You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Data centric’ category.
 This post shares our second interview this year in the PLM Global Green Alliance series, where we talked with PLM-related software vendors and their activities related to Sustainability. Last year, we spoke mainly with the more traditional PLM vendors, but this year, we started with Makersite, a company specialized in Product Lifecycle Intelligence supporting sustainability analysis.
This post shares our second interview this year in the PLM Global Green Alliance series, where we talked with PLM-related software vendors and their activities related to Sustainability. Last year, we spoke mainly with the more traditional PLM vendors, but this year, we started with Makersite, a company specialized in Product Lifecycle Intelligence supporting sustainability analysis.
And now we are happy to talk this time with Mark Rushton, Senior Product Marketing Manager and Ryan Flavelle, Associate Product Owner, both at aPriori Technologies. For my PGGA partner Mark Reisig and me, it was an interesting discussion in a domain where the focus was not on product design at the time.
aPriori
 aPriori, according to their website, focuses on Digital Manufacturing, digitizing the entire manufacturing process, from design to production, and therefore able to asses environmental impact in a reliable manner.
aPriori, according to their website, focuses on Digital Manufacturing, digitizing the entire manufacturing process, from design to production, and therefore able to asses environmental impact in a reliable manner.
It was an informative dialogue. Watch the 35-minute discussion here and learn how aPriori uniquely digitizes the manufacturing processes to support Sustainability.
Slides shown during the interview combined with additional company information can be found HERE.
What we have learned
- aPriori’s customers have pushed the company to provide faster and digital sustainability insights in their manufacturing processes, illustrating that companies are really acting to understand their environmental impact. To measure is to know.
- In this interview, we saw the concepts of the digital twin of manufacturing processes and the digital twin of a plant.
- aPriori uniquely starts their impact analysis based on the 3d CAD geometry, being more accurate than what most LCA tools do, a BOM-based assessment,
Want to learn more?
Here are some links to the topics discussed in our meeting:
- How does aPriori software work – watch this demo
- aPriori’s Sustainability resources can be found here
- The blog Mark Reisig liked: the aPriori blog
- And the famous Manufacturing Insights Podcast
Conclusions
When it comes to sustainability in action, you need to be able measure and understand your environmental impact. Where traditional PLM activities focus on the design phase, there is also a lot to learn during the manufacturing phase. aPriori is doing this on a unique manner, not just based on BOM-analysis. In addition companies like aPriori have already a longer term experience with the virtual twin for manufacturing, originally used for cost and manufacturability analysis. Now extended to sustainability and their customers are working on it.
 We are happy to start the year with the next round of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability. This year, we will speak with some new companies, and we will also revisit some of our previous guests to learn about their progress.
We are happy to start the year with the next round of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability. This year, we will speak with some new companies, and we will also revisit some of our previous guests to learn about their progress.
Where we talked with Aras, Autodesk, CIMdata, Dassault Systèmes, PTC, SAP, Sustaira and Transition Technologies PSC, there are still a lot of software companies with an exciting portfolio related to sustainability.
Therefore, we are happy to talk this time with Makersite, a company whose AI-powered Product Lifecycle Intelligence software, according to their home page, brings together your cost, environment, compliance, and risk data in one place to make smarter, greener decisions powered by the deepest understanding of your supply chain. Let’s explore
Makersite
![]() We were lucky to have a stimulating discussion with Neil D’Souza, Makersite’s CEO and founder, who was active in the field of sustainability for almost twenty years, even before it became a cool (or disputed) profession.
We were lucky to have a stimulating discussion with Neil D’Souza, Makersite’s CEO and founder, who was active in the field of sustainability for almost twenty years, even before it became a cool (or disputed) profession.
It was an exciting dialogue where we enjoyed realistic answers without all the buzzwords and marketing terms often used in the new domain of sustainability. Enjoy the 39 minutes of interaction below:
Slides shown during the interview combined with additional company information can be found HERE.
What we have learned
- Makersite’s mission, to enable manufacturers to make better products, faster, initially applied to economic parameters, can be easily extended with sustainability parameters.The power of Makersite is that it connects to enterprise systems and sources using AI, Machine Learning and algorithms to support reporting views on compliance, sustainability, costs and risk.
- Compliance and sustainability are the areas where I see a significant need for companies to invest. It is not a revolutionary business change but an extension of scope.We discussed this in the context of the stage-gate process, where sustainability parameters should be added at each gate.
- Neil has an exciting podcast, Five Lifes to Fifty, where he discusses the path to sustainable products with co-hosts Shelley Metcalfe and Jim Fava, and recently, they discussed sustainability in the context of the stage-gate process.
- Again, to move forward with sustainability, it is about creating the base and caring about the data internally to understand what’s happening, and from there, enable value engineering, including your supplier where possible (IP protection remains a topic) – confirming digital transformation (the connected way of working) is needed for business and sustainability.
Want to learn more?
Here are some links to the topics discussed in our meeting:
- The Website – Makersite.io
- Makersite data foundation – makersite-data-foundation
- Makersite demo video – makersite-platform-demo
- Neil’s LinkedIn – neilsaviodsouza
Conclusions
With Makersite, we discovered an experienced company that used its experience in cost, compliance and risk analysis, including supply chains, to extend it to the domain of sustainability. As their technology partners page shows, they can be complementary in many industries and enterprises.
We will see another complementary solution soon in our following interview. Stay tuned.
 One year ago, I wrote the post: Time to Split PLM, which reflected a noticeable trend in 2022 and 2023.
One year ago, I wrote the post: Time to Split PLM, which reflected a noticeable trend in 2022 and 2023.
If you still pursue the Single Source of Truth or think that PLM should be supported by a single system, the best you can buy, then you are living in the past.
It is now the time to move from a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh (Yousef Hooshmand) or the Heliple Federated PLM project (Erik Herzog) – you may have read about these concepts.
When moving from a traditional coordinated, document-driven business towards a modern, connected, and data-driven business, there is a paradigm shift. In many situations, we still need the document-driven approach to manage baselines for governance and traceability, where we create the required truth for manufacturing, compliance, and configuration management.
However, we also need an infrastructure for multidisciplinary collaboration nowadays. Working with systems, a combination of hardware and software, requires a model-based approach and multidisciplinary collaboration. This infrastructure needs to be data-driven to remain competitive despite more complexity, connecting stakeholders along value streams.
 Traditional PLM vendors still push all functionality into one system, often leading to frustration among the end-users, complaining about lack of usability, bureaucracy, and the challenge of connecting to external stakeholders, like customers, suppliers, design or service partners.
Traditional PLM vendors still push all functionality into one system, often leading to frustration among the end-users, complaining about lack of usability, bureaucracy, and the challenge of connecting to external stakeholders, like customers, suppliers, design or service partners.
Systems of Engagement
It is in modern PLM infrastructures where I started the positioning of Systems or Record (the traditional enterprise siloes – PDM/PLM, ERP, CM) and the Systems of Engagement (modern environments designed for close to real-time collaboration between stakeholders within a domain/value stream). In the Heliple project (image below), the Systems of Record are the vertical bars, and the Systems of Engagement are the horizontal bars.
The power of a System of Engagement is the data-driven connection between stakeholders even when working in different enterprises. Last year, I discussed with Andre Wegner from Authentise, MJ Smith from CoLab, and Oleg Shilovitsky from OpenBOM.
They all focus on modern, data-driven, multidisciplinary collaboration. You can find the discussion here: The new side of PLM? Systems of Engagement!
Where is the money?
 Business leaders usually are not interested in a technology or architectural discussion – too many details and complexity, they look for the business case. Look at this recent post and comments on LinkedIn – “When you try to explain PLM to your C-suite, and they just don’t get it.”
Business leaders usually are not interested in a technology or architectural discussion – too many details and complexity, they look for the business case. Look at this recent post and comments on LinkedIn – “When you try to explain PLM to your C-suite, and they just don’t get it.”
It is hard to build evidence for the need for systems of engagement, as the concepts are relatively new and experiences from the field are bubbling up slowly. With the Heliple team, we are now working on building the business case for Federated PLM in the context of the Heliple project scope.
Therefore, I was excited to read the results of this survey: Quantifying the impact of design review methods on NPD, a survey among 250 global engineering leaders initiated by CoLab.
![]() CoLab is one of those companies that focus on providing a System of Engagement, and their scope is design collaboration. In this post, I am discussing the findings of this survey with Taylor Young, Chief Strategy Officer of CoLab.
CoLab is one of those companies that focus on providing a System of Engagement, and their scope is design collaboration. In this post, I am discussing the findings of this survey with Taylor Young, Chief Strategy Officer of CoLab.
