You are currently browsing the tag archive for the ‘PLM’ tag.
 In the last two weeks, I have had mixed discussions related to PLM, where I realized the two different ways people can look at PLM. Are implementing PLM capabilities driven by a cost-benefit analysis and a business case? Or is implementing PLM capabilities driven by strategy providing business value for a company?
In the last two weeks, I have had mixed discussions related to PLM, where I realized the two different ways people can look at PLM. Are implementing PLM capabilities driven by a cost-benefit analysis and a business case? Or is implementing PLM capabilities driven by strategy providing business value for a company?
Most companies I am working with focus on the first option – there needs to be a business case.
 This observation is a pleasant passageway into a broader discussion started by Rob Ferrone recently with his article Money for nothing and PLM for free. He explains the PDM cost of doing business, which goes beyond the software’s cost. Often, companies consider the other expenses inescapable.
This observation is a pleasant passageway into a broader discussion started by Rob Ferrone recently with his article Money for nothing and PLM for free. He explains the PDM cost of doing business, which goes beyond the software’s cost. Often, companies consider the other expenses inescapable.
 At the same time, Benedict Smith wrote some visionary posts about the potential power of an AI-driven PLM strategy, the most recent article being PLM augmentation – Panning for Gold.
At the same time, Benedict Smith wrote some visionary posts about the potential power of an AI-driven PLM strategy, the most recent article being PLM augmentation – Panning for Gold.
It is a visionary article about what is possible in the PLM space (if there was no legacy ☹), based on Robust Reasoning and how you could even start with LLM Augmentation for PLM “Micro-Tasks.
Interestingly, the articles from both Rob and Benedict were supported by AI-generated images – I believe this is the future: Creating an AI image of the message you have in mind.
![]() When you have digested their articles, it is time to dive deeper into the different perspectives of value and costs for PLM.
When you have digested their articles, it is time to dive deeper into the different perspectives of value and costs for PLM.
From a system to a strategy
 The biggest obstacle I have discovered is that people relate PLM to a system or, even worse, to an engineering tool. This 20-year-old misunderstanding probably comes from the fact that in the past, implementing PLM was more an IT activity – providing the best support for engineers and their data – than a business-driven set of capabilities needed to support the product lifecycle.
The biggest obstacle I have discovered is that people relate PLM to a system or, even worse, to an engineering tool. This 20-year-old misunderstanding probably comes from the fact that in the past, implementing PLM was more an IT activity – providing the best support for engineers and their data – than a business-driven set of capabilities needed to support the product lifecycle.
The System approach
Traditional organizations are siloed, and initially, PLM always had the challenge of supporting product information shared throughout the whole lifecycle, where there was no conventional focus per discipline to invest in sharing – every discipline has its P&L – and sharing comes with a cost.
 At the management level, the financial data coming from the ERP system drives the business. ERP systems are transactional and can provide real-time data about the company’s performance. C-level management wants to be sure they can see what is happening, so there is a massive focus on implementing the best ERP system.
At the management level, the financial data coming from the ERP system drives the business. ERP systems are transactional and can provide real-time data about the company’s performance. C-level management wants to be sure they can see what is happening, so there is a massive focus on implementing the best ERP system.
In some cases, I noticed that the investment in ERP was twenty times more than the PLM investment.
 Why would you invest in PLM? Although the ERP engine will slow down without proper PLM, the complexity of PLM compared to ERP is a reason for management to look at the costs, as the PLM benefits are hard to grasp and depend on so much more than just execution.
Why would you invest in PLM? Although the ERP engine will slow down without proper PLM, the complexity of PLM compared to ERP is a reason for management to look at the costs, as the PLM benefits are hard to grasp and depend on so much more than just execution.
See also my old 2015 article: How do you measure collaboration?
As I mentioned, the Cost of Non-Quality, too many iterations, time lost by searching, material scrap, manufacturing delays or customer complaints – often are considered inescapable parts of doing business (like everyone else) – it happens all the time..
The strategy approach
 It is clear that when we accept the modern definition of PLM, we should be considering product lifecycle management as the management of the product lifecycle (as Patrick Hillberg says eloquently in our Share PLM podcast – see the image at the bottom of this post, too).
It is clear that when we accept the modern definition of PLM, we should be considering product lifecycle management as the management of the product lifecycle (as Patrick Hillberg says eloquently in our Share PLM podcast – see the image at the bottom of this post, too).
When you implement a strategy, it is evident that there should be a long(er) term vision behind it, which can be challenging for companies. Also, please read my previous article: The importance of a (PLM) vision.
 I cannot believe that, although perhaps not fully understood, the importance of a data-driven approach will be discussed at many strategic board meetings. A data-driven approach is needed to implement a digital thread as the foundation for enhanced business models based on digital twins and to ensure data quality and governance supporting AI initiatives.
I cannot believe that, although perhaps not fully understood, the importance of a data-driven approach will be discussed at many strategic board meetings. A data-driven approach is needed to implement a digital thread as the foundation for enhanced business models based on digital twins and to ensure data quality and governance supporting AI initiatives.
It is a process I have been preaching: From Coordinated to Coordinated and Connected.
We can be sure that at the board level, strategy discussions should be about value creation, not about reducing costs or avoiding risks as the future strategy.

Understanding the (PLM) value
The biggest challenge for companies is to understand how to modernize their PLM infrastructure to bring value.
* Step 1 is obvious. Stop considering PLM as a system with capabilities, but investigate how you transform your infrastructure from a collection of systems and (document) interfaces towards a federated infrastructure of connected tools.
![]() Note: the paradigm shift from a Single Source of Truth (in my system) towards a Nearest Source of Truth and a Single Source of Change.
Note: the paradigm shift from a Single Source of Truth (in my system) towards a Nearest Source of Truth and a Single Source of Change.
* Step 2 is education. A data-driven approach creates new opportunities and impacts how companies should run their business. Different skills are needed, and other organizational structures are required, from disciplines working in siloes to hybrid organizations where people can work in domain-driven environments (the Systems of Record) and product-centric teams (the System of Engagement). AI tools and capabilities will likely create an effortless flow of information within the enterprise.
* Step 3 is building a compelling story to implement the vision. Implementing new ways of working based on new technical capabilities requires also organizational change. If your organization keeps working similarly, you might gain some percentage of efficiency improvements.
 The real benefits come from doing things differently, and technology allows you to do it differently. However, this requires people to work differently, too, and this is the most common mistake in transformational projects.
The real benefits come from doing things differently, and technology allows you to do it differently. However, this requires people to work differently, too, and this is the most common mistake in transformational projects.
Companies understand the WHY and WHAT but leave the HOW to the middle management.
 People are squeezed into an ideal performance without taking them on the journey. For that reason, it is essential to build a compelling story that motivates individuals to join the transformation. Assisting companies in building compelling story lines is one of the areas where I specialize.
People are squeezed into an ideal performance without taking them on the journey. For that reason, it is essential to build a compelling story that motivates individuals to join the transformation. Assisting companies in building compelling story lines is one of the areas where I specialize.
Feel free to contact me to explore the opportunity for your business.
It is not the technology!
With the upcoming availability of AI tools, implementing a PLM strategy will no longer depend on how IT understands the technology, the systems and the interfaces needed.
As Yousef Hooshmand‘s above image describes, a federated infrastructure of connected (SaaS) solutions will enable companies to focus on accurate data (priority #1) and people creating and using accurate data (priority #1). As you can see, people and data in modern PLM are the highest priority.
Therefore, I look forward to participating in the upcoming Share PLM Summit on 27-28 May in Jerez.
It will be a breakthrough – where traditional PLM conferences focus on technology and best practices. This conference will focus on how we can involve and motivate people. Regardless of which industry you are active in, it is a universal topic for any company that wants to transform.
Conclusion
Returning to this article’s introduction, modern PLM is an opportunity to transform the business and make it future-proof. It needs to be done for sure now or in the near future. Therefore PLM initiatives should be considered from the value point first instead of focusing on the costs. How well are you connected to your management’s vision to make PLM a value discussion?
Enjoy the podcast – several topics discuss relate to this post.
 This year, I will celebrate 25 years since I started my company, TacIT, to focus on knowledge management. However, quickly, I was back in the domain of engineering data management, which became a broader topic, which we now call PLM.
This year, I will celebrate 25 years since I started my company, TacIT, to focus on knowledge management. However, quickly, I was back in the domain of engineering data management, which became a broader topic, which we now call PLM.
Looking back, there have been significant changes in these 25 years, from systems to strategy, for documents to data, from linear to iterative. However, in this post, I want to look at my 2024 observations to see where we can progress. This brings me to the first observation.
PLM is human
Despite many academic and marketing arguments describing WHAT and WHY companies need specific business or software capabilities, there is, above all, the need for people to be personally inspired and connected. We want to belong to a successful group of people, teams and companies because we are humans, not resources.
It is all about people, which was also the title of my session during the March 2024 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference in Eindhoven (NL). I led a panel discussion on the importance of people with Dr. Cara Antoine, Daniel Schöpf, and Florens Wolters, each of whom actively led transformational initiatives within their companies.
 Through Dr. Cara Antoine, e at Capgemini and a key voice for women in tech, I learned about her book Make It Personal. The book inspired me and motivated me to continue using a human-centric approach. Give this book to your leadership and read it yourself. It is practical, easy to read, and encouraging
Through Dr. Cara Antoine, e at Capgemini and a key voice for women in tech, I learned about her book Make It Personal. The book inspired me and motivated me to continue using a human-centric approach. Give this book to your leadership and read it yourself. It is practical, easy to read, and encouraging
Recently, in my post “PLM in real life and Gen AI“, I shared insights related to PLM blogs and Gen AI – original content is becoming increasingly the same, and the human touch is disappearing, while generating more and longer blogs.
 I propose keeping Gen AI-generated text for the boring part of PLM and exploring the human side of PLM engagements in blogs. What does this mean? In the post, I also shared the highlights of the Series 2 podcast I did together with Helena Gutierrez from Share PLM. Every recording had its unique human touch and knowledge.
I propose keeping Gen AI-generated text for the boring part of PLM and exploring the human side of PLM engagements in blogs. What does this mean? In the post, I also shared the highlights of the Series 2 podcast I did together with Helena Gutierrez from Share PLM. Every recording had its unique human touch and knowledge.
We are now in full preparation for Series 3—let us know who your hero is and who should be our guest in 2025!
PLM is business
One of the most significant changes I noticed in my PLM-related projects was that many of the activities connected the PLM activities to the company’s business objectives. Not surprisingly, it was mostly a bottom-up activity, explaining to the upper management that a modern, data-driven PLM strategy is crucial to achieving business or sustainability goals.
I wrote two long posts about these experiences. The first one,” PLM – business first,” zooms in on the changing mindset that PLM is not an engineering system anymore but part of a digital infrastructure that supports companies in achieving their business goals. The image below from Dr. Yousef Hooshmand is one of my favorites in this context. The 5 + 1 steps, where the extra step is crucial: Long Executive Commitment.
So, to get an executive commitment, you need to explain and address business challenges.
Executive commitment and participation can be achieved through a Benefits Dependency Network approach, as illustrated in this webinar I did with the Heliple-2 team, where we were justifying the business needs for Federated PLM. More about the Federated PLM part in the next paragraph.
Another point to consider is that when the PLM team is part of the IT organization (the costs side), they have a big challenge in leading or even participating in business discussions. In this context, read (again) Jan Bosch’s post: Structure Eats Strategy.
 The second post, more recent, summarized the experiences I had with several customer engagements. The title says it all: “Don’t use the P**-word! – 5 lessons learned“, with an overlap in content with the first post.
The second post, more recent, summarized the experiences I had with several customer engagements. The title says it all: “Don’t use the P**-word! – 5 lessons learned“, with an overlap in content with the first post.
Conclusion: A successful PLM strategy starts with the business and needs storytelling to align all stakeholders with a shared vision or goal.
PLM is technology
This year has seen the maturation of PLM technology concepts. We are moving away from a monolithic PLM system and exploring federated and connected infrastructures, preferably a mix of Systems of Record (the old PLMs/ERPs) and Systems of Engagement (the new ways of domain collaboration). The Heliple project manifests such an approach, where the vertical layers are Systems of Record, and the horizontal modules could be Systems of Engagement.
I had several discussions with typical System of Engagement vendors, like Colab (“Where traditional PLM fails”) and Partful (“Connected Digital Thread for Lower and Mid-market OEMs“), but I also had broader discussions during the PLM Roadmap PDT Europe conference – see: R-evolutionizing PLM and ERP and Heliple.
 I also follow Dr. Jorg Fischer, who lectures about digital transformation concepts in the manufacturing business domain. Unfortunately, for a broader audience, Jörg published a lot in German, and typically, his references for PLM and ERP are based on SAP and Teamcenter. His blog posts are always interesting to follow – have a look at his recent blog in English: 7 keys to solve PLM & ERP.
I also follow Dr. Jorg Fischer, who lectures about digital transformation concepts in the manufacturing business domain. Unfortunately, for a broader audience, Jörg published a lot in German, and typically, his references for PLM and ERP are based on SAP and Teamcenter. His blog posts are always interesting to follow – have a look at his recent blog in English: 7 keys to solve PLM & ERP.
 Of course, Oleg Shilovitsky’s impressive and continuous flow of posts related to modern PLM concepts is amazing—just browse through his Beyond PLM home page to read about the actual topics happening in his PLM ecosystem or for example, read about modern technology concepts in this recent OpenBOM article.
Of course, Oleg Shilovitsky’s impressive and continuous flow of posts related to modern PLM concepts is amazing—just browse through his Beyond PLM home page to read about the actual topics happening in his PLM ecosystem or for example, read about modern technology concepts in this recent OpenBOM article.
Conceptually, we are making progress. As a commonality, all future concepts focus on data, not so much on managing documents—and here comes the focus on data.
PLM needs accurate data
In a data-driven environment, apps or systems will use a collection of datasets to provide a user with a working environment, either a dashboard or an interactive real-time environment. Below is my AI (Artist Impression) of a digital enterprise.
Of course, it seems logical; the data must be accurate as you no longer have control over access to the data in a data-driven environment. You can be accountable for the data; others can consume the data you created without checking its accuracy by your guidance.
Therefore, data governance and an excellent enterprise architecture are crucial to support the new paradigm:
The nearest source of truth supported by a single source of change
Quote: Yousef Hoohmand
Forget the Single Source of Truth idea, a previous century paradigm.
With data comes Artificial intelligence and algorithms that can play an essential role in your business, providing solutions or insights that support decision-making.
![]() In 2024, most of us have been exploring the benefits of ChatGPT and Generative AI. You can describe examples of where AI could assist in every aspect of the product lifecycle. I saw great examples from Eaton, Ocado, and others at the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference.
In 2024, most of us have been exploring the benefits of ChatGPT and Generative AI. You can describe examples of where AI could assist in every aspect of the product lifecycle. I saw great examples from Eaton, Ocado, and others at the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference.
See my review here: A long week after the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference.
Still, before benefiting from AI in your organization, it remains essential that the AI runs on top of accurate data.
Sustainability needs (digital) PLM
 This paragraph is the only reverse dependency towards PLM and probably the one that is less in people’s minds, perhaps because PLM is already complex enough. In 2024, with the PLM Green Global Alliance, we had good conversations with PLM-related software vendors or service partners (aPriori, Configit, Makersite, PTC, SAP, Siemens and Transition Technologies PSC) where we discussed their solutions and how they are used in the field by companies.
This paragraph is the only reverse dependency towards PLM and probably the one that is less in people’s minds, perhaps because PLM is already complex enough. In 2024, with the PLM Green Global Alliance, we had good conversations with PLM-related software vendors or service partners (aPriori, Configit, Makersite, PTC, SAP, Siemens and Transition Technologies PSC) where we discussed their solutions and how they are used in the field by companies.
We discovered here that most activities are driven by regulations, like ESG reporting, the new CSRD directive for Europe and the implementation of the Digital Product Passport. What is clear from all these activities is that companies need to have a data-driven PLM infrastructure to connect product data to environmental impacts, like carbon emissions equivalents.
Besides complying with regulations, I have been discussing the topic of Product-As-A-Service, or the Product Service System, this year, with excellent feedback from Dave Duncan. You can find a link to his speech: Improving Product Sustainability – PTC with PGGA.
Also, during the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, I discussed this topic, explaining that achieving a circular economy is a long-term vision, and the starting point is to establish a connected infrastructure within your organizations and with your customers/users in the field.
 Sustainability should be on everyone’s agenda. From the interactions on LinkedIn, you can see that we prefer to discuss terms like PDM/PLM or eBOM/mBOM in the PLM domain. Very few connect PLM to sustainability.
Sustainability should be on everyone’s agenda. From the interactions on LinkedIn, you can see that we prefer to discuss terms like PDM/PLM or eBOM/mBOM in the PLM domain. Very few connect PLM to sustainability.
Sustainability is a long-term mission; however, as we have seen from long-term missions, they can be overwhelmed by the day’s madness and short-term needs.
PLM is Politics
You might not expect this paragraph in my log, as most PLM discussions are about the WHAT and the WHY of a PLM solution or infrastructure. However, the most challenging part of PLM is the HOW, and this is the area that I am still focused on.
In the early days of mediating mainly in SmarTeam implementations, it became clear that the technology was not the issue. A crisis was often due to a lack of (technical) skills or methodology and misplaced expectations.
When the way out became clear, politics often started. Sometimes, there was the HIPPO (HIghest Paid Person’s Opinion) in the company, as Peter Vind explained, or there was the blame game, which I described in my 2019 “The PLM blame game post”.
What makes it even more difficult is that people’s opinions in PLM discussions are often influenced by their friendly relations or history with a particular vendor or implementer from the past, which troubles a proper solution path.
These aspects are challenging to discuss, and nobody wants to discuss them openly. A company (and a country) must promote curiosity instead of adhering to mainstream thinking and working methods. In our latest Share PLM podcast, Brian Berger, a VP at Metso, mentions the importance of diversity within an organization.
“It is a constant element of working in a global business, and the importance cannot be overstated.”
This observation should make us think again when we want to simplify everything and dim the colors.
Conclusion
Initially, I thought this would be a shorter post, but again, it became a long read – therefore, perhaps ideal when closing 2024 and looking forward to activities and focus for 2025. Use this time to read books and educate yourself beyond the social media posts (even my blogs are limited 😉)
In addition, I noticed the build-up of this post was unconsciously influenced by Martijn Dullaart‘s series of messages titled “Configuration Management is ……”. Thanks, Martijn, for your continuous contributions to our joint passion – a digital enterprise where PLM and CM flawlessly interact based on methodology and accurate data.

