 I hope you all remained curious after last week’s report from day 1 of the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022 conference in Gothenburg. The networking dinner after day 1 and the Share PLM after-party allowed us to discuss and compare our businesses. Now the highlights of day 2
I hope you all remained curious after last week’s report from day 1 of the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022 conference in Gothenburg. The networking dinner after day 1 and the Share PLM after-party allowed us to discuss and compare our businesses. Now the highlights of day 2
The Power of Curiosity
We started with a keynote speech from Stefaan van Hooydonk, Founder of the Global Curiosity Institute. It was a well-received opener of the day and an interesting theme concerning PLM.
 According to Stefaan, in the previous century, curiosity had a negative connotation. Curiosity killing the cat is one of these expressions confirming the mindset. It was all about conformity to the majority, the company, and curiosity was non-conformant.
According to Stefaan, in the previous century, curiosity had a negative connotation. Curiosity killing the cat is one of these expressions confirming the mindset. It was all about conformity to the majority, the company, and curiosity was non-conformant.
The same mindset I would say we have with traditional PLM; we all have to work the same way with the same processes.
In the 21st century, modern enterprises stimulate curiosity as we understand that throughout history, curiosity has been the engine of individual, organizational, and societal progress. And in particular, in modern, unpredictable times, curiosity becomes important, for the world, the others around us and ourselves.
As Stefaan describes in his book, the Curiosity Manifesto, organizations and individuals can develop curiosity. Stefaan pushed us to reflect on our personal curiosity behavior.
- Are we really interested in the person, the topic I do not know or do not like?
- Are we avoiding curious steps out of fear? Fear for failing, judgment?
After Stefaan’s curiosity storm, you could see that the audience was inspired to apply it to themselves and their PLM mission(s).
I hope the latter – as here there is a lot to discover.
Digital Transformation – Time to roll up your sleeves
In his presentation, Torbjörn Holm, co-founder of Eurostep, addressed one of the bigger elephants in the modern enterprise: how to deal with data?
Thanks to digitization, companies are gathering ad storing data, and there seem to be no limits. However, data centers compete for electricity from the grid with civilians.
 Torbjörn also introduced the term “Dark data – the dirty secret of the ICT sector. We store too much data; some research mentions that only 12 % of the data stored is critical, and the rest clogs up on some file servers. Storing unstructured and unused data generates millions of greenhouse gasses yearly.
Torbjörn also introduced the term “Dark data – the dirty secret of the ICT sector. We store too much data; some research mentions that only 12 % of the data stored is critical, and the rest clogs up on some file servers. Storing unstructured and unused data generates millions of greenhouse gasses yearly.
It is time for a data cleanup day, and inspired by Torbjörn’s story, I have already started to clean up my cloud storage. However, I did not touch my backup hard disks as they do not use energy when switched off.
Further, Torbjörn elaborated that companies need to have end-to-end data policies. Which data is required? And in the case of contracted work or suppliers, data is crucial.
Ultimately companies that want to benefit from a virtual twin of their asset in operation need to have processes in place to acquire the correct data and maintain the valid data. Digital twins do not run on documents; as mentioned in some of my blog posts, they need accurate data.
Torbjörn once more reminded us that the PLCS objective is designed for that.
Heterogeneous and federated PLM – is it feasible?
One of the sessions that upfront had most of my attention was the presentation from Erik Herzog, Technical Fellow at Saab Aeronautics and Jad El-Khoury, Researcher at the KTH/Royal Institute of Technology.
Their presentation was closely related to the pre-conference workshop we had organized by Erik and Eurostep. More about this topic in the future.
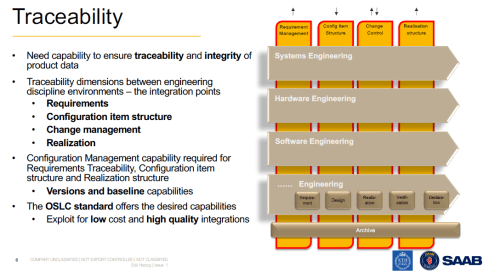
Saab, Eurostep and KTH conducted a research project named Helipe to analyze and test a federated PLM architecture. The concept was strongly driven by engineering. The idea is shown in the images below.
First are the four main modular engineering environments; in the image, we see mechanical, electrical, software and engineering environments. The target is to keep these environments as standard as possible towards the outside world so that later, an environment could be swapped for a better environment. Inside an environment, automation should provide optimal performance for the users.