CoLab – the company /the mission
 Taylor, thanks for helping me explain the complementary value of CoLab based on some of the key findings from the survey. But first of all, can you briefly introduce CoLab as a company and the unique value you are offering to your clients?
Taylor, thanks for helping me explain the complementary value of CoLab based on some of the key findings from the survey. But first of all, can you briefly introduce CoLab as a company and the unique value you are offering to your clients?
 Hi Jos, CoLab is a Design Engagement System – we exist to help engineering teams make design decisions.
Hi Jos, CoLab is a Design Engagement System – we exist to help engineering teams make design decisions.
Product decision-making has never been more challenging – or more essential – to get right – that’s why we built CoLab. In today’s world of product complexity, excellent decision-making requires specialized expertise. That means decision-making is no longer just about people engaging with product data – it’s about people engaging with other people.
PLM provides a strong foundation where product data is controlled (and therefore reliable). But PLM has a rigid architecture that’s optimized for data (and for human-to-data interaction). To deal with increased complexity in product design, engineers now need a system that’s built for human-to-human interaction complimentary to PLM.
CoLab allows you to interrogate a rich dataset, even an extended team, outside your company borders in real-time or asynchronously. With CoLab, decisions are made with context, input from the right people, and as early as possible in the process. Reviews and decision-making get tracked automatically and can be synced back to PLM. Engineers can do what they do best, and CoLab will support them by documenting everything in the background.
Design Review Quality
 It is known that late-stage design errors are very costly, both impacting product launches and profitability. The report shows design review quality has been rated as the #1 most important factor affecting an engineering team’s ability to deliver projects on time.
It is known that late-stage design errors are very costly, both impacting product launches and profitability. The report shows design review quality has been rated as the #1 most important factor affecting an engineering team’s ability to deliver projects on time.
Is it a severe problem for companies, and what are they trying to do to improve the quality of design reviews? Can you quantify the problem?
 Our survey report demonstrated that late-stage design errors delay product launches for 90% of companies. The impact varies significantly from organization to organization, but we know that for large manufacturing companies, just one late-stage design error can be a six to seven-figure problem.
Our survey report demonstrated that late-stage design errors delay product launches for 90% of companies. The impact varies significantly from organization to organization, but we know that for large manufacturing companies, just one late-stage design error can be a six to seven-figure problem.
There are a few factors that lead to a “quality” design review – some of the most important ones we see leading manufacturing companies doing differently are:
- Who they include – the highest performing teams include manufacturing, suppliers, and customers within the proper context.
- When they happen – the highest performing teams focus on getting CAD to these stakeholders early in the process (during detailed design) and paralleling these processes (i.e., they don’t wait for one group to sign off before getting early info to the next)
- Rethinking the Design Review meeting – the highest performing teams aren’t having issue-generation meetings – they have problem-solving meetings. Feedback is collected from a broad audience upfront, and meetings are used to solve nuanced problems – not to get familiar with the project for the first time.
Multidisciplinary collaboration
 An interesting observation is that providing feedback to engineers mainly comes from peers or within the company. Having suppliers or customers involved seems to be very difficult. Why do you think this is happening, and how can we improve their contribution?
An interesting observation is that providing feedback to engineers mainly comes from peers or within the company. Having suppliers or customers involved seems to be very difficult. Why do you think this is happening, and how can we improve their contribution?
 When we talk to manufacturing companies about “collaboration” or how engineers engage with other engineers – however good or bad the processes are internally, it almost always is significantly more challenging/less effective when they go external. External teams often use different CAD systems, work in different time zones, speak other first languages, and have varying levels of access to core engineering information.
When we talk to manufacturing companies about “collaboration” or how engineers engage with other engineers – however good or bad the processes are internally, it almost always is significantly more challenging/less effective when they go external. External teams often use different CAD systems, work in different time zones, speak other first languages, and have varying levels of access to core engineering information.
However, as we can read from the HBR article What the Most Productive Companies Do Differently, we know that the most productive manufacturing companies “collaborate with suppliers and customers to form new ecosystems that benefit from agglomeration effects and create shared pools of value”.
They leverage the expertise of their suppliers and customers to do things more effectively. But manufacturing companies struggle to create engaging, high-value, external collaboration and ‘co-design’ without the tools purpose-built for person-to-person external communication.
Traceability and PLM
 One of the findings is that keeping track of the feedback and design issues is failing in companies. One of my recommendations from the past was to integrate Issue management into your PLM systems – why is this not working?
One of the findings is that keeping track of the feedback and design issues is failing in companies. One of my recommendations from the past was to integrate Issue management into your PLM systems – why is this not working?
 We believe that the task of completing a design review and the task of documenting the output of that review should not be two separate efforts. Suppose we are to reduce the amount of time engineers spend on admin work and decrease the number of issues that are never tracked or documented (43%, according to our survey).
We believe that the task of completing a design review and the task of documenting the output of that review should not be two separate efforts. Suppose we are to reduce the amount of time engineers spend on admin work and decrease the number of issues that are never tracked or documented (43%, according to our survey).
In that case, we need to introduce a purpose-built, engaging design review system that is self-documenting. It is crucial for the quality of design reviews that issues aren’t tracked in a separate system from where they are raised/developed, but that instead, they are automatically tracked just by doing the work.
Learn More?
Below is the recording of a recent webinar, where Taylor said that your PLM alone isn’t enough: Why you need a Design Engagement System during product development.
- A traditional PLM system is the system of record for product data – from ideation through sustaining engineering.
- However one set of critical data never makes it to the PLM. For many manufacturing companies today, design feedback and decisions live almost exclusively in emails, spreadsheets, and PowerPoint decks. At the same time, 90% of engineering teams state that product launches are delayed due to late-stage changes.
- Engineering teams need to implement a true Design Engagement System (DES) for more effective product development and a more holistic digital thread.
Conclusion
Traditional PLM systems have always been used to provide quality and data governance along the product lifecycle. However, most end users dislike the PLM system as it is a bureaucratic overhead to their ways of working. CoLab, with its DES solution, provides a System of Engagement focusing on design reviews, speed, and quality of multidisciplinary collaboration complementary to the PLM System of Record – a modern example of how digitization is transforming the PLM domain.
 Another year passed, and as usual, I took the time to look back. I always feel that things are going so much slower than expected. But that’s reality – there is always friction, and in particular, in the PLM domain, there is so much legacy we cannot leave behind.
Another year passed, and as usual, I took the time to look back. I always feel that things are going so much slower than expected. But that’s reality – there is always friction, and in particular, in the PLM domain, there is so much legacy we cannot leave behind.
It is better to plan what we can do in 2024 to be prepared for the next steps or, if lucky, even implement the next steps in progress.
In this post, I will discuss four significant areas of attention (AI – DATA – PEOPLE – SUSTAINABILITY) in an alphabetic order, not prioritized.
Here are some initial thoughts. In the upcoming weeks I will elaborate further on them and look forward to your input.

AI (Artificial Intelligence)
![]() Where would I be without talking about AI?
Where would I be without talking about AI?
When you look at the image below, the Gartner Hype Cycle for AI in 2023, you see the potential coming on the left, with Generative AI at the peak.
Part of the hype comes from the availability of generative AI tools in the public domain, allowing everyone to play with them or use them. Some barriers are gone, but what does it mean? Many AI tools can make our lives easier, and there is for sure no threat if our job does not depend on standard practices.
AI and People
 When I was teaching physics in high school, it was during the introduction of the pocket calculator, which replaced the slide rule.You need to be skilled to uyse the slide rule, now there was a device that gave immediate answers. Was this bad for the pupils?
When I was teaching physics in high school, it was during the introduction of the pocket calculator, which replaced the slide rule.You need to be skilled to uyse the slide rule, now there was a device that gave immediate answers. Was this bad for the pupils?
If you do not know a slide rule, it was en example of new technology replacing old tools, providing more time for other details. Click on the image or read more about the slide rule here on Wiki.
![]() Or today you would ask the question about the slide rule to ChatGPT? Does generative AI mean the end of Wikipedia? Or does generative AI need the common knowledge of sites like Wikipedia?
Or today you would ask the question about the slide rule to ChatGPT? Does generative AI mean the end of Wikipedia? Or does generative AI need the common knowledge of sites like Wikipedia?
AI can empower people in legacy environments, when working with disconnected systems. AI will be a threat for to people and companies that rely on people and processes to bring information together without adding value. These activities will disappear soon and you must consider using this innovative approach.