 Recently, I noticed I reduced my blogging activities as many topics have already been discussed and repeatably published without new content.
Recently, I noticed I reduced my blogging activities as many topics have already been discussed and repeatably published without new content.
With the upcoming of Gen AI and ChatGPT, I believe my PLM feeds are flooded by AI-generated blog posts.
The ChatGPT option
 Most companies are not frontrunners in using extremely modern PLM concepts, so you can type risk-free questions and get common-sense answers.
Most companies are not frontrunners in using extremely modern PLM concepts, so you can type risk-free questions and get common-sense answers.
I just tried these five questions:
- Why do we need an MBOM in PLM, and which industries benefit the most?
- What is the difference between a PLM system and a PLM strategy?
- Why do so many PLM projects fail?
- Why do so many ERP projects fail?
- What are the changes and benefits of a model-based approach to product lifecycle management?
![]() Note: Questions 3 and 4 have almost similar causes and impacts, although slightly different, which is to be expected given the scope of the domain.
Note: Questions 3 and 4 have almost similar causes and impacts, although slightly different, which is to be expected given the scope of the domain.
All these questions provided enough information for a blog post based on the answer. This illustrates that if you are writing about what are current best practices in the field – stop writing – the knowledge is there.
PLM in the real life
Recently, I had several discussions about which skills a PLM expert should have or which topics a PLM project should address.
PLM for the individual
 For the individual, there are often certifications to obtain. Roger Tempest has been fighting for PLM professional recognition through certification – a challenge due to the broad scope and possibilities. Read more about Roger’s work in this post: PLM is complex (and we have to accept it?)
For the individual, there are often certifications to obtain. Roger Tempest has been fighting for PLM professional recognition through certification – a challenge due to the broad scope and possibilities. Read more about Roger’s work in this post: PLM is complex (and we have to accept it?)
PLM vendors and system integrators often certify their staff or resellers to guarantee the quality of their solution delivery. Potential topics will be missed as they do not fulfill the vendor’s or integrator’s business purpose.
Asking ChatGPT about the required skills for a PLM expert, these were the top 5 answers:
- Technical skills
- Domain Knowledge
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills
- Interpersonal and Management Skills
- Strategic Thinking
 It was interesting to see the order proposed by ChatGPT. Fist the tools (technology), then the processes (domain knowledge / analytical thinking), and last the people and business (strategy and interpersonal and management skills) It is hard to find individuals with all these skills in a single person.
It was interesting to see the order proposed by ChatGPT. Fist the tools (technology), then the processes (domain knowledge / analytical thinking), and last the people and business (strategy and interpersonal and management skills) It is hard to find individuals with all these skills in a single person.
Although we want people to be that broad in their skills, job offerings are mainly looking for the expert in one domain, be it strategy, communication, industry or technology. To get an impression of the skills read my PLM and Education concluding blog post.
Now, let’s see what it means for an organization.
PLM for the organization
In this area, one of the most consistent frameworks I have seen over time is CIMdata‘s Critical Dozen. Although they refer less to skills and more to trends and enablers, a company should invest in – educate people & build skills – to support a successful digital transformation in the PLM domain.
 Oleg Shilovitsky’s recent blog post, The 12 “P” s of PLM Explained by Role: How to Make PLM More Than Just a Buzzword describes in an AI manner the various aspects of the term PLM, using 12 P**-words, reacting to Lionel Grealou’ s post: Making PLM Great Again
Oleg Shilovitsky’s recent blog post, The 12 “P” s of PLM Explained by Role: How to Make PLM More Than Just a Buzzword describes in an AI manner the various aspects of the term PLM, using 12 P**-words, reacting to Lionel Grealou’ s post: Making PLM Great Again
The challenge I see with these types of posts is: “OK, what to do now? Where to start?”
I believe where to start at the first place is a commonly agreed topic.
Everything starts from having a purpose and a vision. And this vision should be supported by a motivating story about the WHY that inspires everyone.
 It is teamwork to define such a strategy, communicate it through a compelling story and make it personal. An excellent book to read is Make it personal from Dr. Cara Antoine – click on the image to discover the content and find my review why I believe this book is so compelling.
It is teamwork to define such a strategy, communicate it through a compelling story and make it personal. An excellent book to read is Make it personal from Dr. Cara Antoine – click on the image to discover the content and find my review why I believe this book is so compelling.
An important reason why we have to make transformations personal is because we are dealing first of all with human beings. And human beings are driven by emotions first even before ratio kicks in. We see it everywhere and unfortunately also in politics.
The HOW from real-life
 This question cannot be answered by external PLM vendors, consultants or system integrators. Forget the Out-of-the-Box templates or the industry best practices (from the past), but start from your company’s culture and vision, introducing step-by-step new technologies, ways of working and business models to move towards the company’s vision target.
This question cannot be answered by external PLM vendors, consultants or system integrators. Forget the Out-of-the-Box templates or the industry best practices (from the past), but start from your company’s culture and vision, introducing step-by-step new technologies, ways of working and business models to move towards the company’s vision target.
Building the HOW is not an easy journey, and to illustrate the variety of skills needed to be successful, I worked with Share PLM on their Series 2 podcast. You can find the complete overview here. There is one more to come to conclude this year.
 Our focus was to speak only with PLM experts from the field, understanding their day-to-day challenges with a focus on HOW they did it and WHAT they learned.
Our focus was to speak only with PLM experts from the field, understanding their day-to-day challenges with a focus on HOW they did it and WHAT they learned.
And this is what we learned:
Unveiling FLSmidth’s Industrial Equipment PLM Transformation: From Projects to Products
 It was our first episode of Series 2, and we spoke with Johan Mikkelä, Head of the PLM Solution Architecture at FLSmidth.
It was our first episode of Series 2, and we spoke with Johan Mikkelä, Head of the PLM Solution Architecture at FLSmidth.
FLSmidth provides the global mining and cement industries with equipment and services, which is very much an ETO business moving towards CTO.
We discussed their Industrial Equipment PLM Transformation and the impact it has made.
Start With People: ABB’s Engineering Approach to Digital Transformation
 We spoke with Issam Darraj, who shared his thoughts on human-centric digitalization. Issam talks us through ABB’s engineering perspective on driving transformation and discusses the importance of focusing on your people. Our favorite quote:
We spoke with Issam Darraj, who shared his thoughts on human-centric digitalization. Issam talks us through ABB’s engineering perspective on driving transformation and discusses the importance of focusing on your people. Our favorite quote:
To grow, you need to focus on your people. If your people are happy, you will automatically grow. If your people are unhappy, they will leave you or work against you.
Enabling change: Exploring the human side of digital transformations
 We spoke with Antonio Casaschi as he shared his thoughts on the human side of digital transformation. When discussing the PLM expert, he agrees it is difficult. Our favorite part here:
We spoke with Antonio Casaschi as he shared his thoughts on the human side of digital transformation. When discussing the PLM expert, he agrees it is difficult. Our favorite part here:
“I see a PLM expert as someone with a lot of experience in organizational change management. Of course, maybe people with a different background can see a PLM expert with someone with a lot of knowledge of how you develop products, all the best practices around products, etc. We first need to agree on what a PLM expert is, and then we can agree on how you become an expert in such a domain.”
Revolutionizing PLM: Insights from Yousef Hooshmand
 With Dr. Yousef Hooshmand, writer of the paper: From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and
With Dr. Yousef Hooshmand, writer of the paper: From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and
Data Mesh, with over 15 years of experience in the PLM domain, currently PLM Lead at NIO, we discussed the complexity of digital transformation in the PLM domain and How to deal with legacy, meanwhile implementing a user-centric, data-driven future.
My favorite quote: The End of Single Source of Truth, now it is about The nearest Source of Truth and Single Source of Change.
Steadfast Consistency: Delving into Configuration Management with Martijn Dullaart
 Martijn Dullaart, who is the man behind the blog MDUX: The Future of CM and author of the book The Essential Guide to Part Re-Identification: Unleash the Power of Interchangeability and Traceability, has been active both in the PLM and CM domain and with Martijn the similarities and differences between PLM and CM and why organizations need to be educated on the topic of CM
Martijn Dullaart, who is the man behind the blog MDUX: The Future of CM and author of the book The Essential Guide to Part Re-Identification: Unleash the Power of Interchangeability and Traceability, has been active both in the PLM and CM domain and with Martijn the similarities and differences between PLM and CM and why organizations need to be educated on the topic of CM
The ROI of Digitalization: A Deep Dive into Business Value with Susanna Maëntausta
 With Susanna Maëntausta, we discussed how to implement PLM in non-traditional manufacturing industries, such as the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
With Susanna Maëntausta, we discussed how to implement PLM in non-traditional manufacturing industries, such as the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Susanna teaches us to ensure PLM projects are value-driven, connecting business objectives and KPIs to the implementation and execution steps in the field. Susanna is highly skilled in connecting people at any level of the organization.
Narratives of Change: Grundfos Transformation Tales with Björn Axling
 As Head of PLM and part of the Group Innovation management team at Grundfos, Bjorn Axling aims to drive a Group-wide, cross-functional transformation into more innovative, more efficient, and data-driven ways of working through the product lifecycle from ideation to end-of-life.
As Head of PLM and part of the Group Innovation management team at Grundfos, Bjorn Axling aims to drive a Group-wide, cross-functional transformation into more innovative, more efficient, and data-driven ways of working through the product lifecycle from ideation to end-of-life.
In this episode, you will learn all the various aspects that come together when leading such a transformation in terms of culture, people, communication, and modern technology.
The Next Lane: Marel and the Digital Product Highway with Roger Kabo
 With Roger Kabo, we discussed the steps needed to replace a legacy PLM environment and be open to a modern, federated, and data-driven future.
With Roger Kabo, we discussed the steps needed to replace a legacy PLM environment and be open to a modern, federated, and data-driven future.
Step 1: Start with the end in mind. Every successful business starts with a clear and compelling vision. Your vision should be specific, inspiring, and something your team can rally behind.
Next, build on value and do it step by step.
How do you manage technology and data when you have a diverse product portfolio?
 We talked with Jim van Oss, the former CIO of Moog Inc., for a deep dive into the fascinating world of technology transformations.
We talked with Jim van Oss, the former CIO of Moog Inc., for a deep dive into the fascinating world of technology transformations.
Key Takeaway: Evolving technology requires a clear strategy!
Jim underscores the importance of having a north star to guide your technological advancements, ensuring you remain focused and adaptable in an ever-changing landscape.
Diverse Products, Unified Systems: MBSE Insights with Max Gravel from Moog
 We discussed the future of the Model-Based approaches with Max Gravel – MBD at Gulfstream and MBSE at Moog.
We discussed the future of the Model-Based approaches with Max Gravel – MBD at Gulfstream and MBSE at Moog.
Max Gravel, Manager of Model-Based Engineering at Moog Inc., who is also active in modern CM, emphasizes that understanding your company’s goals with MBD is crucial.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution: it’s about tailoring the strategy to drive real value for your business. The tools are available, but the key lies in addressing the right questions and focusing on what matters most. A great, motivating story containing all the aspects of digital transformation in the PLM domain/
Customer-First PLM: Insights on Digital Transformation and Leadership
 With Helene Arlander, who has been involved in big transformation projects in the telecom industry. Starting from a complex legacy environment, implementing new data-driven approaches. We discussed the importance of managing product portfolios end-to-end and the leadership strategies needed for engaging people in charge.
With Helene Arlander, who has been involved in big transformation projects in the telecom industry. Starting from a complex legacy environment, implementing new data-driven approaches. We discussed the importance of managing product portfolios end-to-end and the leadership strategies needed for engaging people in charge.
We also discussed the role of AI in shaping the future of PLM and the importance of vision, diverse skill sets, and teamwork in transformations.
Conclusion
I believe the time of traditional blogging is over – current PLM concepts and issues can be easily queried by using ChatGPT-like solutions. The fundamental understanding of what you can do now comes from learning and listening to people, not as fast as a TikTok video or Insta message. For me, a podcast is a comfortable method of holistic learning.
Let us know what you think and who should be in Season 3
And for my friends in the United States – Happy Thanksgiving and think about the day after ……..