In my terminology, these environments serve as systems of engagement.
The second dimension of this architecture is the traceability layer(s) – the requirements management layer, the configuration item structures, change control and realization structures.
These traceability structures look much like what we have been doing with traditional PLM, CM and ERP systems. In my terminology, they are the systems or record, not mentioned to directly serve end-users but to provide traceability, baselines for configuration, compliance and more.
The team chose the OSLC standard to realize these capabilities. One of the main reasons because OSLC is an existing open standard based on linked data, not replicating data. In this way, a federated environment would be created with designated connections between datasets.
 Jad El-Koury demonstrated how to link an existing requirement in Siemens Polarion to a Defect in IBM ELM and then create a new requirement in Polarion and link this requirement to the same defect. I never get excited from technical demos; more important to learn is the effort to build such integration and its stability over time. Click on the image for the details
Jad El-Koury demonstrated how to link an existing requirement in Siemens Polarion to a Defect in IBM ELM and then create a new requirement in Polarion and link this requirement to the same defect. I never get excited from technical demos; more important to learn is the effort to build such integration and its stability over time. Click on the image for the details
The conclusions from the team below give the right indicators where the last two points seem feasible.
 Still, we need more benchmarking in other environments to learn.
Still, we need more benchmarking in other environments to learn.
I remain curious about this approach as I believe it is heading toward what is necessary for the future, the mix of systems of record and systems of engagement connected through a digital web.
The bold part of the last sentence may be used by marketers.
Sustainability and Data-driven PLM – the perfect storm
 For those familiar with my blog (virtualdutchman.com) and my contribution to the PLM Global Green Alliance, it will be no surprise that I am currently combining new ways of working for the PLM domain (digitization) with an even more hot topic, sustainability.
For those familiar with my blog (virtualdutchman.com) and my contribution to the PLM Global Green Alliance, it will be no surprise that I am currently combining new ways of working for the PLM domain (digitization) with an even more hot topic, sustainability.
More hot is perhaps a cynical remark.
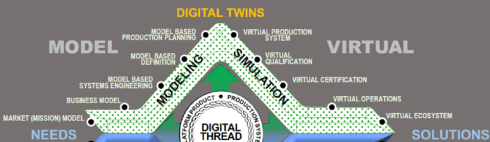
In my presentation, I explained that a model-based, data-driven enterprise will be able to use digital twins during the design phase, the manufacturing process planning and twins of products in operation. Each twin has a different purpose.
The virtual product during the design phase does not have a real physical twin yet, so some might say it is not a twin at this stage. The virtual product/twin allows companies to perform trade-offs, verification and validation relatively fast and inexpensively. The power of analyzing this virtual twin will enable companies to design products not only at the best price/performance range but even as important, with the lowest environmental impact during manufacturing and usage in the field.
As the Boeing diamond nicely shows, there is a whole virtual world for digital twins. The manufacturing digital twin allows companies to analyze their manufacturing process and virtually analyze the most effective manufacturing process, preferably with the lowest environmental impact.
For digital twins from a product in the field, we can analyze its behavior and optimize performance, hopefully with environmental performance indicators in mind.
For a sustainable future, it is clear that we need to implement concepts of the circular economy as the earth does not have enough resources and renewables to support our current consumption behavior and ways of living.
Note: not for everybody on the globe, a quote from the European Environment Agency below:
Europe consumes more resources than most other regions. An average European citizen uses approximately four times more resources than one in Africa and three times more than one in Asia, but half of that of a citizen of the USA, Canada, or Australia
To reduce consumption, one of the recommendations is to switch the business model from owning products to products as a service. In the case of products as a service, the manufacturer becomes the owner of the full product lifecycle. Therefore, the manufacturer will have business reasons to make the products repairable, upgradeable, recyclable and using energy efficiently, preferably with renewables. If not, the product might become too expensive; fossil energy will be too expensive as carbon taxes will increase, and virgin materials might become too expensive.
 It is a business change; however, sustainability will push organizations to change faster than we are used to. For example, we learned this week that the peeking energy prices and Russia’s current war in Ukraine have led to strong investments in renewables.
It is a business change; however, sustainability will push organizations to change faster than we are used to. For example, we learned this week that the peeking energy prices and Russia’s current war in Ukraine have led to strong investments in renewables.