 During the recent holiday period, there was an interesting discussion about why companies are reluctant to change and implement better solution concepts. Initially launched by Alex Bruskin here on LinkedIn , the debate spilled over into the topic of TECHNICAL DEBT , well addressed here by Lionel Grealou.
During the recent holiday period, there was an interesting discussion about why companies are reluctant to change and implement better solution concepts. Initially launched by Alex Bruskin here on LinkedIn , the debate spilled over into the topic of TECHNICAL DEBT , well addressed here by Lionel Grealou.
![]() Both articles and the related discussion in the comments are recommended to follow and learn.
Both articles and the related discussion in the comments are recommended to follow and learn.
AI and Sustainability
![]() Similar to the introduction of Bitcoin using blockchain technology, some people are warning about the vast energy consumption required for training and interaction with Large Language Models (LLM), as Sasha Luccioni explains in her interesting TED talk when addressing sustainability.
Similar to the introduction of Bitcoin using blockchain technology, some people are warning about the vast energy consumption required for training and interaction with Large Language Models (LLM), as Sasha Luccioni explains in her interesting TED talk when addressing sustainability.
She proposes that tech companies should be more transparent on this topic, the size and the type of the LLM matters, as the indicative picture below illustrates.

Carbon Emissions of LLMs compared
In addition, I found an interesting article discussing the pros and cons of AI related to Sustainability. The image below from the article Risks and Benefits of Large Language Models for the Environment illustrates nicely that we must start discussing and balancing these topics.
![]() To conclude, in discussing AI related to sustainability, I see the significant advantage of using generative AI for ESG reporting.
To conclude, in discussing AI related to sustainability, I see the significant advantage of using generative AI for ESG reporting.
ESG reporting is currently a very fragmented activity for organizations, based on (marketing) people’s goodwill and currently these reports are not always be evidence-based.
Data
 The transformation from a coordinated, document-driven enterprise towards a hybrid coordinated/connected enterprise using a data-driven approach became increasingly visible in 2023. I expect this transformation to grow faster in 2024 – the momentum is here.
The transformation from a coordinated, document-driven enterprise towards a hybrid coordinated/connected enterprise using a data-driven approach became increasingly visible in 2023. I expect this transformation to grow faster in 2024 – the momentum is here.
 We saw last year that the discussions related to Federated PLM nicely converged at the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference in Paris. I shared most of the topics in this post: The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2023. In addition, there is now the Heliple Federated PLM LinkedIn group with regular discussions planned.
We saw last year that the discussions related to Federated PLM nicely converged at the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference in Paris. I shared most of the topics in this post: The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2023. In addition, there is now the Heliple Federated PLM LinkedIn group with regular discussions planned.
In addition, if you read here Jan Bosch’s reflection on 2023, he mentions (quote):
… 2023 was the year where many of the companies in the center became serious about the use of data. Whether it is historical analysis, high-frequency data collection during R&D, A/B testing or data pipelines, I notice a remarkable shift from a focus on software to a focus on data. The notion of data as a product, for now predominantly for internal use, is increasingly strong in the companies we work with
 I am a big fan of Jan’s posting; coming from the software world, he describes the same issues that we have in the PLM world, except he does not carry the hardware legacy that much and, therefore, acts faster than us in the PLM world.
I am a big fan of Jan’s posting; coming from the software world, he describes the same issues that we have in the PLM world, except he does not carry the hardware legacy that much and, therefore, acts faster than us in the PLM world.
An interesting illustration of the slow pace to a data-driven environment is the revival of the PLM and ERP integration discussion. Prof. Jörg Fischer and Martin Eigner contributed to the broader debate of a modern enterprise infrastructure, not based on systems (PLM, ERP, MES, ….) but more on the flow of data through the lifecycle and an organization.
It is a great restart of the debate, showing we should care more about data semantics and the flow of information.
The articles: The Future of PLM & ERP: Bridging the Gap. An Epic Battle of Opinions! and Is part master in PLM and ERP equal or not) combined with the comments to these posts, are a must read to follow this change towards a more connected flow of information.
While writing this post, Andreas Lindenthal expanded the discussion with his post: PLM and Configuration Management Best Practices: Part Traceability and Revisions. Again thanks to data-driven approaches, there is an extending support for the entire product lifecycle. Product Lifecycle Management, Configuration Management and AIM (Asset Information Management) have come together.
![]() PLM and CM are more and more overlapping as I discussed some time ago with Martijn Dullaart, Maxime Gravel and Lisa Fenwick in the The future of Configuration Management. This topic will be “hot”in 2024.
PLM and CM are more and more overlapping as I discussed some time ago with Martijn Dullaart, Maxime Gravel and Lisa Fenwick in the The future of Configuration Management. This topic will be “hot”in 2024.
People
 From the people’s perspective towards AI, DATA and SUSTAINABILITY, there is a noticeable divide between generations. Of course, for the sake of the article, I am generalizing, assuming most people do not like to change their habits or want to reprogram themselves.
From the people’s perspective towards AI, DATA and SUSTAINABILITY, there is a noticeable divide between generations. Of course, for the sake of the article, I am generalizing, assuming most people do not like to change their habits or want to reprogram themselves.
Unfortunate, we have to adapt our skills as our environment is changing. Most of my generation was brought up with the single source of truth idea, documented and supported by science papers.
In my terminology, information processing takes place in our head by combining all the information we learned or collected through documents/books/newspapers – the coordinated approach.
 For people living in this mindset, AI can become a significant threat, as their brain is no longer needed to make a judgment, and they are not used to differentiate between facts and fake news as they were never trained to do so
For people living in this mindset, AI can become a significant threat, as their brain is no longer needed to make a judgment, and they are not used to differentiate between facts and fake news as they were never trained to do so
The same is valid for practices like the model-based approach, working data-centric, or considering sustainability. It is not in the DNA of the older generations and, therefore, hard to change.
The older generation is mostly part of an organization’s higher management, so we are returning to the technical debt discussion.

Later generations that grew up as digital natives are used to almost real-time interaction, and when applied consistently in a digital enterprise, people will benefit from the information available to them in a rich context – in my terminology – the connected approach.
 AI is a blessing for people living in this mindset as they do not need to use old-fashioned methods to acquire information.
AI is a blessing for people living in this mindset as they do not need to use old-fashioned methods to acquire information.
“Let ChatGPT write my essay.”
However, their challenge could be what I would call “processing time”. Because data is available, it does not necessarily mean it is the correct information. For that reason it remains important to spend time digesting the impact of information you are reading – don’t click “Like”based on the tittle, read the full article and then decide.
Experience is what you get, when you don’t get what you expect.
meaning you only become experienced if you learn from failures.
Sustainability
 Unfortunately, sustainability is not only the last topic in alphabetic order, as when you look at the image below, you see that discussions related to sustainability are in a slight decline at C-level at the moment.
Unfortunately, sustainability is not only the last topic in alphabetic order, as when you look at the image below, you see that discussions related to sustainability are in a slight decline at C-level at the moment.
I share this observation in my engagements when discussing sustainability with the companies I interact with.
 The PLM software and services providers are all on a trajectory of providing tools and an infrastructure to support a transition to a more circular economy and better traceability of materials and carbon emissions.
The PLM software and services providers are all on a trajectory of providing tools and an infrastructure to support a transition to a more circular economy and better traceability of materials and carbon emissions.
In the PLM Global Green Alliance, we talked with Aras, Autodesk, Dassault Systems, PTC, SAP, Sustaira, TTPSC(Green PLM) and more to come in 2024. The solution offerings in the PLM domain are available to start, now the people and processes.
For sure, AI tools will help companies to get a better understanding of their sustainability efforts. As mentioned before AI could help companies in understanding their environmental impact and build more accurate ESG reports.
Next, being DATA-driven will be crucial. As discussed during the latest PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference: The Need for a Governance Digital Thread.
And regarding PEOPLE, the good news is that younger generations want to take care of their future. They are in a position to choose the company to work for or influence companies by their consumer behavior. Unfortunately, climate disasters will remind us continuously in the upcoming decades that we are in a critical phase.
With the PLM Global Green Alliance, we strive to bring people together with a PLM mindset, sharing news and information on how to move forward to a sustainable future.
![]() Mark Reisig (CIMdata – moderator for Sustainability & Energy) and Patrice Quencez (CIMPA – moderator for the Circular Economy) joined the PGGA last year and you will experience their inputs this year.
Mark Reisig (CIMdata – moderator for Sustainability & Energy) and Patrice Quencez (CIMPA – moderator for the Circular Economy) joined the PGGA last year and you will experience their inputs this year.