Recently, I attended several events related to the various aspects of product lifecycle management; most of them were tool-centric, explaining the benefits and values of their products.
 In parallel, I am working with several companies, assisting their PLM teams to make their plans understood by the upper management, which has always been my mission in the past.
In parallel, I am working with several companies, assisting their PLM teams to make their plans understood by the upper management, which has always been my mission in the past.
However, nowadays, people working in the business are feeling more and more challenged and pained by not acting adequately to the upcoming business demands.
The image below has been shown so many times, and every time, the context becomes more relevant.

Too often, an evolutionary mindset with small steps is considered instead of looking toward the future and reasoning back for what needs to be done.
Let me share some experiences and potential solutions.
Don’t use the P** word!
 The title of this post is one of the most essential points to consider. By using the term PLM, the discussion is most of the time framed in a debate related to the purchase or installation of a system, the PLM system, which is an engineering tool.
The title of this post is one of the most essential points to consider. By using the term PLM, the discussion is most of the time framed in a debate related to the purchase or installation of a system, the PLM system, which is an engineering tool.
PLM vendors, like Dassault Systèmes and Siemens, have recognized this, and the word PLM is no longer on their home pages.
They are now delivering experiences or digital industries software.
Other companies, such as PTC and Aras, broadened the discussion by naming other domains, such as manufacturing and services, all connected through a digital thread.
 The challenge for all these software vendors is why a company would consider buying their products. A growing issue for them is also why would they like to change their existing PLM system to another one, as there is so much legacy.
The challenge for all these software vendors is why a company would consider buying their products. A growing issue for them is also why would they like to change their existing PLM system to another one, as there is so much legacy.
For all of these vendors, success can come if champions inside the targeted company understand the technology and can translate its needs into their daily work.
 Here, we meet the internal PLM team, which is motivated by the technology and wants to spread the message to the organization. Often, with no or limited success, as the value and the context they are considering are not understood or felt as urgent.
Here, we meet the internal PLM team, which is motivated by the technology and wants to spread the message to the organization. Often, with no or limited success, as the value and the context they are considering are not understood or felt as urgent.
Lesson 1:
Don’t use the word PLM in your management messaging.
 In some of the current projects I have seen, people talk about the digital highway or a digital infrastructure to take this hurdle. For example, listen to the SharePLM podcast with Roger Kabo from Marel, who talks about their vision and digital product highway.
In some of the current projects I have seen, people talk about the digital highway or a digital infrastructure to take this hurdle. For example, listen to the SharePLM podcast with Roger Kabo from Marel, who talks about their vision and digital product highway.
As soon as you use the word PLM, most people think about a (costly) system, as this is how PLM is framed. Engineering, like IT, is often considered a cost center, as money is made by manufacturing and selling products.
 According to experts (CIMdata/Gartner), Product Lifecycle Management is considered a strategic approach. However, the majority of people talk about a PLM system. Of course, vendors and system integrators will speak about their PLM offerings.
According to experts (CIMdata/Gartner), Product Lifecycle Management is considered a strategic approach. However, the majority of people talk about a PLM system. Of course, vendors and system integrators will speak about their PLM offerings.
To avoid this framing, first of all, try to explain what you want to establish for the business. The terms Digital Product Highway or Digital Infrastructure, for example, avoid thinking in systems.
Lesson 2:
Don’t tell your management why they need to reward your project – they should tell you what they need.
This might seem like a bit of strange advice; however, you have to realize that most of the time, people do not talk about the details at the management level. At the management level, there are strategies and business objectives, and you will only get attention when your proposal addresses the business needs. At the management level, there should be an understanding of the business need and its potential value for the organization. Next, analyzing the business changes and required tools will lead to an understanding of what value the PLM team can bring.
Yousef Hooshmand’s 5 + 1 approach illustrates this perfectly. It is crucial to note that long-term executive commitment is needed to have a serious project, and therefore, the connection to their business objective is vital.
 Therefore, if you can connect your project to the business objectives of someone in management, you have the opportunity to get executive sponsorship. A crucial advice you hear all the time when discussing successful PLM projects.
Therefore, if you can connect your project to the business objectives of someone in management, you have the opportunity to get executive sponsorship. A crucial advice you hear all the time when discussing successful PLM projects.
Lesson 3:
Alignment must come from within the organization.
Last week, at the 20th anniversary of the Dutch PLM platform, Yousef Hooshmand gave the keynote speech starting with the images below:
On the left side, we see the medieval Catholic church sincerely selling salvation through indulgences, where the legend says Luther bought the hell, demonstrating salvation comes from inside, not from external activities – read the legend here.
 On the right side, we see the Digital Transformation expert sincerely selling digital transformation to companies. According to LinkedIn, there are about 1.170.000 people with the term Digital Transformation in their profile.
On the right side, we see the Digital Transformation expert sincerely selling digital transformation to companies. According to LinkedIn, there are about 1.170.000 people with the term Digital Transformation in their profile.
As Yousef mentioned, the intentions of these people can be sincere, but also, here, the transformation must come from inside (the company).
When I work with companies, I use the Benefits Dependency Network methodology to create a storyboard for the company. The BDN network then serves as a base for creating storylines that help people in the organization have a connected view starting from their perspective.
Companies might hire strategic consultancy firms to help them formulate their long-term strategy. This can be very helpful where, in the best case, the consultancy firm educates the company, but the company should decide on the direction.
In an older blog post, I wrote about this methodology, presented by Johannes Storvik at the Technia Innovation forum, and how it defines a value-driven implementation.
Dassault Systèmes and its partners use this methodology in their Value Engagement process, which is tuned to their solution portfolio.
You can also watch the webinar Federated PLM Webinar 5 – The Business Case for the Federated PLM, in which I explained the methodology used.
Lesson 4:
PLM is a business need not an IT service
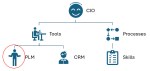 This lesson is essential for those who believe that PLM is still a system or an IT service. In some companies, I have seen that the (understaffed) PLM team is part of a larger IT organization. In this type of organization, the PLM team, as part of IT, is purely considered a cost center that is available to support the demand from the business.
This lesson is essential for those who believe that PLM is still a system or an IT service. In some companies, I have seen that the (understaffed) PLM team is part of a larger IT organization. In this type of organization, the PLM team, as part of IT, is purely considered a cost center that is available to support the demand from the business.
The business usually focuses on incremental and economic profitability, less on transformational ways of working.
In this context, it is relevant to read Chris Seiler’s post: How to escape the vicious circle in times of transformation? Where he reflects on his 2002 MBA study, which is still valid for many big corporate organizations.
It is a long read, but it is gratifying if you are interested. It shows that PLM concepts should be discussed and executed at the business level. Of course, I read the article with my PLM-twisted brain.
The image above from Chris’s post could be a starting point for a Benefits-Dependent Network diagram, expanded with Objectives, Business Changes and Benefits to fight this vicious downturn.
As PLM is no longer a system but a business strategy, the PLM team should be integrated into the business potential overlooked by the CIO or CDO, as a CEO is usually not able to give this long-term executive commitment.
Lesson 5:
Educate yourselves and your management
![]() The last lesson is crucial, as due to improving technologies like AI and, earlier, the concepts of the digital twin, traditional ways of coordinated working will become inefficient and redundant.
The last lesson is crucial, as due to improving technologies like AI and, earlier, the concepts of the digital twin, traditional ways of coordinated working will become inefficient and redundant.
However, before jumping on these new technologies, everyone, at every level in the organization, should be aware of:
WHY will this be relevant for our business? Is it to cut costs – being more efficient as fewer humans are in the process? Is it to be able to comply with new upcoming (sustainability) regulations? Is it because the aging workforce leaves a knowledge gap?
WHAT will our business need in the next 5 to 10 years? Are there new ways of working that we want to introduce, but we lack the technology and the tools? Do we have skills in-house? Remember, digital transformation must come from the inside.
HOW are we going to adapt our business? Can we do it in a learning mode, as the end target is not clear yet—the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach? Are we moving from selling products to providing a Product Service System?
 My lesson: Get inspired by the software vendors who will show you what might be possible. Get educated on the topic and understand what it would mean for your organization. Start from the people and the business needs before jumping on the tools.
My lesson: Get inspired by the software vendors who will show you what might be possible. Get educated on the topic and understand what it would mean for your organization. Start from the people and the business needs before jumping on the tools.
 In the upcoming PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference on 23-24 October, we will be meeting again with a group of P** experts to discuss our experiences and progress in this domain. I will give a lecture here about what it takes to move to a sustainable economy based on a Product-as-a-service concept.
In the upcoming PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference on 23-24 October, we will be meeting again with a group of P** experts to discuss our experiences and progress in this domain. I will give a lecture here about what it takes to move to a sustainable economy based on a Product-as-a-service concept.
If you want to learn more – join us – here is the link to the agenda.
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed reading a blog post not generated by ChatGPT, although I am using bullet points. With the overflow of information, it remains crucial to keep a holistic overview. I hope that with this post, I have helped the P** teams in their mission, and I look forward to learning from your experiences in this domain.
![]() I attended the PDSVISION forum for the first time, a two-day PLM event in Gothenburg organized by PTC’s largest implementer in the Nordics, also active in North America, the UK, and Germany.
I attended the PDSVISION forum for the first time, a two-day PLM event in Gothenburg organized by PTC’s largest implementer in the Nordics, also active in North America, the UK, and Germany.
The theme of the conference: Master your Digital Thread – a hot topic, as it has been discussed in various events, like the recent PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference in November 2023.
The event drew over 200 attendees, showing the commitment of participants, primarily from the Nordics, to knowledge sharing and learning.
The diverse representation included industry leaders like Vestas, pioneers in Sustainable Energy, and innovative startups like CorPower Ocean, who are dedicated to making wave energy reliable and competitive. Notably, the common thread among these diverse participants was their focus on sustainability, a growing theme in PLM conferences and an essential item on every board’s strategic agenda.
I enjoyed the structure and agenda of the conference. The first day was filled with lectures and inspiring keynotes. The second day was a day of interactive workshops divided into four tracks, which were of decent length so we could really dive into the topics. As you can imagine, I followed the sustainability track.
Here are some of my highlights of this conference.
Catching the Wind: A Digital Thread From Design to Service
 Simon Saandvig Storbjerg, unfortunately remote, gave an overview of the PLM-related challenges that Vestas is addressing. Vestas, the undisputed market leader in wind energy, is indirectly responsible for 231 million tonnes of CO2 per year.
Simon Saandvig Storbjerg, unfortunately remote, gave an overview of the PLM-related challenges that Vestas is addressing. Vestas, the undisputed market leader in wind energy, is indirectly responsible for 231 million tonnes of CO2 per year.
One of the challenges of wind power energy is the growing complexity and need for variants. With continuous innovation and the size of the wind turbine, it is challenging to achieve economic benefits of scale.
As an example, Simon shared data related to the Lost Production Factor, which was around 5% in 2009 and reduced to 2% in 2017 and is now growing again. This trend is valid not only for Vestas but also for all wind turbine manufacturers, as variability is increasing.
Vestas is introducing modularity to address these challenges. I reported last year about their modularity journey related to the North European Modularity biannual meeting held at Vestas in Ringkøbing – you can read the post here.
Simon also addressed the importance of Model-Based Definition (MBD), which is crucial if you want to achieve digital continuity between engineering and manufacturing. In particular, in this industry, MBD is a challenge to involve the entire value chain, despite the fact that the benefits are proven and known. Change in people skills and processes remains a challenge.
The Future of Product Design and Development
 The session led by PTC from Mark Lobo, General Manager for the PLM Segment, and Brian Thompson, General Manager of the CAD Segment, brought clarity to the audience on the joint roadmap of Windchill and Creo.
The session led by PTC from Mark Lobo, General Manager for the PLM Segment, and Brian Thompson, General Manager of the CAD Segment, brought clarity to the audience on the joint roadmap of Windchill and Creo.
 Mark and Brian highlighted the benefits of a Model-Based Enterprise and Model-Based Definition, which are musts if you want to be more efficient in your company and value chain.
Mark and Brian highlighted the benefits of a Model-Based Enterprise and Model-Based Definition, which are musts if you want to be more efficient in your company and value chain.
The WHY is known, see the benefits described in the image, and requires new ways of working, something organizations need to implement anyway when aiming to realize a digital thread or digital twin.
In addition, Mark addressed PTC’s focus on Design for Sustainability and their partner network. In relation to materials science, the partnership with Ansys Granta MI is essential. It was presented later by Ansys and discussed on day two during one of the sustainability workshops.
Mark and Brian elaborated on the PTC SaaS journey – the future atlas platform and the current status of WindChill+ and Creo+, addressing a smooth transition from existing customers to a new future architecture.
And, of course, there was the topic of Artificial Intelligence.
 Mark explained that PTC is exploring AI in various areas of the product lifecycle, like validating requirements, optimizing CAD models, streamlining change processes on the design side but also downstream activities like quality and maintenance predictions, improved operations and streamlined field services and service parts are part of the PTC Copilot strategy.
Mark explained that PTC is exploring AI in various areas of the product lifecycle, like validating requirements, optimizing CAD models, streamlining change processes on the design side but also downstream activities like quality and maintenance predictions, improved operations and streamlined field services and service parts are part of the PTC Copilot strategy.
PLM combined with AI is for sure a topic where the applicability and benefits can be high to improve decision-making.
PLM Data Merge in the PTC Cloud: The Why & The How
 Mikael Gustafson from Xylem, a leading Global Water Solutions provider, described their recently completed project: merging their on-premise Windchill instance TAPIR and their cloud Windchill XGV into a single environment.
Mikael Gustafson from Xylem, a leading Global Water Solutions provider, described their recently completed project: merging their on-premise Windchill instance TAPIR and their cloud Windchill XGV into a single environment.
TAPIR stands for Technical Administration, Part Information Repository and is very much part-centric and used in one organization. XGV stands for Xylem Global Vault, and it is used in 28 organizations with more of a focus on CAD data (Creo and AutoCAD). Two different siloes are to be joined in one instance to build a modern, connected, data-driven future or, as Mikael phrased it: “A step towards a more manageable Virtual Product“.
 It was a severe project involving a lot of resources and time, again showing the challenges of migrations. I am planning to publish a blog post, the draft title “Migration Migraine,” as this type of migration is prevalent in many places because companies want to implement a single PLM backbone beyond (mechanical) engineering.
It was a severe project involving a lot of resources and time, again showing the challenges of migrations. I am planning to publish a blog post, the draft title “Migration Migraine,” as this type of migration is prevalent in many places because companies want to implement a single PLM backbone beyond (mechanical) engineering.