As a result, many countries no longer want to depend on Russian energy. The peak of carbon emissions for the world is now expected in 2025.
(Although we had a very bad year so far)
 Therefore, my presentation concluded that we should use sustainability as an additional driver for our digital transformation in the PLM domain. The planet cannot wait until we slowly change our traditional working methods.
Therefore, my presentation concluded that we should use sustainability as an additional driver for our digital transformation in the PLM domain. The planet cannot wait until we slowly change our traditional working methods.
Therefore, the need for digital twins to support sustainability and systems thinking are the perfect storm to speed up our digitization projects.
You can find my presentation as usual, here on SlideShare and a “spoken” version on our PGGA YouTube channel here
Digitalization for the Development and Industrialization of Innovative and Sustainable Solutions
This session, given by Ola Isaksson, Professor, Product Development & Systems Engineering Design Research Group Leader at Chalmers University, was a great continuation on my part of sustainability. Ola went deeper into the aspects of sustainable products and sustainable business models.
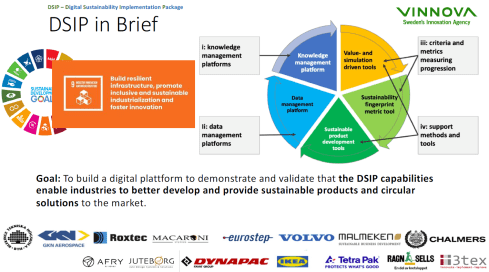
The DSIP project (Digital Sustainability Implementation Package – image above) aims to help companies understand all aspects of sustainable development. Ola mentioned that today’s products’ evolution is insufficient to ensure a sustainable outcome. Currently, not products nor product development practices are adequate enough as we do not understand all the aspects.
For example, Ola used the electrification process, taking the Lithium raw material needed for the batteries. If we take the Nissan Leaf car as the point of measure, we would have used all Lithium resources within 50 years.
Therefore, other business models are also required, where the product ownership is transferred to the manufacturer. This is one of the 9Rs (or 10), as the image shows moving from a linear economy towards a circular economy.
Also, as I mentioned in my session, Ola referred to the upcoming regulations forcing manufacturers to change their business model or product design. All these aspects are discussed in the DSIP project, and I look forward to learning the impact this project had on educating and supporting companies in their sustainability journey.
A day 2 summary
 We had Bernd Feldvoss, Value Stream Leader PLM Interoperability Standards at Airbus, reporting on the progress of the A&D action group focusing on Collaboration. At this stage, the project team has developed an open-service Collaboration Management System (CMS) web application, providing navigation through the eight-step guidelines and offering the potential to improve OEM-supplier collaboration consistency and efficiency within the A&D community.
We had Bernd Feldvoss, Value Stream Leader PLM Interoperability Standards at Airbus, reporting on the progress of the A&D action group focusing on Collaboration. At this stage, the project team has developed an open-service Collaboration Management System (CMS) web application, providing navigation through the eight-step guidelines and offering the potential to improve OEM-supplier collaboration consistency and efficiency within the A&D community.
 We had Henrik Lindblad, Group Leader PLM & Process Support at the European Spallation Source, building and soon operating the world’s most powerful neutron source, enabling scientific breakthroughs in research related to materials, energy, health and the environment. Besides a scientific breakthrough, this project is also an example of starting with building a virtual twin of the facility from the start providing a multidisciplinary collaboration space.
We had Henrik Lindblad, Group Leader PLM & Process Support at the European Spallation Source, building and soon operating the world’s most powerful neutron source, enabling scientific breakthroughs in research related to materials, energy, health and the environment. Besides a scientific breakthrough, this project is also an example of starting with building a virtual twin of the facility from the start providing a multidisciplinary collaboration space.
Conclusion
I left the conference with a lot of positive energy. The Curiosity session from Stefaan van Hooydonk energized us all, but as important for our PLM domain, I saw the trend towards more federated PLM environments, more discussions related to sustainability, and people in 3D again. So far, my takeaways this time. Enough to explore till the next event.










1 comment
Comments feed for this article
October 31, 2022 at 5:11 am
Jorge Ivan Moreno
Definitely… the digital mesh is here to stay !!!!
Thanks for your confidence Jorge
LikeLike