Conclusion
As you can see from this long post, there is so much to learn. The topics described are all actual, and each topic requires education, experience (success & failures) combined with understanding of the technology concepts. Make sure you consider all of them, as focusing on a single topic will not make move faster forward – they are all related. Please share your experiences this year—Happy New Year of Learning.
 Two weeks ago, this post from Ilan Madjar drew my attention. He pointed to a demo movie, explaining how to support Smart Part Numbering on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform. You can watch the recording here.
Two weeks ago, this post from Ilan Madjar drew my attention. He pointed to a demo movie, explaining how to support Smart Part Numbering on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform. You can watch the recording here.
I was surprised that Smart Part Numbering is still used, and if you read through the comments on the post, you see the various arguments that exist.
- “Many mid-market customers are still using it”
me: I think it is not only the mid-market – however, the argument is no reason to keep it alive. - “The problem remains in the customer’s desire (or need or capability) for change.”
me: This is part of the lowest resistance. - “User resistance to change. Training and management sponsorship has proven to be not enough.”
me: probably because discussions are feature-oriented, not starting from the business benefits. - “Cost and effort- rolling this change through downstream systems. The cost and effort of changing PN in PLM,ERP,MES, etc., are high. Trying to phase it out across systems is a recipe for a disaster.”
me: The hidden costs of maintaining Smart Numbers inside an organization are high and invisible, reducing the company’s competitiveness. - “Existing users often complain that it takes seconds to minutes more for unintelligent PN vs. using intelligent PN.”
me: If we talk about a disconnected user without access to information, it could be true if the number of Smart Numbers to comprehend is low.
There were many other arguments for why you should not change. It reminded me of the image below:

Smart Numbers related to the Coordinated approach
Smart Part Numbers are a characteristic of best practices from the past. Where people were working in different systems, the information moving from one system to another was done manually.

For example, it is re-entering the Bill of Materials from the PDM system into the ERP system or attaching drawings to materials/parts in the ERP system. The filename often reflects the material or part number in the latter case.
The problems with the coordinated, smart numbering approach are:
 New people in the organization need to learn the meaning of the numbering scheme. This learning process reduces the flexibility of an organization and increases the risk of making errors.
New people in the organization need to learn the meaning of the numbering scheme. This learning process reduces the flexibility of an organization and increases the risk of making errors.- Typos go unnoticed when transferring numbers from one system to another and only get noticed late when the cost of fixing the error might be 10 -100 fold.
- The argument that people will understand the meaning of a part is partly valid. A person can have a good guess of the part based on the smart part number; however, the details can be different unless you work every day with the same and small range of parts.
- Smart Numbers created a legacy. After Mergers and Acquisitions, there will be multiple part number schemes. Do you want to renumber old parts, meaning non-value-added, risky activities? Do you want to continue with various numbering schemes, meaning people need to learn more than one numbering schema – a higher entry barrier and risk of errors?

There were and still are many advanced smart numbering systems.
 In one of my first PDM implementations in the Netherlands, I learned about the 12NC code system from Philips – introduced at Philips in 1963 and used to identify complete products, documentation, and bare components, up to the finest detail. At this moment, many companies in the Philips family (suppliers or offspring) still use this numbering system, illustrating that it is not only the small & medium enterprises that are reluctant to change their numbering system.
In one of my first PDM implementations in the Netherlands, I learned about the 12NC code system from Philips – introduced at Philips in 1963 and used to identify complete products, documentation, and bare components, up to the finest detail. At this moment, many companies in the Philips family (suppliers or offspring) still use this numbering system, illustrating that it is not only the small & medium enterprises that are reluctant to change their numbering system.
The costs of working with Smart Part Numbers are often unnoticed as they are considered a given.
From Coordinated to Connected
Digital transformation in the PLM domain means moving from coordinated practices toward practices that benefit from connected technology. In many of my blog posts, you can read why organizations need to learn to work in a connected manner. It is both for their business sustainability and also for being able to deal with regulations related to sustainability in the short term.
GHG reporting, ESG reporting, material compliance, and the DPP are all examples of the outside world pushing companies to work connected. Besides the regulations, if you are in a competitive business, you must be more efficient, innovative and faster than your competitors.

In a connected environment, relations between artifacts (datasets) are maintained in an IT infrastructure without requiring manual data transformations and people to process the data. In a connected enterprise, this non-value-added work will be reduced.
How to move away from Smart Numbering systems?
 Several comments related to the Smart Numbering discussion mentioned that changing the numbering system is too costly and risky to implement and that no business case exists to support it. This statement only makes sense if you want your business to become obsolete slowly. Modern best practices based on digitization should be introduced as fast as possible, allowing companies to learn and adapt. There is no need for a big bang.
Several comments related to the Smart Numbering discussion mentioned that changing the numbering system is too costly and risky to implement and that no business case exists to support it. This statement only makes sense if you want your business to become obsolete slowly. Modern best practices based on digitization should be introduced as fast as possible, allowing companies to learn and adapt. There is no need for a big bang.
 Start with mapping, prioritizing, and mapping value streams in your company. Where do we see the most significant business benefits related to cost of handling, speed, and quality?
Start with mapping, prioritizing, and mapping value streams in your company. Where do we see the most significant business benefits related to cost of handling, speed, and quality?
 Note: It is not necessary to start with engineering as they might be creators of data – start, for example, with the xBOM flow, where the xBOM can be a concept BOM, the engineering BOM, the Manufacturing BOM, and more. Building this connected data flow is an investment for every department; do not start from the systems.
Note: It is not necessary to start with engineering as they might be creators of data – start, for example, with the xBOM flow, where the xBOM can be a concept BOM, the engineering BOM, the Manufacturing BOM, and more. Building this connected data flow is an investment for every department; do not start from the systems.
- Next point: Do not rename or rework legacy data. These activities do not add value; they can only create problems. Instead, build new process definitions that do not depend on the smartness of the number.
 Make sure these objects have, besides the part number, the right properties, the right status, and the right connections. In other words, create a connected digital thread – first internally in your company and next with your ecosystem (OEMs, suppliers, vendors)
Make sure these objects have, besides the part number, the right properties, the right status, and the right connections. In other words, create a connected digital thread – first internally in your company and next with your ecosystem (OEMs, suppliers, vendors)
- Next point: Give newly created artifacts a guaranteed unique ID independent of others. Each artifact has its status, properties and context. In this step, it is time to break any 1 : 1 relation between a physical part and a CAD-part or drawing. If a document gets revised, it gets a new version, but the version change should not always lead to a part number change. You can find many discussions on why to decouple parts and documents and the flexibility it provides.
- Next point: New generated IDs are not necessarily generated in a single system. The idea of a single source of truth is outdated. Build your infrastructure upon existing standards if possible. For example, the UID of the Digital Product Passport will be based on the ISO/IEC 15459 standard, similar to the UID for retail products managed by the GS1 standard. Or, probably closer to home, look into your computer’s registry, and you will discover a lot of software components with a unique ID that specific programs or applications can use in a shared manner.
When will it happen?
In January 2016, I wrote about “the impact of non-intelligent part numbers” and surprisingly almost 8 years later and we are still in the same situation.
 I just read Oleg Shilovitsky’s post The Data Dilemma: Why Engineers and Manufacturing Companies Struggle to Find Time for Data Management where he mentions Legacy Systems and Processes, Overwhelming Workloads, Lack of (Data) Expertise, Short-Term Focus and Resource Constraints as inhibitors.
I just read Oleg Shilovitsky’s post The Data Dilemma: Why Engineers and Manufacturing Companies Struggle to Find Time for Data Management where he mentions Legacy Systems and Processes, Overwhelming Workloads, Lack of (Data) Expertise, Short-Term Focus and Resource Constraints as inhibitors.
You probably all know the above cartoon. How can companies get out of this armor or habits? Will they be forced by the competition or by regulations. What do you think ?
Conclusion
Despite proven business benefits and insights, it remains challenging for companies to move toward modern, data-driven practices where Smart Number generators are no longer needed. When talking one-on-one to individuals, they are convinced a change is necessary, and they are pointing to the “others”.
I wish you all a prosperous 2024 and the power to involve the “others”.
 This is the third and last post related to the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, held from 15-16 November in Paris. The first post reported more about “traditional” PLM engagements, whereas the second post focused on more data-driven and federated PLM. If you missed them, here they are:
This is the third and last post related to the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, held from 15-16 November in Paris. The first post reported more about “traditional” PLM engagements, whereas the second post focused on more data-driven and federated PLM. If you missed them, here they are:
Now, I want to conclude on what I would call, in my terminology, the connected digital thread. This topic was already addressed when I reported on the federated PLM story from NIO (Yousef Hooshmand) and SAAB Aeronautics (Erik Herzog).