What I liked about the approach was its focus on assessing the risks and prioritizing a mitigation strategy if necessary. As the list below shows, even the COVID-19 pandemic was challenging the project.
Often, big migration projects fail due to optimism or by assessing some of the risks at the start and then giving it a go.
 When failures happen, there is often the blame game: Was it the software, the implementer, or the customer (past or present) that caused the troubles? Mediating in such environments has been a long time my mission as the “Flying Dutchman,” and from my experience, it is not about the blame game; it is, most of the time, too high expectations and not enough time or resources to fully control this journey.
When failures happen, there is often the blame game: Was it the software, the implementer, or the customer (past or present) that caused the troubles? Mediating in such environments has been a long time my mission as the “Flying Dutchman,” and from my experience, it is not about the blame game; it is, most of the time, too high expectations and not enough time or resources to fully control this journey.
As Michael said, Xylem was successful, and during the go-live, only a few non-critical issues popped up.
 When asked what he would do differently with the project’s hindsight, Mikael mentioned he would do the migrations not as a big project but as smaller projects.
When asked what he would do differently with the project’s hindsight, Mikael mentioned he would do the migrations not as a big project but as smaller projects.
I can relate a lot to this answer as, by experience, the “one-time” migration projects have created a lot of stress for the company, and only a few of them were successful.
Starting being coordinated and then connected
Several sessions were held where companies shared their PLM journey, to be mapped along the maturity slide (slide 8) I shared in my session: The Why, What and How of Digital Transformation in the PLM domain. You can review the content here on SlideShare.
There was Evolabel, a company starting its PLM journey because they are suffering from ineffective work procedures, information islands and the increasing complexity of its products.
 Evolabel realized it needed PLM to realize its market ambition: To be a market leader within five years. For Evolabel, PLM is a must that is repeatable and integrated internally.
Evolabel realized it needed PLM to realize its market ambition: To be a market leader within five years. For Evolabel, PLM is a must that is repeatable and integrated internally.
They shared how they first defined the required understanding and mindset for the needed capabilities before implementing them. In my terminology, they started to implement a coordinated PLM approach.
 Teddy Svenson from JBT, a well-known manufacturer of food-tech solutions, described their next step in PLM. From an old AS/400 system with very little integration to PDM to a complete PLM system with parts, configurations, and change management.
Teddy Svenson from JBT, a well-known manufacturer of food-tech solutions, described their next step in PLM. From an old AS/400 system with very little integration to PDM to a complete PLM system with parts, configurations, and change management.
It is not an easy task but a vital stepping stone for future development and a complete digital thread, from sales to customer care. In my terminology, they were upgrading their technology to improve their coordinated approach to be ready for the next digital evolution.
![]() There were several other presentations on Day One – See the agenda here I cannot cover them all given the limited size of this blog post.
There were several other presentations on Day One – See the agenda here I cannot cover them all given the limited size of this blog post.
The Workshops
As I followed the Sustainability track, I cannot comment much on the other track; however, given the presenters and the topics, they all appeared to be very pragmatic and interactive – given the format.
Achieving sustainability goals by integrating material intelligence into the design process
![]() In the sustainability track, we started with Manuelle Clavel from Ansys Granta, who explained in detail how material data and its management are crucial for designing better-performing, more sustainable, and compliant products.
In the sustainability track, we started with Manuelle Clavel from Ansys Granta, who explained in detail how material data and its management are crucial for designing better-performing, more sustainable, and compliant products.
With the importance of compliance with (upcoming) regulations and the usage of material characteristics in the context of more sustainable products and being able to perform a Life Cycle Assessment, it is crucial to have material information digitally available, both in the CAD design environment as well in the PLM environment.
For me, a dataset of material properties is an excellent example of how it is used in a connected enterprise. You do not want to copy the information from system to system; it needs to be connected and available in real-time.
How can we design more sustainable products?
Together with Martin Lundqvist from QCM, I conducted an interactive session. We started with the need for digitalization, then looked at RoHS and REACH compliance and discussed the upcoming requirements of the Digital Product Passport.
We closed the session with a dialogue on the circular economy.
From the audience, we learned that many companies are still early in understanding the implementation of sustainability requirements and new processes. However, some were already quite advanced and acting. In particular, it is essential to know if your company is involved with batteries (DPP #1) or is close to consumers.
Conclusion
The PDSFORUM was for me an interesting experience for meeting companies at all different stages of their PLM journey. All sessions I attended were realistic, and the solutions were often pragmatic. In my day-to-day life, inspiring companies to understand a digital and sustainable future, you sometimes forget the journey everyone is going through.
Thanks, PDVISION, for inviting me to speak and learn at this conference.
and some sad news …..
I was sorry to learn that last week, Dr. Ken Versprille suddenly passed away. I know Ken, as shown in the picture – a passionate moderator and timekeeper of the PLM Roadmap / PDT conferences, well prepared for the details. May his spirit live through the future conferences – the next one already on May 8-9th in Washington, DC.
 Today I read Rhiannon Gallagherer’s LinkedIn post: If Murray Isn’t Happy, No One Is Happy: Value Your Social Nodes. The story reminded me of a complementary blog post I wrote in 2014, although with a small different perspective.
Today I read Rhiannon Gallagherer’s LinkedIn post: If Murray Isn’t Happy, No One Is Happy: Value Your Social Nodes. The story reminded me of a complementary blog post I wrote in 2014, although with a small different perspective.
After reviewing my post, I discovered that nine years later, we are still having the same challenges of how to involve people in a business transformation.
People are the most important assets companies claim, but where do they focus their spending and efforts?
Probably more on building the ideal processes and having the best IT solution.
 Organisational Change Management is not in their comfort zone. People like Rhiannon Gallagher, but also in my direct network, the team from Share PLM, are focusing on this blind spot. Don’t forget this part of your digital transformation efforts.
Organisational Change Management is not in their comfort zone. People like Rhiannon Gallagher, but also in my direct network, the team from Share PLM, are focusing on this blind spot. Don’t forget this part of your digital transformation efforts.
And just for fun, there rest of the post below is the article from 2014. At that time, I was not yet focusing on digital transformation in the PLM domain. That started end of 2014 – the beginning of 2015.
PLM and Blockers
(read it with 2014 in mind – where were you?)
In the past month (April 2014), I had several discussions related to the complexity of PLM.
- Why is PLM conceived as complex?
- Why is it hard to sell PLM internally into an organization?
- Or, to phrase it differently: “What makes PLM so difficult for normal human beings. As conceptually it is not so complex”
(2023 addition: PLM is complex (and we have to accept it?) )
So what makes it complex? What is behind PLM?
 The main concept behind PLM is that people need to share data. It can be around a project, a product, or a plant through the whole lifecycle. In particular, during the early lifecycle phases, there is a lot of information that is not yet 100 percent mature.
The main concept behind PLM is that people need to share data. It can be around a project, a product, or a plant through the whole lifecycle. In particular, during the early lifecycle phases, there is a lot of information that is not yet 100 percent mature.
You could decide to wait till everything is mature before sharing it with others (the classical sequential manner). However, the chances of doing it right the first time are low. Several iterations between disciplines will be required before the data is approved.
The more and more a company works sequentially, the higher the costs of changes and the longer the time to market. Due to the rigidness of this sequential approach, it becomes difficult to respond rapidly to changing customer or market demands.
Therefore, in theory (and it is not only a PLM theory), concurrent engineering should reduce the number of iterations and the total time to market by working in parallel on not yet approved data.
 PLM goes further. It is about the sharing of data, and as it originally started in the early phases of the product lifecycle, the concept of PLM was considered something related to engineering. And to be fair, most of the PLM (CAD-related) vendors have a high focus on the early stages of the lifecycle and have strengthened this idea.
PLM goes further. It is about the sharing of data, and as it originally started in the early phases of the product lifecycle, the concept of PLM was considered something related to engineering. And to be fair, most of the PLM (CAD-related) vendors have a high focus on the early stages of the lifecycle and have strengthened this idea.
However, sharing can go much further, e.g., early involvement of suppliers (still engineering) or downstream support for after-sales/services (the new acronym SLM – Service Lifecycle Management).
In my recent (2014) blog posts, I discussed the concepts of SLM and the required data model for that.
Anticipated sharing
The complexity lies in the word “sharing”. What does sharing mean for an organization, where historically, every person was awarded for their knowledge instead of being awarded for sharing and spreading knowledge. Guarding your knowledge was job protection.
Many so-called PLM implementations have failed to reach the sharing target as the implementation focus was on storing data per discipline and not necessarily storing data to become shareable and used by others. This is a huge difference.
(2023 addition: At that time, all PLM systems were Systems of Record)
 Some famous (ERP) vendors claim if you store everything in their system, you have a “single version of the truth”.
Some famous (ERP) vendors claim if you store everything in their system, you have a “single version of the truth”.
Sounds attractive. However, my garbage bin at home is also a place where everything ends up in a single place, but a garbage bin has not been designed for sharing. Another person has no clue or time to analyze what is inside.
Even data stored in the same system can be hidden from others as the way to find data is not anticipated.
Data sharing instead of document deliverables
The complexity of PLM is that data should be created and shared in a matter not necessarily in the most efficient manner for a single purpose. With some extra effort, you can make the information usable and searchable for others. Typical examples are drawings and document management, where the whole process for a person is focused on delivering a specific document on time. Ok, for that purpose, but this document becomes a legacy for the long term as you need to know (or remember) what is inside the document.
 A logical implication of data sharing is that, instead of managing documents, organizations start to collect and share data elements (a 3D model, functional properties, requirements, physical properties, logistical properties, etc.). Data can be connected and restructured easily through reports and dashboards, therefore, providing specific views for different roles in the organization. Sharing has become possible, and it can be done online. Nobody needed to consolidate and extract data from documents (Excels ?)
A logical implication of data sharing is that, instead of managing documents, organizations start to collect and share data elements (a 3D model, functional properties, requirements, physical properties, logistical properties, etc.). Data can be connected and restructured easily through reports and dashboards, therefore, providing specific views for different roles in the organization. Sharing has become possible, and it can be done online. Nobody needed to consolidate and extract data from documents (Excels ?)
(2023 addition: The data-driven PLM infrastructure talking about datasets)
This does not fit older generations and departmental-managed business units that are rewarded only for their individual efficiency.
 Here is an extract of a LinkedIn discussion from 2014, where the two extremes are visible. Unfortunately (or perhaps good), LinkedIn does not keep everything online. There is already so much “dark data” on the internet.
Here is an extract of a LinkedIn discussion from 2014, where the two extremes are visible. Unfortunately (or perhaps good), LinkedIn does not keep everything online. There is already so much “dark data” on the internet.
Joe stating:
“The sad thing about PLM is that only PLM experts can understand it! It seems to be a very tight knit club with very little influence from any outside sources.
I think PLM should be dumped. It seems to me that computerizing engineering documentation is relatively easy process. I really think it has been over complicated. Of course we need to get the CAD vendors out of the way. Yes it was an obvious solution, but if anyone took the time to look down the road they would see that they were destroying a well established standard that were so cost effective and simple. But it seems that there is no money in simple”
And at the other side, Kais stated:
“If we want to be able to use state-of-the art technology to support the whole enterprise, and not just engineering, and through-life; then product information, in its totality, must be readily accessible and usable at all times and not locked in any perishable CAD, ERP or other systems. The Data Centric Approach that we introduced in the Datamation PLM Model is built on these concepts”
Readers from my blog will understand I am very much aligned with Kais, and PLM guys have a hard time convincing Joe of the benefits of PLM (I did not try).
Making the change happen
 Besides this LinkedIn discussion, I had discussions with several companies where my audience understood the data-centric approach. It was nice to be in the room together, sharing ideas of what would be possible. However, the outside world is hard to convince, and here the challenge is organizational change management. Who will support you and who will work against you?.
Besides this LinkedIn discussion, I had discussions with several companies where my audience understood the data-centric approach. It was nice to be in the room together, sharing ideas of what would be possible. However, the outside world is hard to convince, and here the challenge is organizational change management. Who will support you and who will work against you?.
BLOCKERS: I read an interesting article in IndustryWeek from John Dyer with the title: What Motivates Blockers to Resist Change?
John describes the various types of blockers, and when reading the article combined with my PLM twisted brain, I understood again that this is one of the reasons why PLM is perceived as complex – you need to change, and there are blockers:
Blocker (noun) – Someone who purposefully opposes any change (improvement) to a process for personal reasons
“Blockers” can occupy any position in a company. They can be any age, gender, education level or pay rate. We tend to think of blockers as older, more experienced workers who have been with the company for a long time, and they don’t want to consider any other way to do things. While that may be true in some cases, don’t be surprised to find blockers who are young, well-educated and fairly new to the company.”
The problem with blockers
The combination of business change and the existence of blockers is one of the biggest risks for companies to go through a business transformation. By the way, this is not only related to PLM; it is related to any required change in business.
Some examples:
 A company I worked with was eager to study its path to the future, which required more global collaboration, a competitive business model and a more customer-centric approach. After a long evaluation phase, they decided they needed PLM, which was new for most of the people in the company. Although the project team was enthusiastic, they were not able to pass the blockers for a change – so no PLM. Ironically enough, they lost a significant part of their business to companies that have implemented PLM. Defending the past is not a guarantee for the future.
A company I worked with was eager to study its path to the future, which required more global collaboration, a competitive business model and a more customer-centric approach. After a long evaluation phase, they decided they needed PLM, which was new for most of the people in the company. Although the project team was enthusiastic, they were not able to pass the blockers for a change – so no PLM. Ironically enough, they lost a significant part of their business to companies that have implemented PLM. Defending the past is not a guarantee for the future.
A second example is Nokia. Nokia was famous for the ways they were able to transform their business in the past. How come they did not see the smartphone and touch screens upcoming? Apparently, based on several articles presented recently, it was Nokia´s internal culture and superior feeling that they were dominating the market that made it impossible to switch. The technology was known, and the concepts were there; however, the (middle) management was full of blockers.
Two examples where blockers had a huge impact on the company.
Conclusion:
Staying in business and remaining competitive is crucial for companies. In particular, the changes that currently happen require people to work differently in order to stay competitive. Documents will become reports generated from data. People handling and collecting documents to generate new documents will become obsolete as a modern data-centric approach makes them redundant. Keeping the old processes might destroy a company. This should convince the blockers to give up.

