progress.
 For that reason, I wrote this post in 2015: PLM and Global Warming, where I compared the progress we made within our PLM community with the lack of progress we are making in solving global warming. We know the problem, but we are unable to act due to the lack of feeling the urgency.
For that reason, I wrote this post in 2015: PLM and Global Warming, where I compared the progress we made within our PLM community with the lack of progress we are making in solving global warming. We know the problem, but we are unable to act due to the lack of feeling the urgency.
This blog post triggered Rich McFall to start together in 2018 the PLM Global Green Alliance.
In my PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe session Sustainability and Data-driven PLM – the perfect storm, I raised the awareness that we need to speed up. We have 10 perhaps 15 years to implement radical changes, according to scientists, before we reach irreversible tipping points.
Why PLM and Sustainability?
Sustainability starts with the business strategy. How does your company want to contribute to a more sustainable future? The strategy to follow with probably the most impact is the concept of a circular economy – image below and more info here.
The idea behind the circular economy is to minimize the need for new finite materials (the right side) and to use for energy delivery only renewables. Implementing these principles clearly requires a more holistic design of products and services. Each loop should be analyzed and considered when delivering solutions to the market.
Therefore, a logical outcome of the circular economy would be transforming from selling products to the market towards a product-as-a-service model. In this case, the product manufacturer becomes responsible for the full product lifecycle and its environmental impact.
And here comes the importance of PLM. You can measure and tune your environmental impact during production in your ERP or MES environment. However, 80 % of the environmental impact is defined during the design phase, the domain of PLM. All these analysis together are called Life Cycle Analysis or Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). A practice that starts at the moment you start to think about a product or solution – a specialized systems thinking approach.
So how to define and select the right options for future products?
Virtual products / Digital Twins
 This is where sustainability is pushing for digitization of the product lifecycle. Building and analyzing products in the virtual world is much cheaper than working with physical prototypes.
This is where sustainability is pushing for digitization of the product lifecycle. Building and analyzing products in the virtual world is much cheaper than working with physical prototypes.
The importance of a model-based approach here allows companies efficiently deal with trade-off studies for each solution.
In addition, the choice and the behavior of materials also have an impact. These material properties will come from various databases, some based on hazardous substances, others on environmental parameters. Connecting these databases to the virtual model is crucial to remain efficient.
Imagine you need manually collect and process in these properties whenever studying an alternative. The manual process will be too costly (fewer trade-offs and not finding the optimum) and too slow (time-to-market impact).
 That’s why I am greatly interested in all the developments related to a federated PLM infrastructure. A monolithic system cannot be the solution for such a model-based environment. In my terminology, here we need an architecture with systems of engagement combined with system(s) of record.
That’s why I am greatly interested in all the developments related to a federated PLM infrastructure. A monolithic system cannot be the solution for such a model-based environment. In my terminology, here we need an architecture with systems of engagement combined with system(s) of record.
I will publish more on this topic in the future.
In the previous paragraphs, I wrote about the virtual product environment, which some companies call the virtual twin. However, besides the virtual twin, we also need several digital twins. These digital models allow us to monitor and optimize the production process, which can lead to design changes.
Also, monitoring the product in operation using a digital twin allows us to optimize the performance and execution of the solutions in the field.

The feedback from these digital twins will then help the company to improve the design and calibrate their simulation models. It should be a closed loop. You can find a more recent discussion related to the above image here.
Our mission
 At this moment, sustainability is at the top of my personal agenda, and I hope for many of you. However, besides the choices we can make in our personal lives, there is also an area where we, as PLM interested parties, should contribute: The digitization of the product lifecycle as an enabler for a sustainable business.
At this moment, sustainability is at the top of my personal agenda, and I hope for many of you. However, besides the choices we can make in our personal lives, there is also an area where we, as PLM interested parties, should contribute: The digitization of the product lifecycle as an enabler for a sustainable business.
Without mature concepts for a connected enterprise, implementing sustainable products and business processes will be a wish, not a strategy. So add digitization to your skillset and use it in the context of sustainability.
Conclusion
It might look like this PLM blog has become an environmental blog. This might be right, as the environmental impact of products and solutions is directly related to product lifecycle management. However, do not worry. In the upcoming time, I will focus on the aspects and experiences of a connected enterprise. I will leave the easier discussions (EBOM/MBOM/FFF/Smart Numbers) from a coordinated enterprise as they are. There is work to do shortly. Your thoughts?

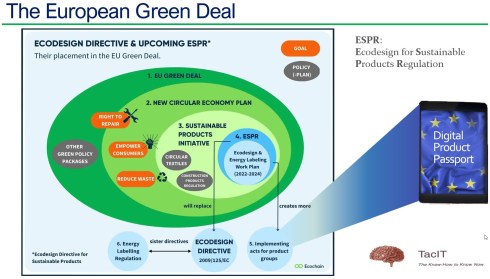
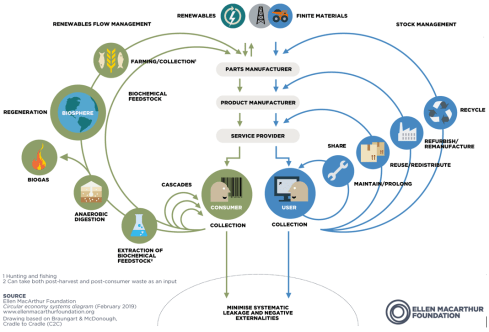




























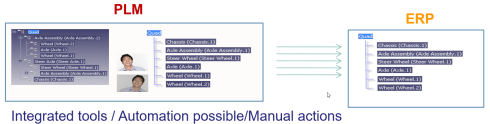

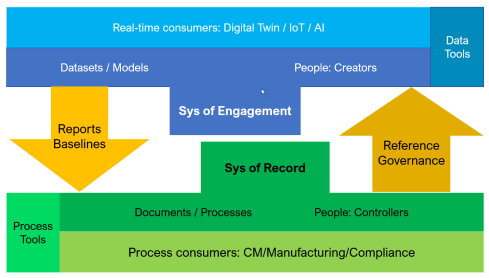




[…] (The following post from PLM Green Global Alliance cofounder Jos Voskuil first appeared in his European PLM-focused blog HERE.) […]
[…] recent discussions in the PLM ecosystem, including PSC Transition Technologies (EcoPLM), CIMPA PLM services (LCA), and the Design for…
Jos, all interesting and relevant. There are additional elements to be mentioned and Ontologies seem to be one of the…
Jos, as usual, you've provided a buffet of "food for thought". Where do you see AI being trained by a…
Hi Jos. Thanks for getting back to posting! Is is an interesting and ongoing struggle, federation vs one vendor approach.…