The Need for a Governance Digital Thread
This time, my presentation was a memory refresher related to digital transformation in the PLM domain – moving from coordinated ways of working towards connected ways of working.
A typology that is also valid for the digital thread definition.
- A Coordinated Digital Thread is a digital thread that connects various artifacts in an enterprise. These relations are created and managed to support traceability and an impact analysis. The coordinated digital thread requires human interpretation to process the information. The image below from Aras is a perfect example of a coordinated digital thread.
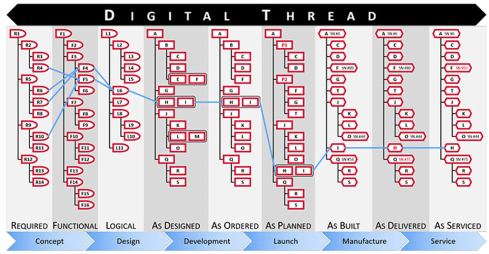
- The Connected Digital Thread is the digital thread where the artifacts are datasets stored in a federated infrastructure of databases. A connected digital thread provides real-time access to data through applications or dashboards for users. The real-time access makes the connected digital thread a solution for real-time, multidisciplinary collaboration activities.
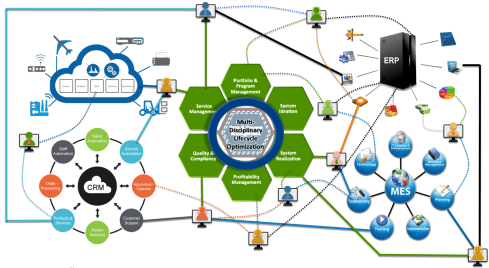
The image above illustrates the connected digital thread as an infrastructure on top of five potential business platforms, i.e., the IoT platform, the CRM platform, the ERP platform, the MES platform and ultimately, the Product Innovation Platform.
Note: These platforms are usually a collection of systems that logically work together efficiently.
The importance of the Connected Digital Thread
When looking at the benefits of the Connected Digital Thread, the most essential feature is that it allows people in an organization to have all relevant data and its context available for making changes, analysis and design choices.
Due to the rich context, people can work proactively and reduce the number of iterations and fixes later.
The above image from Accenture (2014) describing the business benefits can be divided into two categories:
- The top, Connected and Scalable describing capabilities
- The bottom, Intelligent and Rapid, describes the business impact
The connected digital thread for governance
 In my session, I gave examples of why companies must invest in the connected digital thread. If you are interested in the slides from the session you can download them here on SlideShare: The Need for a Governance Digital Thread
In my session, I gave examples of why companies must invest in the connected digital thread. If you are interested in the slides from the session you can download them here on SlideShare: The Need for a Governance Digital Thread
 First of all, as more and more companies need to provide ESG reporting related to the business, either by law or demanded by their customers, this is an area where data needs to be collected from various sources in the organization.
First of all, as more and more companies need to provide ESG reporting related to the business, either by law or demanded by their customers, this is an area where data needs to be collected from various sources in the organization.
The PLM system will be one of the sources; other sources can be fragmented in an organization. Bringing them together manually in one report is a significant human effort, time-consuming and not supporting the business.
 By creating a connected digital thread between these sources, reporting becomes a push on the button, and the continuous availability of information will help companies assess and improve their products to reduce environmental and social risks.
By creating a connected digital thread between these sources, reporting becomes a push on the button, and the continuous availability of information will help companies assess and improve their products to reduce environmental and social risks.
According to a recent KPMG report, only a quarter of companies are ready for ESG Reporting Requirements.
 Sustaira, a company we reported in the PGGA, provides such an infrastructure based on Mendix, and during the conference, I shared a customer case with the audience. You can find more about Sustaira in our interview with them: PLM and Sustainability: talking with Sustaira.
Sustaira, a company we reported in the PGGA, provides such an infrastructure based on Mendix, and during the conference, I shared a customer case with the audience. You can find more about Sustaira in our interview with them: PLM and Sustainability: talking with Sustaira.
The Connected Digital Thread and the Digital Product Passport
 One of the areas where the connected digital thread will become important is the implementation of the Digital Product Passport (DPP), which is an obligation coming from the European Green Deal, affecting all companies that want to sell their product to the European market in 2026 and beyond.
One of the areas where the connected digital thread will become important is the implementation of the Digital Product Passport (DPP), which is an obligation coming from the European Green Deal, affecting all companies that want to sell their product to the European market in 2026 and beyond.
The DPP is based on the GS1 infrastructure, originating from the retail industry. Each product will have a unique ID (UID based on ISO/IEC 15459:2015), and this UID will provide digital access to product information, containing information about the product’s used materials, its environmental impact, and recycle/reuse–ability.
It will serve both for regulatory compliance and as an information source for consumers to make informed decisions about the products they buy. The DPP aims to stimulate and enforce a more circular economy.
![]() Interesting to note is that the infrastructure needed for the DPP is based on the GS1 infrastructure, where GS1 is a not-for-profit organization providing data services.
Interesting to note is that the infrastructure needed for the DPP is based on the GS1 infrastructure, where GS1 is a not-for-profit organization providing data services.
The Connected Digital Thread and Catena-X
 So far, I have discussed the connected digital thread as an internal infrastructure in a company. Also, the examples of the connected digital thread at NIO and Saab Aeronautics focused on internal interaction.
So far, I have discussed the connected digital thread as an internal infrastructure in a company. Also, the examples of the connected digital thread at NIO and Saab Aeronautics focused on internal interaction.
A new exciting trend is the potential rise of not-for-profit infrastructure for a particular industry. Where the GS1-based infrastructure is designed to provide visibility on sustainable targets and decisions, Catena-X is focusing on the automotive industry.
Catena-X is the establishment of a data-driven value chain for the German automotive industry and is now in the process of expanding to become a global network.
It is a significant building block in what I would call the connected or even adaptive enterprise, using a data-driven infrastructure to let information flow through the whole value chain.
It is one of the best examples of a Connected Digital Thread covering an end-to-end value chain.
 Although sustainability is mentioned in their vision statement, the main business drivers are increased efficiency, improved competitiveness, and cost reduction by removing the overhead and latency of such a network.
Although sustainability is mentioned in their vision statement, the main business drivers are increased efficiency, improved competitiveness, and cost reduction by removing the overhead and latency of such a network.
So Sustainability and Digitization go hand in hand.
Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense
 Following the inter-company digital thread story, Mattias Johansson‘s presentation was an excellent continuation of this concept. The full title of Mattias’ session was: Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense, Why It Goes Beyond Manufacturing, and Why It Should Be Standards-based.
Following the inter-company digital thread story, Mattias Johansson‘s presentation was an excellent continuation of this concept. The full title of Mattias’ session was: Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense, Why It Goes Beyond Manufacturing, and Why It Should Be Standards-based.
Eurostep, recently acquired by BAE Systems, is known for its collaboration hub or information backbone, ShareAspace. The interesting trend here is switching from a traditional PLM infrastructure to an asset-centric one.
This approach makes a lot of sense for complex assets with a long lifecycle, as the development phase is usually done with a consortium of companies. Still, the owner/operator wants to maintain a digital twin of the asset – for maintenance and upgrades.
A standards-based backbone makes much sense in such an environment due to the various data formats. This setup also means we are looking at a Coordinated Digital Thread at this stage, not a Connected Digital Thread.
Mattias concluded with the question of who owns and who decides on the coordinated digital thread – a discussion also valid in the construction industry when discussing Building Information Management (BIM) and a Common Data Environment(CDE).
I believe software vendors can provide the Coordinated Digital Thread option when they can demonstrate and provide a positive business case for their solution. Still, it will be seen as an overhead to connect the dots.
For a Connected Digital Thread, I think it might be provided as an infrastructure like the World Wide Web (W3C) organization. Here, the business case is much easier to demonstrate as it is really a digital highway.
Such an infrastructure could be provided by not-for-profit organizations like GS1 (Digital Product Passport/Retail), Catena-X (Automotive) and others (Gaia-X).
![]() For sure, these networks will leverage blockchain concepts (affordable now) and data sovereignty concepts now developed for web3, and of course, an aspect of AI will reduce the complexity of maintaining such an environment.