 Two weeks ago, I shared my post: Modern PLM is (too) complex on LinkedIn, and apparently, it was a topic that touched many readers. Almost a hundred likes, fifty comments and six shares. Not the usual thing you would expect from a PLM blog post.
Two weeks ago, I shared my post: Modern PLM is (too) complex on LinkedIn, and apparently, it was a topic that touched many readers. Almost a hundred likes, fifty comments and six shares. Not the usual thing you would expect from a PLM blog post.
In addition, the article led to offline discussions with peers, giving me an even better understanding of what people think. Here is a summary of the various talks.
What is PLM?
 In particular, since the inception of Product Lifecycle Management, software vendors have battled with the various PLM definitions.
In particular, since the inception of Product Lifecycle Management, software vendors have battled with the various PLM definitions.
Initially, PLM was considered an engineering tool for product development, with an extensive potential set of capabilities supported by PowerPoint. Most companies actually implemented a collaborative PDM system at that time and named it PLM.
Was PLM really understood? Look at the infamous Autodesk CEO Carl Bass’s anti-PLM rap from 2007. Next, in 2012, Autodesk introduced its PLM solution called Autodesk PLM 360 as one of the first cloud solutions.
 Only with growing connectivity and enterprise information sharing did the definition of PLM start to change.
Only with growing connectivity and enterprise information sharing did the definition of PLM start to change.
PLM became a product information backbone serving downstream deployment with product data – the traditional Teamcenter, Windchill and ENOVIA implementations are typical examples of this phase.
With a digitization effort taking place in the non-PLM domain, connecting product development, design and delivery data to a company’s digital business became necessary. You could say, and this is the CIMdata definition:
PLM is a strategic business approach that applies a consistent set of business solutions that support the collaborative creation, management, dissemination, and use of product definition information. PLM supports the extended enterprise (customers, design and supply partners, etc.)
I agree with this definition; perhaps 80 % of our PLM community does. But how many times have we been trapped again in the same thinking: PLM is a system.
The most recent example is the post from Oleg Shilovitsky last week where he claims: Discover why OpenBOM reigns supreme in the world of PLM!