For sure, these networks will leverage blockchain concepts (affordable now) and data sovereignty concepts now developed for web3, and of course, an aspect of AI will reduce the complexity of maintaining such an environment.
AI
And then there was AI. During the conference, people spoke more about AI than Sustainability topics, illustrating that our audience is more interested in understanding the next hype instead of feeling the short-term need to address climate change and planet sustainability.
 David Henstock, Chief Data Scientist at BAE Systems Digital Intelligence, talked about turning AI into an Operational Reality, sharing some lessons & challenges from Defence. David mentioned that he was not an expert in PLM but shared various viewpoints on the usage (benefits & risks) of implementing AI in an organization.
David Henstock, Chief Data Scientist at BAE Systems Digital Intelligence, talked about turning AI into an Operational Reality, sharing some lessons & challenges from Defence. David mentioned that he was not an expert in PLM but shared various viewpoints on the usage (benefits & risks) of implementing AI in an organization.
 Erdal Tekin, Senior Chief Leader for Digital Transformation at Turkish Aerospace, talked about AI-powered collaboration. I am a bit skeptical on this topic as AI always comes with a flavor.
Erdal Tekin, Senior Chief Leader for Digital Transformation at Turkish Aerospace, talked about AI-powered collaboration. I am a bit skeptical on this topic as AI always comes with a flavor.
And we closed the conference with a roundtable discussion: AI, PLM and the Digital Thread: Why should we care about AI?
From the roundtable, I concluded that we are all convinced AI will have a significant impact in the upcoming years and are all in the early phases of the AI hype.
Will AI introduction go faster than digital transformation?
Conclusion
The conference gave me confidence that digital transformation in the PLM domain has reached the next level. Many sessions were related to collaboration concepts outside the traditional engineering domain – coordinated and connected digital threads.
The connected digital thread is the future, and as we saw it, it heralds the downfall of monolithic PLM. The change is needed for business efficiency AND compliance with more and more environmental regulations.
I am looking forward to seeing the pace of progress here next year.
 Last week, I shared my first impressions from my favorite conference, in the post: The weekend after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2023, where most impressions could be classified as traditional PLM and model-based.
Last week, I shared my first impressions from my favorite conference, in the post: The weekend after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2023, where most impressions could be classified as traditional PLM and model-based.
There is nothing wrong with conventional PLM, as there is still much to do within this scope. A model-based approach for MBSE (Model-Based Systems Engineering) and MBD (Model-Based Definition) and efficient supplier collaboration are not topics you solve by implementing a new system.
 Ultimately, to have a business-sustainable PLM infrastructure, you need to structure your company internally and connect to the outside world with a focus on standards to avoid a vendor lock-in or a dead end.
Ultimately, to have a business-sustainable PLM infrastructure, you need to structure your company internally and connect to the outside world with a focus on standards to avoid a vendor lock-in or a dead end.
In short, this is what I described so far in The weekend after ….part 1.
Now, let’s look at the relatively new topics for this audience.
Enabling the Marketing, Engineering & Manufacturing Digital Thread
 Cyril Bouillard, the PLM & CAD Tools Referent at the Mersen Electrical Protection (EP) business unit, shared his experience implementing an end-to-end digital backbone from marketing through engineering and manufacturing.
Cyril Bouillard, the PLM & CAD Tools Referent at the Mersen Electrical Protection (EP) business unit, shared his experience implementing an end-to-end digital backbone from marketing through engineering and manufacturing.
Cyril showed the benefits of a modern PLM infrastructure that is not CAD-centric and focused on engineering only. The advantages of this approach are a seamless integrated flow of PLM and PIM (Product Information Management).

I wrote about this topic in 2019: PLM and PIM – the complementary value in a digital enterprise. Combining the concepts of PLM and PIM in an integrated, connected environment could also provide a serious benefit when collaborating with external parties.
 Another benefit Cyril demonstrated was the integration of RoHS compliance to the BOM as an integrated environment. In my session, I also addressed integrated RoHS compliance as a stepping stone to efficiency in future compliance needs.
Another benefit Cyril demonstrated was the integration of RoHS compliance to the BOM as an integrated environment. In my session, I also addressed integrated RoHS compliance as a stepping stone to efficiency in future compliance needs.
Read more later or in this post: Material Compliance – as a stepping-stone towards Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Cyril concluded with some lessons learned.
Data quality is essential in such an environment, and there are significant time savings implementing the connected Digital Thread.
Meeting the Challenges of Sustainability in Critical Transport Infrastructures
 Etienne Pansart, head of digital engineering for construction at SYSTRA, explained how they address digital continuity with PLM throughout the built assets’ lifecycle.
Etienne Pansart, head of digital engineering for construction at SYSTRA, explained how they address digital continuity with PLM throughout the built assets’ lifecycle.
Etienne’s story was related to the complexity of managing a railway infrastructure, which is a linear and vertical distribution at multiple scales; it needs to be predictable and under constant monitoring; it is a typical system of systems network, and on top of that, maintenance and operational conditions need to be continued up to date.
Regarding railway assets – a railway needs renewal every two years, bridges are designed to last a hundred years, and train stations should support everyday use.
When complaining about disturbances, you might have a little more respect now (depending on your country). However, on top of these challenges, Etienne also talked about the additional difficulties expected due to climate change: floods, fire, earth movements, and droughts, all of which will influence the availability of the rail infrastructure.
In that context, Etienne talked about the MINERVE project – see image below:
As you can see from the main challenges, there is an effort of digitalization for both the assets and a need to provide digital continuity over the entire asset lifecycle. This is not typically done in an environment with many different partners and suppliers delivering a part of the information.
Etienne explained in more detail how they aim to establish digital twins and MBSE practices to build and maintain a data-driven, model-based environment.
Having digital twins allows much more granular monitoring and making accurate design decisions, mainly related to sustainability, without the need to study the physical world.
His presentation was again a proof point that through digitalization and digital twins, the traditional worlds of Product Lifecycle Management and Asset Information Management become part of the same infrastructure.
 And it may be clear that in such a collaboration environment, standards are crucial to connect the various stakeholder’s data sources – Etienne mentioned ISO 16739 (IFC), IFC Rail, and ISO 19650 (BIM) as obvious standards but also ISO 10303 (PLCS) to support the digital thread leveraged by OSLC.
And it may be clear that in such a collaboration environment, standards are crucial to connect the various stakeholder’s data sources – Etienne mentioned ISO 16739 (IFC), IFC Rail, and ISO 19650 (BIM) as obvious standards but also ISO 10303 (PLCS) to support the digital thread leveraged by OSLC.
I am curious to learn more about the progress of such a challenging project – having worked with the high-speed railway project in the Netherlands in 1995 – no standards at that time (BIM did not exist) – mainly a location reference structure with documents. Nothing digital.
The connected Digital Thread
The theme of the conference was The Digital Thread in a Heterogeneous, Extended Enterprise Reality, and in the next section, I will zoom in on some of the inspiring sessions for the future, where collaboration or information sharing is all based on a connected Digital Thread – a term I will explain in more depth in my next blog post.
Transforming the PLM Landscape:
The Gateway to Business Transformation
 Yousef Hooshmand‘s presentation was the highlight of this conference for me.
Yousef Hooshmand‘s presentation was the highlight of this conference for me.
Yousef is the PLM Architect and Lead for the Modernization of the PLM Landscape at NIO, and he has been active before in the IT-landscape transformation at Daimler, on which he published the paper: From a monolithic PLM landscape to a federated domain and data mesh.
 If you read my blog or follow Share PLM, you might seen the reference to Yousef’s work before, or recently, you can hear the full story at the Share PLM Podcast: Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights.
If you read my blog or follow Share PLM, you might seen the reference to Yousef’s work before, or recently, you can hear the full story at the Share PLM Podcast: Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights.
It was the first time I met Yousef in 3D after several virtual meetings, and his passion for the topic made it hard to fit in the assigned 30 minutes.
There is so much to share on this topic, and part of it we already did before the conference in a half-day workshop related to Federated PLM (more on this in the following review).
First, Yousef started with the five steps of the business transformation at NIO, where long-term executive commitment is a must.
His statement: “If you don’t report directly to the board, your project is not important”, caused some discomfort in the audience.
As the image shows, a business transformation should start with a systematic description and analysis of which business values and objectives should be targeted, where they fit in the business and IT landscape, what are the measures and how they can be tracked or assessed and ultimately, what we need as tools and technology.
In his paper From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh, Yousef described the targeted federated landscape in the image below.
And now some vendors might say, we have all these domains in our product portfolio (or we have slides for that) – so buy our software, and you are good.