Nothing wrong with that, as software vendors will always tweak definitions as they need marketing to make a profit, but PLM is not a system.
My main point is that PLM is a “vague” community label with many interpretations. Software vendors have the most significant marketing budget to push their unique definitions. However, also various practitioners in the field have their interpretations.
And maybe Martin Haket’s comment to the post says it all (partly quote):
I’m a bit late to this discussion, but in my opinion, the complexity is mainly due to the fact that the ownership of the processes and data models underlying PLM are not properly organized. ‘Everybody’ in the company is allowed to mix in the discussion and have their opinion; legacy drives departments to undesirable requirements leading to complex implementations.
My intermediate conclusion: Our legacy and lack of a single definition of PLM make it complex.
The PLM professional
 On LinkedIn, there are approximately 14.000 PLM consultants in my first and second levels of connections. This number indicates that the label “PLM Consultant” has a specific recognition.
On LinkedIn, there are approximately 14.000 PLM consultants in my first and second levels of connections. This number indicates that the label “PLM Consultant” has a specific recognition.
During my “PLM is complex” discussion, I noticed Roger Tempest’s Professional PLM White paper and started the dialogue with him.
Roger Tempest is one of the co-founders of the PLM Interest Group. He has been trying to create a baseline for a foundational PLM certification with several others. We discussed the challenges of getting the PLM Professional recognized as an essential business role. Can we certify the PLM professional the same way as a certified Configuration Manager or certified Project Manager?
I shared my thoughts with Roger, claiming that our discipline is too vague and diverse and that finding a common baseline is hard.
 Therefore, we are curious about your opinion too. Please tell us in the comments to this post what you think about recognizing the PLM professional and what skills should be the minimum. What are the basics of a PLM professional?
Therefore, we are curious about your opinion too. Please tell us in the comments to this post what you think about recognizing the PLM professional and what skills should be the minimum. What are the basics of a PLM professional?
In addition, I participated in some of the SharePLM podcast recordings with PLM experts from the field (follow us here). I raised the PLM professional question either during the podcast or during the preparation of the after-party. Also, there was no single unique answer.
 So much is part of PLM: people (culture, skills), processes & data, tools & infrastructures (architectures, standards) combined with execution (waterfall/agile?)
So much is part of PLM: people (culture, skills), processes & data, tools & infrastructures (architectures, standards) combined with execution (waterfall/agile?)
My intermediate conclusion: The broadness of PLM makes it complex to have a common foundation.
More about complexity
 PEOPLE: Let’s zoom in on the aspects of complexity. Starting from the People, Processes, Data and Tools discussion. The first thing mentioned is “the people,” organizations usually claim: “the most important assets in our organization are the people”.
PEOPLE: Let’s zoom in on the aspects of complexity. Starting from the People, Processes, Data and Tools discussion. The first thing mentioned is “the people,” organizations usually claim: “the most important assets in our organization are the people”.
However, people are usually the last dimension considered in business changes. Companies start with the tools, try to build the optimal processes and finally push the people into that framework by training, incentives or just force.
The reason for the last approach is that dealing with people is complex. People have their beliefs, their legacy and their motivation. And if people do not feel connected to the business (change), they will become an obstacle to change – look at the example below from my 2014 PI Apparel presentation:
To support the importance of people, I am excited to work with Share PLM and the Season 2 podcast series.
![]() In these episodes, we talk with successful PLM experts about their lessons learned during PLM implementation. You will discover it is a learning process, and connecting to people in different cultures is essential. As it is a learning process, you will find it takes time and human skills to master this complexity.
In these episodes, we talk with successful PLM experts about their lessons learned during PLM implementation. You will discover it is a learning process, and connecting to people in different cultures is essential. As it is a learning process, you will find it takes time and human skills to master this complexity.
Often human skills are called “soft skills”, but actually, they are “vital skills”!
 PROCESSES: Regarding the processes part, this is another challenging topic. Often we try to simplify processes to make them workable (sounds like a good idea). With many seasoned PLM practitioners coming from the mechanical product development world, it is not a surprise that many proposed PLM processes are BOM-centric – building on PDM and ERP capabilities.
PROCESSES: Regarding the processes part, this is another challenging topic. Often we try to simplify processes to make them workable (sounds like a good idea). With many seasoned PLM practitioners coming from the mechanical product development world, it is not a surprise that many proposed PLM processes are BOM-centric – building on PDM and ERP capabilities.
In my post: The rise and fall of the BOM? I started with this quote from Jan Bosch:
An excessive focus on the bill of materials leads to significant challenges for companies that are undergoing a digital transformation and adopting continuous value delivery. The lack of headroom, high coupling and versioning hell may easily cause an explosion of R&D expenditure over time.
Today’s organization and product complexity does not allow us to keep the processes simple to remain competitive. In that context, have a look at Erik Herzog’s comment on PLM complexity:
I believe a contributing factor to making PLM complex lies in our tendency to make too many simplifications. Do we understand a simple thing such as configuration change management in incremental development? At least in my organization, there is room for improvement.
In the comment, Erik also provided a link to his conference paper: Introducing the 4-Box Development Model describing the potential interaction between Systems Engineering and Configuration Management. A topic that is too complex for your current company; however, it illustrates that you cannot generalize and simplify PLM overall.
 In addition to Erik’s comments, I want to mention again that we can change our business processes thanks to a modern, connected, data-driven infrastructure. From coordinated to connected working with a mix of Systems of Engagement (new) and Systems of Record (traditional). There are no solid best practices yet, but the real PLM geeks are becoming visible.
In addition to Erik’s comments, I want to mention again that we can change our business processes thanks to a modern, connected, data-driven infrastructure. From coordinated to connected working with a mix of Systems of Engagement (new) and Systems of Record (traditional). There are no solid best practices yet, but the real PLM geeks are becoming visible.
 TOOLS & DATA: When discussing the future: From Coordinated to Connected, there has always been a discussion about the legacy.
TOOLS & DATA: When discussing the future: From Coordinated to Connected, there has always been a discussion about the legacy.
Should we migrate the legacy data and systems and replace them with new tools and data models? Or are there other options? The interaction of tools and data is often the domain of Enterprise Solution Architects. The Solution Architect’s role becomes increasingly important in a modern, data-driven company, and several are pretty active in PLM, if you know how to find them, because they are not in the mainstream of PLM.
 This week we made a SharePLM podcast recording with Yousef Hooshmand. I wrote about his paper “From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh” last year as Yousef describes the complex process, that time working at Daimler, to slowly replace old legacy infrastructure with a new modern user/role-centric data-driven infrastructure.
This week we made a SharePLM podcast recording with Yousef Hooshmand. I wrote about his paper “From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh” last year as Yousef describes the complex process, that time working at Daimler, to slowly replace old legacy infrastructure with a new modern user/role-centric data-driven infrastructure.
Watch out for this recording to be published soon as Yousef shares various provoking experiences. Not to provoke our community but to create the awareness that a transformation is possible when you have the right long-term vision, strategy and C-level support.
Fighting complexity

 Note: We have CM people involved in many of the PLM discussions. I think they are fighting similar complexity like others in the PLM domain. However, they have the benefit that their role: Configuration Manager, is recognized and supported by a commercial certification organization( the Institute of Process Excellence – IpX ).
Note: We have CM people involved in many of the PLM discussions. I think they are fighting similar complexity like others in the PLM domain. However, they have the benefit that their role: Configuration Manager, is recognized and supported by a commercial certification organization( the Institute of Process Excellence – IpX ).
While completing this post, I read this article from Oleg Shilovitsky: PLM User Groups and Communities. At first glance, you might think that PLM User Groups and Communities might be the solution to address the complexity.
 And I think they do; there are within most PLM vendors orchestrated User Groups and Communities. Depending on your tool vendor, you will find like-minded people supported by vendor experts. Are they reducing the complexity? Probably not, as they are at the end of the People, Processes, Data and Tools discussion. You are already working within a specific boundary.
And I think they do; there are within most PLM vendors orchestrated User Groups and Communities. Depending on your tool vendor, you will find like-minded people supported by vendor experts. Are they reducing the complexity? Probably not, as they are at the end of the People, Processes, Data and Tools discussion. You are already working within a specific boundary.
 Based on my experience as a core PLM Global Green Alliance member, I think PLM-neutral communities are not viable. There is very little interaction in this community, with currently 686 members, although the topics are very actual. Yes, people want to consume and learn, but making time available to share is, unfortunately, impossible when not financially motivated. Sharing opinions, yes, but working on topics: we are too busy.
Based on my experience as a core PLM Global Green Alliance member, I think PLM-neutral communities are not viable. There is very little interaction in this community, with currently 686 members, although the topics are very actual. Yes, people want to consume and learn, but making time available to share is, unfortunately, impossible when not financially motivated. Sharing opinions, yes, but working on topics: we are too busy.
Conclusion
The term PLM seems adequate to identify a group with a common interest (and skills?) Due to the broad scope and aspects – it is impossible to create a standard job description for the PLM professional, and we must learn to live with that- see my arguments.
What do you think?
 In the past two weeks, I had several discussions with peers in the PLM domain about their experiences.
In the past two weeks, I had several discussions with peers in the PLM domain about their experiences.
Some of them I met after a long time again face-to-face at the LiveWorx 2023 event. See my review of the event here: The Weekend after LiveWorx 2023.
And there were several interactions on LinkedIn, leading to a more extended discussion thread (an example of a digital thread ?) or a Zoom discussion (a so-called 2D conversation).
 To complete the story, I also participated in two PLM podcasts from Share PLM, where we interviewed Johan Mikkelä (currently working at FLSmidth) and, in the second episode Issam Darraj (presently working at ABB) about their PLM experiences. Less a discussion, more a dialogue, trying to grasp the non-documented aspects of PLM. We are looking for your feedback on these podcasts too.
To complete the story, I also participated in two PLM podcasts from Share PLM, where we interviewed Johan Mikkelä (currently working at FLSmidth) and, in the second episode Issam Darraj (presently working at ABB) about their PLM experiences. Less a discussion, more a dialogue, trying to grasp the non-documented aspects of PLM. We are looking for your feedback on these podcasts too.
All these discussions led to a reconfirmation that if you are a PLM practitioner, you need a broad skillset to address the business needs, translate them into people and process activities relevant to the industry and ultimately implement the proper collection of tools.
![]() As a sneaky preview for the podcast sessions, we asked both Johan and Issam about the importance of the tools. I will not disclose their answers here; you have to listen.
As a sneaky preview for the podcast sessions, we asked both Johan and Issam about the importance of the tools. I will not disclose their answers here; you have to listen.
Let’s look at some of the discussions.
 NOTE: Just before pushing the Publish button, Oleg Shilovitsky published this blog article PLM Project Failures and Unstoppable PLM Playbook. I will comment on his points at the end of this post. It is all part of the extensive discussion.
NOTE: Just before pushing the Publish button, Oleg Shilovitsky published this blog article PLM Project Failures and Unstoppable PLM Playbook. I will comment on his points at the end of this post. It is all part of the extensive discussion.
PLM, LinkedIn and complexity
 The most popular discussions on LinkedIn are often related to the various types of Bills of Materials (eBOM, mBOM, sBOM), Part numbering schemes (intelligent or not), version and revision management and the famous FFF discussions.
The most popular discussions on LinkedIn are often related to the various types of Bills of Materials (eBOM, mBOM, sBOM), Part numbering schemes (intelligent or not), version and revision management and the famous FFF discussions.
This post: PLM and Configuration Management Best Practices: Working with Revisions, from Andreas Lindenthal, was a recent example that triggered others to react.
I had some offline discussions on this topic last week, and I noticed Frédéric Zeller wrote his post with the title PLM, LinkedIn and complexity, starting his post with (quote):
I am stunned by the average level of posts on the PLM on LinkedIn.
I’m sorry, but in 2023 :
- Part Number management (significant, non-significant) should no longer be a problem.
- Revision management should no longer be a question.
- Configuration management theory should no longer be a question.
- Notions of EBOMs, MBOMs … should no longer be a question.
So why are there still problems on these topics?
You can see from the at least 40+ comments that this statement created a lot of reactions, including mine. Apparently, these topics are touching many people worldwide, and there is no simple, single answer to each of these topics. And there are so many other topics relevant to PLM.
 Talking later with Frederic for one hour in a Zoom session, we discussed the importance of the right PLM data model.
Talking later with Frederic for one hour in a Zoom session, we discussed the importance of the right PLM data model.
I also wrote a series about the (traditional) PLM data model: The importance of a (PLM) data model.
Frederic is more of a PLM architect; we even discussed the wording related to the EBOM and the MBOM. A topic that I feel comfortable discussing after many years of experience seeing the attempts that failed and the dreams people had. And this was only one aspect of PLM.
 You also find the discussion related to a PLM certification in the same thread. How would you certify a person as a PLM expert?
You also find the discussion related to a PLM certification in the same thread. How would you certify a person as a PLM expert?
There are so many dimensions to PLM. Even more important, the PLM from 10-15 years ago (more of a system discussion) is no longer the PLM nowadays (a strategy and an infrastructure) –
This is a crucial difference. Learning to use a PLM tool and implement it is not the same as building a PLM strategy for your company. It is Tools, Process, People versus Process, People, Tools and Data.
Time for Methodology workshops?
I recently discussed with several peers what we could do to assist people looking for best practices discussion and lessons learned. There is a need, but how to organize them as we cannot expect this to be voluntary work.
![]() In the past, I suggested MarketKey, the organizer of the PI DX events, extend its theme workshops. For example, instead of a 45-min Focus group with a short introduction to a theme (e.g., eBOM-mBOM, PLM-ERP interfaces), make these sessions last at least half a day and be independent of the PLM vendors.
In the past, I suggested MarketKey, the organizer of the PI DX events, extend its theme workshops. For example, instead of a 45-min Focus group with a short introduction to a theme (e.g., eBOM-mBOM, PLM-ERP interfaces), make these sessions last at least half a day and be independent of the PLM vendors.
Apparently, it did not fit in the PI DX programming; half a day would potentially stretch the duration of the conference and more and more, we see two days of meetings as the maximum. Longer becomes difficult to justify even if the content might have high value for the participants.
 I observed a similar situation last year in combination with the PLM roadmap/PDT Europe conference in Gothenburg. Here we had a half-day workshop before the conference led by Erik Herzog(SAAB Aeronautics)/ Judith Crockford (Europstep) to discuss concepts related to federated PLM – read more in this post: The week after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2022.
I observed a similar situation last year in combination with the PLM roadmap/PDT Europe conference in Gothenburg. Here we had a half-day workshop before the conference led by Erik Herzog(SAAB Aeronautics)/ Judith Crockford (Europstep) to discuss concepts related to federated PLM – read more in this post: The week after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2022.
It reminded me of an MDM workshop before the 2015 Event, led by Marc Halpern from Gartner. Unfortunately, the federated PLM discussion remained a pretty Swedish initiative, and the follow-up did not reach a wider audience.
 And then there are the Aerospace and Defense PLM action groups that discuss moderated by CIMdata. It is great that they published their findings (look here), although the best lessons learned are during the workshops.
And then there are the Aerospace and Defense PLM action groups that discuss moderated by CIMdata. It is great that they published their findings (look here), although the best lessons learned are during the workshops.
However, I also believe the A&D industry cannot be compared to a mid-market machinery manufacturing company. Therefore, it is helpful for a smaller audience only.
And here, I inserted a paragraph dedicated to Oleg’s recent post, PLM Project Failures and Unstoppable PLM Playbook – starting with a quote:
How to learn to implement PLM? I wrote about it in my earlier article – PLM playbook: how to learn about PLM? While I’m still happy to share my knowledge and experience, I think there is a bigger need in helping manufacturing companies and, especially PLM professionals, with the methodology of how to achieve the right goal when implementing PLM. Which made me think about the Unstoppable PLM playbook ©.
I found a similar passion for helping companies to adopt PLM while talking to Helena Gutierrez. Over many conversations during the last few months, we talked about how to help manufacturing companies with PLM adoption. The unstoppable PLM playbook is still a work in progress, but we want to start talking about it to get your feedback and start the conversation.
It is an excellent confirmation of the fact that there is a need for education and that the education related to PLM on the Internet is not good enough.
 As a former teacher in Physics, I do not believe in the Unstoppable PLM Playbook, even if it is a branded name. Many books are written by specific authors, giving their perspectives based on their (academic) knowledge.
As a former teacher in Physics, I do not believe in the Unstoppable PLM Playbook, even if it is a branded name. Many books are written by specific authors, giving their perspectives based on their (academic) knowledge.
Are they useful? I believe only in the context of a classroom discussion where the applicability can be discussed,
 Therefore my questions to vendor-neutral global players, like CIMdata, Eurostep, Prostep, SharePLM, TCS and others, are you willing to pick up this request? Or are there other entities that I missed? Please leave your thoughts in the comments. I will be happy to assist in organizing them.
Therefore my questions to vendor-neutral global players, like CIMdata, Eurostep, Prostep, SharePLM, TCS and others, are you willing to pick up this request? Or are there other entities that I missed? Please leave your thoughts in the comments. I will be happy to assist in organizing them.
There are many more future topics to discuss and document too.
- What about the potential split of a PLM infrastructure between Systems of Record & Systems of Engagement?
- What about the Digital Thread, a more and more accepted theme in discussions, but what is the standard definition?
- Is it traceability as some vendors promote it, or is it the continuity of data, direct usable in various contexts – the DevOps approach?
Who likes to discuss methodology?
 When asking myself this question, I see the analogy with standards. So let’s look at the various players in the PLM domain – sorry for the immense generalization.
When asking myself this question, I see the analogy with standards. So let’s look at the various players in the PLM domain – sorry for the immense generalization.
Strategic consultants: standards are essential, but spare me the details.
Vendors: standards are limiting the unique capabilities of my products
Implementers: two types – Those who understand and use standards as they see the long-term benefits. Those who avoid standards as it introduces complexity.
Companies: they love standards if they can be implemented seamlessly.
Universities: they love to explore standards and help to set the standards even if they are not scalable
Just replace standards with methodology, and you see the analogy.
We like to discuss the methodology.
 As I mentioned in the introduction, I started to work with Share PLM on a series of podcasts where we interview PLM experts in the field that have experience with the people, the process, the tools and the data side. Through these interviews, you will realize PLM is complex and has become even more complicated when you consider PLM a strategy instead of a tool.
As I mentioned in the introduction, I started to work with Share PLM on a series of podcasts where we interview PLM experts in the field that have experience with the people, the process, the tools and the data side. Through these interviews, you will realize PLM is complex and has become even more complicated when you consider PLM a strategy instead of a tool.
We hope these podcasts might be a starting point for further discussion – either through direct interactions or through contributions to the podcast. If you have PLM experts in your network that can explain the complexity of PLM from various angles and have the experience. Please let us know – it is time to share.
Conclusion
By switching gears, I noticed that PLM has become complex. Too complex for a single person to master. With an aging traditional PLM workforce (like me), it is time to consolidate the best practices of the past and discuss the best practices for the future. There are no simple answers, as every industry is different. Help us to energize the PLM community – your thoughts/contributions?
 With great pleasure, I am writing this post, part of a tradition that started for me in 2014. Posts starting with “The weekend after …. “describing what happened during a PDT conference, later the event merged with CIMdata becoming THE PLM event for discussions beyond marketing.
With great pleasure, I am writing this post, part of a tradition that started for me in 2014. Posts starting with “The weekend after …. “describing what happened during a PDT conference, later the event merged with CIMdata becoming THE PLM event for discussions beyond marketing.
For many of us, this conference was the first time after COVID-19 in 2020. It was a 3D (In person) conference instead of a 2D (digital) conference. With approximately 160 participants, this conference showed that we wanted to meet and network in person and the enthusiasm and interaction were great.

The conference’s theme, Digital Transformation and PLM – a call for PLM Professionals to redefine and re-position the benefits and value of PLM, was quite open.
There are many areas where digitization affects the way to implement a modern PLM Strategy.
Now some of my highlights from day one. I needed to filter to remain around max 1500 words. As all the other sessions, including the sponsor vignettes, were informative, they increased the value of this conference.
Digital Skills Transformation -Often Forgotten Critical Element of Digital Transformation
![]() Day 1 started traditionally with the keynote from Peter Bilello, CIMdata’s president and CEO. In previous conferences, Peter has recently focused on explaining the CIMdata’s critical dozen (image below). If you are unfamiliar with them, there is a webinar on November 10 where you can learn more about them.
Day 1 started traditionally with the keynote from Peter Bilello, CIMdata’s president and CEO. In previous conferences, Peter has recently focused on explaining the CIMdata’s critical dozen (image below). If you are unfamiliar with them, there is a webinar on November 10 where you can learn more about them.
All twelve are equally important; it is not a sequence of priorities. This time Peter spent more time on Organisational Change management (OCM), number 12 of the critical dozen – or, as stated, the Digital Transformation’s Achilles heel. Although we always mention people are important, in our implementation projects, they often seem to be the topic that gets the less focus.
 We all agree on the statement: People, Process, Tools & Data. Often the reality is that we start with the tools, try to build the processes and push the people in these processes. Is it a coincidence that even CIMdata puts Digital Skills transformation as number 12? An unconscious bias?
We all agree on the statement: People, Process, Tools & Data. Often the reality is that we start with the tools, try to build the processes and push the people in these processes. Is it a coincidence that even CIMdata puts Digital Skills transformation as number 12? An unconscious bias?
This time, the people’s focus got full attention. Peter explained the need for a digital skills transformation framework to educate, guide and support people during a transformation. The concluding slide below says it all.
Transformation Journey and PLM & PDM Modernization to the Digital Future
 The second keynote of the day was from Josef Schiöler, Head of Core Platform Area PLM/PDM from the Volvo Group. Josef and his team have a huge challenge as they are working on a foundation for the future of the Volvo Group.
The second keynote of the day was from Josef Schiöler, Head of Core Platform Area PLM/PDM from the Volvo Group. Josef and his team have a huge challenge as they are working on a foundation for the future of the Volvo Group.
The challenge is that it will provide the foundation for new business processes and the various group members, as the image shows below:
As Josef said, it is really the heart of the heart, crucial for the future. Peter Bilello referred to this project as open-heart surgery while the person is still active, as the current business must go on too.
The picture below gives an impression of the size of the operation.
And like any big transformation project also, the Volvo Group has many questions to explore as there is no existing blueprint to use.
To give you an impression:
- How to manage complex documentation with existing and new technology and solution co-existing?
(My take: the hybrid approach) - How to realize benefits and user adoption with user experience principles in mind?
(My take: Understand the difference between a system of engagement and a system of record) - How to avoid seeing modernization as pure an IT initiative and secure that end-user value creation is visible while still keeping a focus on finalizing the technology transformation?
(My take: think hybrid and focus first on the new systems of engagement that can grow) - How to efficiently partner with software vendors to ensure vendor solutions fit well in the overall PLM/PDM enterprise landscape without heavy customization?
(My take: push for standards and collaboration with other similar companies – they can influence a vendor)
![]() Note: My takes are just a starting point of the conversation. There is a discussion in the PLM domain, which I described in my blog post: A new PLM paradigm.
Note: My takes are just a starting point of the conversation. There is a discussion in the PLM domain, which I described in my blog post: A new PLM paradigm.
 The day before the conference, we had a ½ day workshop initiated by SAAB and Eurostep where we discussed the various angles of the so-called Federated PLM.
The day before the conference, we had a ½ day workshop initiated by SAAB and Eurostep where we discussed the various angles of the so-called Federated PLM.
I will return to that topic soon after some consolidation with the key members of that workshop.
Steering future Engineering Processes with System Lifecycle Management
 Patrick Schäfer‘s presentation was different than the title would expect. Patrick is the IT Architect Engineering IT from ThyssenKrupp Presta AG. The company provides steering systems for the automotive industry, which is transforming from mechanical to autonomous driving, e-mobility, car-to-car connectivity, stricter safety, and environmental requirements.
Patrick Schäfer‘s presentation was different than the title would expect. Patrick is the IT Architect Engineering IT from ThyssenKrupp Presta AG. The company provides steering systems for the automotive industry, which is transforming from mechanical to autonomous driving, e-mobility, car-to-car connectivity, stricter safety, and environmental requirements.
 The steering system becomes a system depending on hardware and software. And as current users of Agile PLM, the old Eigner PLM software, you can feel Martin Eigner’s spirit in the project.
The steering system becomes a system depending on hardware and software. And as current users of Agile PLM, the old Eigner PLM software, you can feel Martin Eigner’s spirit in the project.
I briefly discussed Martin’s latest book on System Lifecycle Management in my blog post, The road to model-based and connected PLM (part 5).
Martin has always been fighting for a new term for modern PLM, and you can see how conservative we are – for sometimes good reasons.
Still, ThyssenKrupp Presta has the vision to implement a new environment to support systems instead of hardware products. And in addition, they had to work fast to upgrade their current almost obsolete PLM environment to a new supported environment.
The wise path they chose was first focusing on a traditional upgrade, meaning making sure their PLM legacy data became part of a modern (Teamcenter) PLM backbone. Meanwhile, they started exploring the connection between requirements management for products and software, as shown below.
From my perspective, I would characterize this implementation as the coordinated approach creating a future option for the connected approach when the organization and future processes are more mature and known.
A good example of a pragmatic approach.
Digital Transformation in the Domain of Products and Plants at Siemens Energy
 Per Soderberg, Head of Digital PLM at Siemens Energy, talked about their digital transformation project that started 6 – 7 years ago. Knowing the world of gas- and steam turbines, it is a domain where a lot of design and manufacturing information is managed in drawings.
Per Soderberg, Head of Digital PLM at Siemens Energy, talked about their digital transformation project that started 6 – 7 years ago. Knowing the world of gas- and steam turbines, it is a domain where a lot of design and manufacturing information is managed in drawings.
The ultimate vision from Siemens Energy is to create an Industrial Metaverse for its solutions as the benefits are significant.
Is this target too ambitious, like GE’s 2014 Industrial Transformation with Predix? Time will tell. And I am sure you will soon hear more from Siemens Energy; therefore, I will keep it short. An interesting and ambitious program to follow. Sure you will read about them in the near future.
Accelerating Digitalization at Stora Enso
 Stora Enso is a Finish company, a leading global provider of renewable solutions in packaging, biomaterials, wooden construction and paper. Their director of Innovation Services, Kaisa Suutari, shared Stora Enso’s digital transformation program that started six years ago with a 10 million/year budget (some people started dreaming too). Great to have a budget but then where to start?
Stora Enso is a Finish company, a leading global provider of renewable solutions in packaging, biomaterials, wooden construction and paper. Their director of Innovation Services, Kaisa Suutari, shared Stora Enso’s digital transformation program that started six years ago with a 10 million/year budget (some people started dreaming too). Great to have a budget but then where to start?
In a very systematic manner using an ideas funnel and always starting from the business need, they spend the budget in two paths, shown in the image below.
 Their interesting approach was in the upper path, which Kaisa focused on. Instead of starting with an analysis of how the problem could be addressed, they start by doing and then analyze the outcome and improve.
Their interesting approach was in the upper path, which Kaisa focused on. Instead of starting with an analysis of how the problem could be addressed, they start by doing and then analyze the outcome and improve.
I am a great fan of this approach as it will significantly reduce the time to maturity. However, how much time is often wasted in conducting the perfect analysis?
Their Digi Fund process is a fast process to quickly go from idea to concept, to POC and to pilot, the left side of the funnel. After a successful pilot, an implementation process starts small and scales up.
There were so many positive takeaways from this session. Start with an MVP (Minimal Viable Product) to create value from the start. Next, celebrate failure when it happens, as this is the moment you learn. Finally, continue to create measurable value created by people – the picture below says it all.
 It was the second time I was impressed by Stora Enso’s innovative approach. During the PI PLMX 2020 London, Samuli Savo, Chief Digital Officer at Stora Enso, gave us insights into their innovation process. At that time, the focus was a little bit more on open innovation with startups. See my post: The weekend after PI PLMx London 2020. An interesting approach for other businesses to make their digital transformation business-driven and fun for the people
It was the second time I was impressed by Stora Enso’s innovative approach. During the PI PLMX 2020 London, Samuli Savo, Chief Digital Officer at Stora Enso, gave us insights into their innovation process. At that time, the focus was a little bit more on open innovation with startups. See my post: The weekend after PI PLMx London 2020. An interesting approach for other businesses to make their digital transformation business-driven and fun for the people
A day-one summary
There was Kyle Hall, who talked about MoSSEC and the importance of this standard in a connected enterprise. MoSSEC (Modelling and Simulation information in a collaborative Systems Engineering Context) is the published ISO standard (ISO 10303-243) for improving the decision-making process for complex products. Standards are a regular topic for this conference, more about MoSSEC here.
There was Robert Rencher, Sr. Systems Engineer, Associate Technical Fellow at Boeing, talking about the progress that the A&D action group is making related to Digital Thread, Digital Twins. Sometimes asking more questions than answers as they try to make sense of the marketing definition and what it means for their businesses. You can find their latest report here.
There was Samrat Chatterjee, Business Process Manager PLM at the ABB Process Automation division. Their businesses are already quite data-driven; however, by embedding PLM into the organization’s fabric, they aim to improve effectiveness, manage a broad portfolio, and be more modular and efficient.
The day was closed with a CEO Spotlight, Peter Bilello. This time the CEOs were not coming from the big PLM vendors but from complementary companies with their unique value in the PLM domain. Henrik Reif Andersen, co-founder of Configit; Dr. Mattias Johansson, CEO of Eurostep; Helena Gutierrez, co-founder of Share PLM; Javier Garcia, CEO of The Reuse Company and Karl Wachtel, CEO, XPLM discussed their various perspectives on the PLM domain.
Conclusion
Already so much to say; sorry, I reached the 1500 words target; you should have been there. Combined with the networking dinner after day one, it was a great start to the conference. Are you curious about day 2 – stay tuned, and your curiosity will be rewarded.
 Thanks to Ewa Hutmacher, Sumanth Madala and Ashish Kulkarni, who shared their pictures of the event on LinkedIn. Clicking on their names will lead you to the relevant posts.
Thanks to Ewa Hutmacher, Sumanth Madala and Ashish Kulkarni, who shared their pictures of the event on LinkedIn. Clicking on their names will lead you to the relevant posts.
 It has been busy recently in the context of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability, where we interview PLM-related software vendors, discussing their sustainability mission and offering.
It has been busy recently in the context of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability, where we interview PLM-related software vendors, discussing their sustainability mission and offering.
We talked with SAP, Autodesk, and Dassault Systèmes and last week with Sustaira. Now the discussion was with the team from Aras. Aras is known as a non-traditional PLM player, having the following slogan on their website:
It is a great opening statement for our discussion. Let’s discover more.
Aras
 The discussion was with Patrick Willemsen, Director of Technical Community EMEA and Matthias Fohrer, Director of Global Alliances EMEA at Aras. It was an interesting interview; as we discussed, Aras focuses on the digital thread, connecting data from all sources with an infrastructure designed to support a company in its PLM domain.
The discussion was with Patrick Willemsen, Director of Technical Community EMEA and Matthias Fohrer, Director of Global Alliances EMEA at Aras. It was an interesting interview; as we discussed, Aras focuses on the digital thread, connecting data from all sources with an infrastructure designed to support a company in its PLM domain.
As I mentioned in a previous blog post, PLM and Sustainability – if we want to work efficiently on Sustainability, we need to have a data-driven and connected infrastructure.
And this made this discussion interesting to follow– please look/listen to the 30 minutes conversation below.
Slides shown during the interview and additional company information can be found HERE.
What we have learned
 There were several interesting points in our discussion where we were aligned; first of all, the sustainable value of bringing your solutions to the cloud.
There were several interesting points in our discussion where we were aligned; first of all, the sustainable value of bringing your solutions to the cloud.
So we discussed the topic of Sustainability and the cloud, and it was interesting to read this week McKinsey’s post The green IT revolution: A blueprint for CIOs to combat climate change containing this quote:
“Moving to the cloud has more impact than optimizing data centers”– the article is quite applicable for Aras.
Next, I liked the message that it is all about collaboration between different parties.
 As Matthias mentioned, nobody can do it on their own. According to Aras’ studies, 70% see Sustainability as an important area to improve themselves; nobody can do it on his own. Partnerships are crucial, as well as digital connections between the stakeholders. It is a plea for systems thinking in a connected manner, connecting to existing material libraries.
As Matthias mentioned, nobody can do it on their own. According to Aras’ studies, 70% see Sustainability as an important area to improve themselves; nobody can do it on his own. Partnerships are crucial, as well as digital connections between the stakeholders. It is a plea for systems thinking in a connected manner, connecting to existing material libraries.
 The third point we were aligned with is that PLM and Sustainability are a learning journey. As Patrick explained, it is about embracing the circular economy and learning step by step.
The third point we were aligned with is that PLM and Sustainability are a learning journey. As Patrick explained, it is about embracing the circular economy and learning step by step.
<– Click on the image to enlarge.
Want to learn more?
Aras has published several white papers and surveys and hosted webinars related to Sustainability. Here are a few of them:
Aras Survey Challenges 2022: From Sustainability to Digitalization
White Paper: The Circular Economy as a Model for the Future
Webinar: Greener Business, PLM, Traceability, and Beyond
Webinar: How PLM Paves the Way for Sustainability
Blog: The Circular Economy as a Model for the Future
Conclusions
It is clear that Aras provides an infrastructure for a connected enterprise. They combine digital PLM capabilities with the option to extend their reach by supporting sustainability-related processes, like systems thinking and lifecycle assessments. And as they mention, no one can do it alone; we depend on collaboration and learning for all stakeholders.
On more week to go – join us if you can – click here