And here Yousef added his essential message, illustrated by the image below.
Start by delivering the best user-centric solutions (in an MVP manner – days/weeks – not months/years). Next, be data-centric in all your choices and ultimately build an environment ready for change. As Yousef mentioned: “Make sure you own the data – people and tools can leave!”
And to conclude reporting about his passionate plea for Federated PLM:
“Stop talking about the Single Source of Truth, start Thinking of the Nearest Source of Truth based on the Single Source of Change”.
Heliple-2 PLM Federation:
A Call for Action & Contributions
 A great follow-up on Yousef’s session was Erik Herzog‘s presentation about the final findings of the Heliple 2 project, where SAAB Aeronautics, together with Volvo, Eurostep, KTH, IBM and Lynxwork, are investigating a new way of federated PLM, by using an OSLC-based, heterogeneous linked product lifecycle environment.
A great follow-up on Yousef’s session was Erik Herzog‘s presentation about the final findings of the Heliple 2 project, where SAAB Aeronautics, together with Volvo, Eurostep, KTH, IBM and Lynxwork, are investigating a new way of federated PLM, by using an OSLC-based, heterogeneous linked product lifecycle environment.
Heliple stands for HEterogeneous LInked Product Lifecycle Environment
The image below, which I shared several times before, illustrates the mindset of the project.
Last year, during the previous conference in Gothenburg, Erik introduced the concept of federated PLM – read more in my post: The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022, mentioning two open issues to be investigated: Operational feasibility (is it maintainable over time) and Realisation effectivity (is it affordable and maintainable at a reasonable cost)
As you can see from the slide below, the results were positive and encouraged SAAB to continue on this path.
One of the points to mention was that during this project, Lynxwork was used to speed up the development of the OSLC adapter, reducing costs, time and needed skills.
 After this successful effort, Erik and several others who joined us at the pre-conference workshop agreed that this initiative is valid to be tested, discussed and exposed outside Sweden.
After this successful effort, Erik and several others who joined us at the pre-conference workshop agreed that this initiative is valid to be tested, discussed and exposed outside Sweden.
Therefore, the Federated PLM Interest Group was launched to join people worldwide who want to contribute to this concept with their experiences and tools.
A first webinar from the group is already scheduled for December 12th at 4 PM CET – you can join and register here.
More to come
Given the length of this blog post, I want to stop here.
 Topics to share in the next post are related to my contribution at the conference The Need for a Governance Digital Thread, where I addressed the need for federated PLM capabilities with the upcoming regulations and practices related to sustainability, which require a connected Digital.
Topics to share in the next post are related to my contribution at the conference The Need for a Governance Digital Thread, where I addressed the need for federated PLM capabilities with the upcoming regulations and practices related to sustainability, which require a connected Digital.
 I want to combine this post with the findings that Mattias Johansson, CEO of Eurostep, shared in his session: Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense, goes beyond manufacturing, and should be standards-based.
I want to combine this post with the findings that Mattias Johansson, CEO of Eurostep, shared in his session: Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense, goes beyond manufacturing, and should be standards-based.
There are some interesting findings in these two presentations.
 And there was the introduction of AI at the conference, with some experts’ talks and thoughts. Perhaps at this stage, it is too high on Gartner’s hype cycle to go into details. It will surely be THE topic of discussion or interest you must have noticed.
And there was the introduction of AI at the conference, with some experts’ talks and thoughts. Perhaps at this stage, it is too high on Gartner’s hype cycle to go into details. It will surely be THE topic of discussion or interest you must have noticed.
The recent turmoil at OpenAI is an example of that. More to come for sure in the future.
Conclusion
The PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference was significant for me because I discovered that companies are working on concepts for a data-driven infrastructure for PLM and are (working on) implementing them. The end of monolithic PLM is visible, and companies need to learn to master data using ontologies, standards and connected digital threads.
 It might have been silent in the series of PLM and Sustainability … interviews where we as PLM Green Global Alliance core team members, talk with software vendors, implementers and consultants and their relation to PLM and sustainability. The interviews are still in a stage of exploring what is happening at this moment. More details per vendor or service provider next year.
It might have been silent in the series of PLM and Sustainability … interviews where we as PLM Green Global Alliance core team members, talk with software vendors, implementers and consultants and their relation to PLM and sustainability. The interviews are still in a stage of exploring what is happening at this moment. More details per vendor or service provider next year.
Our last interview was in April this year when we spoke with Mark Reisig, Green Energy Practice Director & Executive Consultant at CIMdata. You can find the interview here, and at that time, I mentioned the good news is that sustainability is no longer a software discussion.
As companies are planning or pushed by regulations to implement sustainable strategies, it becomes clear that education and guidance are needed beyond the tools.
This trend is also noticeable in our PLM Green Global Alliance community, which has grown significantly in the past half year. While writing this post, we have 862 members, not all as active as we hoped. Still, there is more good news related to dedicated contributors and more to come in the next PGGA update.
 This time, we want to share the interview with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services.
This time, we want to share the interview with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services.
I met them during the LiveWorx conference in Boston in May – you can read more about the conference in my post: The weekend after LiveWorx 2023. Here we decided to follow-up on GreenPLM/
GreenPLM
![]() The label “GreenPLM” is always challenging as it could be considered green-washing. However, in this case, GreenPLM is an additional software offering that can be implemented on top of a PLM system, enabling people to make scientifically informed decisions for a more sustainable, greener product.
The label “GreenPLM” is always challenging as it could be considered green-washing. However, in this case, GreenPLM is an additional software offering that can be implemented on top of a PLM system, enabling people to make scientifically informed decisions for a more sustainable, greener product.
For GreenPLM, Rafal’s and Erik’s experiences are based on implementing GreenPLM on top of the PTC Windchill suite. Listen for the next 34 minutes to an educative session and learn.
You can download the slides shown in the recording here.
What I learned
- It was more a general educative session related to the relation PLM and Sustainability, focusing on the importance of design decisions – the 80 % impact number.
- Erik considers sustainability not a disruption for designers; they already work within cost, quality and time parameters. Now, sustainability is the fourth dimension to consider.
- Erik’s opinion is also reflected in the pragmatic approach of GreenPLM as an additional extension of Windchill using PTC Navigate and OSLC standards.
- GreenPLM is more design-oriented than Mendix-based Sustaira, a sustainability platform we discussed in this series – you can find the recording here.
Want to learn more?
Here are some links related to the topics discussed in our meeting:
Conclusions
With GreenPLM, it is clear that the focus of design for sustainability is changing from a vision (led by software vendors and environmental regulations) towards implementations in the field. Pragmatic and an extension of the current PLM infrastructure. System integrators like Transition Technologies are the required bridge between vision and realization. We are looking for more examples from the field.
Two more weeks to go – don’t miss this opportunity when you are in Europe
Click on the image to see the full and interesting agenda/
 Last week, I have been participating in the biannual NEM network meeting, this time hosted by Vestas in Ringkøbing (Denmark).
Last week, I have been participating in the biannual NEM network meeting, this time hosted by Vestas in Ringkøbing (Denmark).
NEM (North European Modularization) is a network for industrial companies with a shared passion and drive for modular products and solutions.
NEM’s primary goal is to advance modular strategies by fostering collaboration, motivation, and mutual support among its diverse members.
 During this two-day conference, there were approximately 80 attendees from around 15 companies, all with a serious interest and experience in modularity. The conference reminded me of the CIMdata Roadmap/PDT conferences, where most of the time a core group of experts meet to share their experiences and struggles.
During this two-day conference, there were approximately 80 attendees from around 15 companies, all with a serious interest and experience in modularity. The conference reminded me of the CIMdata Roadmap/PDT conferences, where most of the time a core group of experts meet to share their experiences and struggles.
The discussions are so much different compared to a generic PLM or software vendor conference where you only hear (marketing) success stories.
Modularity
 When talking about modularity, many people will have Lego in mind, as with the Lego bricks, you can build all kinds of products without the need for special building blocks. In general, this is the concept of modularity.
When talking about modularity, many people will have Lego in mind, as with the Lego bricks, you can build all kinds of products without the need for special building blocks. In general, this is the concept of modularity.
With modularity, a company tries to reduce the amount of custom-made designs by dividing a product into modules with strict interfaces. Modularity aims to offer a wider variety of products to the customer – but configure these from a narrower assortment of modules to streamline manufacturing, sourcing and service. Modularity allows managing changes and new functionality within the modules without managing a new product.