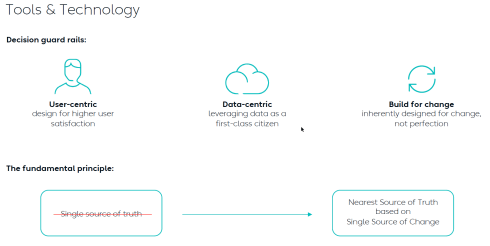



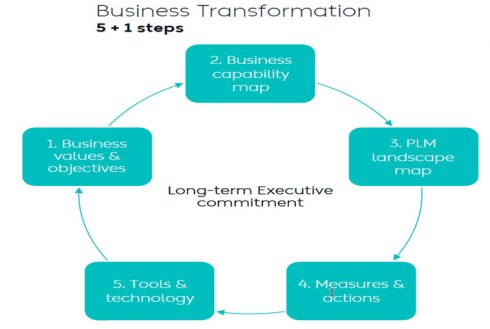

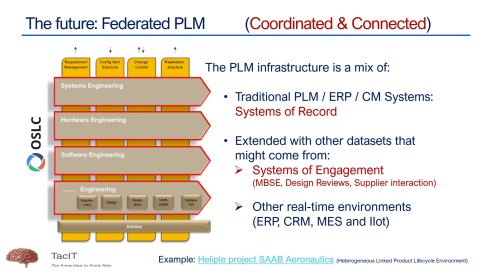

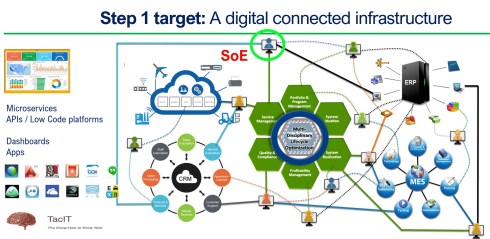
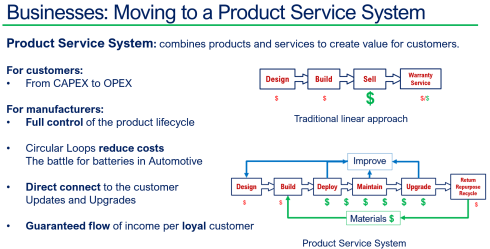
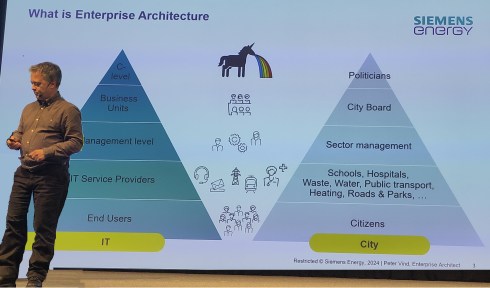
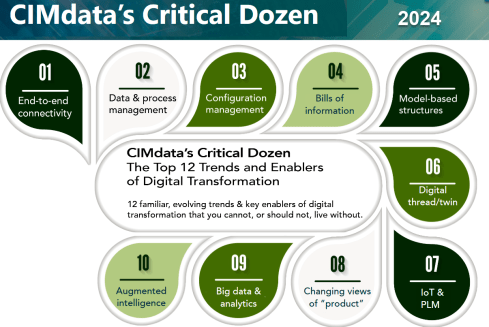
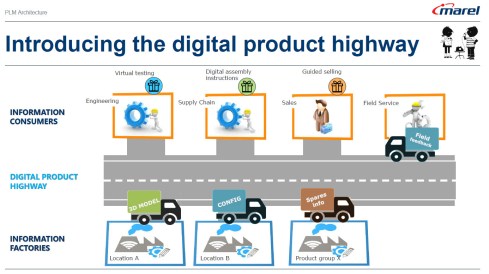
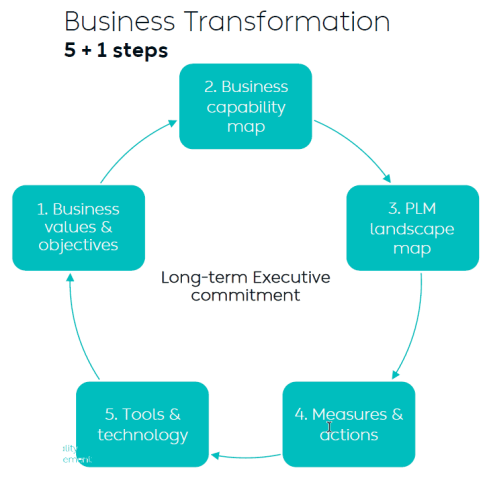

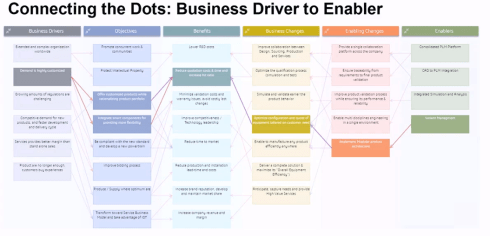











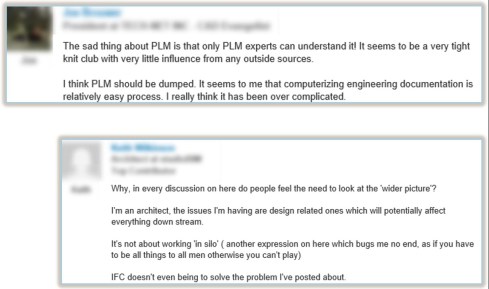

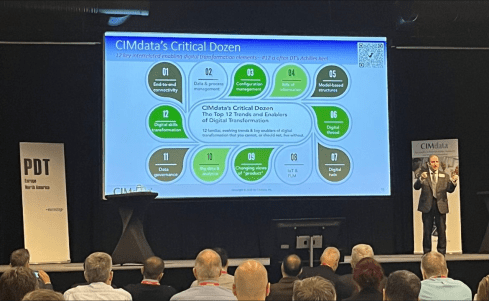




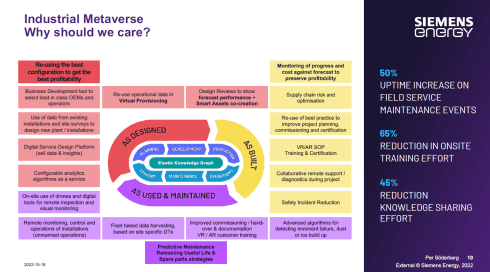





[…] (The following post from PLM Green Global Alliance cofounder Jos Voskuil first appeared in his European PLM-focused blog HERE.) […]
[…] recent discussions in the PLM ecosystem, including PSC Transition Technologies (EcoPLM), CIMPA PLM services (LCA), and the Design for…
Jos, all interesting and relevant. There are additional elements to be mentioned and Ontologies seem to be one of the…
Jos, as usual, you've provided a buffet of "food for thought". Where do you see AI being trained by a…
Hi Jos. Thanks for getting back to posting! Is is an interesting and ongoing struggle, federation vs one vendor approach.…