 From ETO (Engineering To Order) to BTO (Build To Order) or even CTO (Configure to Order) is a statement often heard when companies are investing in a new PLM system. The idea is that with the CTO model, you reduce the engineering costs and risks for new orders.
From ETO (Engineering To Order) to BTO (Build To Order) or even CTO (Configure to Order) is a statement often heard when companies are investing in a new PLM system. The idea is that with the CTO model, you reduce the engineering costs and risks for new orders.
With modularity, you can address more variants and options without investing in additional engineering efforts.
How the PLM system supports modularity is an often-heard question. How do you manage in the best way options and variants? The main issue here is that modularity is often considered an R&D effort – R&D must build the modular architecture. An R&D-only focus is a common mistake in the field similar to PLM. Both
 PLM and Modularity suffer from the framing that it is about R&D and their tools, whereas in reality, PLM and Modularity are strategies concerning all departments in an enterprise, from sales & marketing, engineering, and manufacturing to customer service.
PLM and Modularity suffer from the framing that it is about R&D and their tools, whereas in reality, PLM and Modularity are strategies concerning all departments in an enterprise, from sales & marketing, engineering, and manufacturing to customer service.
PLM and Modularity
 In 2021, I discussed the topic of Modularity with Björn Eriksson & Daniel Strandhammar, who had written during the COVID-19 pandemic their easy-to-read book: The Modular Way. In a blog post, PLM and Modularity, I discussed with Daniel the touchpoints with PLM. A little later, we had a Zoom discussion with Bjorn and Daniel, together with some of the readers of the book. You can find the info still here: The Modular Way – a follow-up discussion.
In 2021, I discussed the topic of Modularity with Björn Eriksson & Daniel Strandhammar, who had written during the COVID-19 pandemic their easy-to-read book: The Modular Way. In a blog post, PLM and Modularity, I discussed with Daniel the touchpoints with PLM. A little later, we had a Zoom discussion with Bjorn and Daniel, together with some of the readers of the book. You can find the info still here: The Modular Way – a follow-up discussion.
What was clear to me at that time is that, in particular, Sweden is a leading country when it comes to Modularity. Companies like Scania, Electrolux are known for their product modularity.
For me it was great to learn the Vestas modularization journey. For sure the Scandinavian region sets the tone. And in addition, there are LEGO and IKEA, also famous Scandinavian companies, but with other modularity concepts.
 The exciting part of the conference was that all the significant modularity players were present. Hosted by Vestas and with a keynote speech from Leif Östling, a former CEO of Scania, all the ingredients were there for an excellent conference.
The exciting part of the conference was that all the significant modularity players were present. Hosted by Vestas and with a keynote speech from Leif Östling, a former CEO of Scania, all the ingredients were there for an excellent conference.
The NEM network
The conference started with Christian Eskildsen, CEO of the NEM organization, who has a long history of leading modularity at Electrolux. The NEM is not only a facilitator for modularity. They also conduct training, certification sessions, and coaching on various levels, as shown below.
Christian mentioned that there are around 400 followers on the NEM LinkedIn group. I can recommend this LinkedIn group as the group shares their activities here.
At this moment, you can find here the results of Workstream 7 – The Cost of Complexity.
Peter Greiner, NEM member, presented the details of this result during the conference on day 2. The conclusion of the workstream team was a preliminary estimate suggesting a minimum cost reduction of 2-5% in terms of the Cost Of Goods Sold (COGS) on top of traditional modularization savings. These estimates are based on real-world cases.
Understanding that the benefits are related to the COGS with a high contribution of the actual material costs, a 2 – 5 % range is significant. There is the intention to dig deeper into this topic.
 Besides these workstreams, there are also other workstreams running or finished. The ones that interest me in the sustainability context are Workstream 1 Modular & Circular and Workstream 10 Modular PLM (Digital Thread).
Besides these workstreams, there are also other workstreams running or finished. The ones that interest me in the sustainability context are Workstream 1 Modular & Circular and Workstream 10 Modular PLM (Digital Thread).
The NEM network has an active group of members, making it an exciting network to follow and contribute as modularity is part of a sustainable future. More on this statement later.
Vestas
![]() The main part of day one was organized by our host, Vestas. Jens Demtröder, Chief Engineer at Vestas for the Modular Turbine Architecture and NEM board member, first introduced the business scope, complexity, and later the future challenges that Vestas is dealing with.
The main part of day one was organized by our host, Vestas. Jens Demtröder, Chief Engineer at Vestas for the Modular Turbine Architecture and NEM board member, first introduced the business scope, complexity, and later the future challenges that Vestas is dealing with.
First, wind energy is the best cost-competitive source for a green energy system, as the image shows when taking the full environmental impact into the equation. As the image below shows
From the outside, wind turbines all look the same; perhaps a difference between on-shore and off-shore? No way! There is a substantial evolution in the size and control of the wind turbine, and even more importantly, as the image shows, each country has its own regulations to certify a wind turbine. Vestas has to comply with 80+ different local regulations, and for that reason, modularity is vital to manage all the different demands efficiently.
A big challenge for the future will be the transport and installation of wind turbines.
 The components become so big that they need to be assembled on-site, requiring new constraints on the structure to be solved.
The components become so big that they need to be assembled on-site, requiring new constraints on the structure to be solved.
As the image to the left, rotor sizes up to 250 m are expected and what about the transport of the nacelle itself?
Click on this link to get an impression.
The audience also participated in a (windy) walk through the manufacturing site to get an impression of the processes & components – an impression below.
Processes, organization and governance
Karl Axel Petursson, Senior Specialist in Architecture and Roadmap, gave insights into the processes, organization and governance needed for the modularity approach at Vestas.
The modularization efforts are always a balance between strategy and execution, where often execution wins. The focus on execution is a claim that I recognize when discussing modularity with the companies I am coaching.
Vestas also created an organization related to the functions it provides, being a follower of Conway’s law, as the image below shows:
With modularity, you will also realize that the modular architecture must rely on stable interfaces between the modules based on clear market needs.
Besides an organizational structure, often more and more a matrix organization, there are also additional roles to set up and maintain a modular approach. As the image below indicates, to integrate all the functions, there are various roles in Vestas, some specialized and some more holistic:
These roles are crucial when implementing and maintaining modularity in your organization. It is not just the job of a clever R&D team.
Just a clever R&D is a misconception I have often discovered in the field. Buying one or more tools that support modularity and then let brilliant engineers do the work. And this is a challenge. Engineers often do not like to be constrained by modular constraints when designing a new capability or feature.
For this reason Vestas has established an Organization Change Management initiative called Modular Minds to make engineers flourish in the organization.
Modular Minds
Madhuri Srinivasan Systems Engineering specialist and Hanh Le Business Transformation leader both at Vestas, presented their approach to the 2020 must-win battle for Modularisation, aiming with various means, like blogs, podcasts, etc., to educate the organization and create Modular Minds for all Vestas employees.
 The team is applying the ADKAR model from Prosci to support this change. As you can see from the (clickable) image to the left, ADKAR is the abbreviation of Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement.
The team is applying the ADKAR model from Prosci to support this change. As you can see from the (clickable) image to the left, ADKAR is the abbreviation of Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability and Reinforcement.
The ADKAR model focuses on driving change at the individual level and achieving organizational results. It is great to see such an approach applied to Modularity, and it would also be valuable in the domain of PLM, as I discussed with Share PLM in my network.
Scania
 The 1 ½ hour keynote speech from Leif Östling supported by Karl-Johan Linghede was more of an interactive discussion with the audience than a speech. Leif took us to the origins of Scania, their collaboration in the beginning with learning the Toyota Way. – customer first, respect for people and focus on quality. And initial research and development together with Modular Management resulting in the MFD-methodology.
The 1 ½ hour keynote speech from Leif Östling supported by Karl-Johan Linghede was more of an interactive discussion with the audience than a speech. Leif took us to the origins of Scania, their collaboration in the beginning with learning the Toyota Way. – customer first, respect for people and focus on quality. And initial research and development together with Modular Management resulting in the MFD-methodology.
It led to the understanding that:
- The #1 cost driver is the amount of parts you need to manage,
- The #2 crucial point is to have standardized interfaces and keep the flexibility inside the module
With Ericsson, Scania yearly on partnered to work on the connected vehicle. If you are my age, you will remember connectivity at that time was not easy. The connected vehicle was the first step of what we now would call a digital twin
An interesting topic discussed was that Scania has approximately 25 interfaces at Change Level 1. This is a C-level/Executive discussion to approve potential interface changes. This level shows the commitment of the organization to keep modularity operational.
 Another benefit mentioned was that the move to electrification of the vehicle was not such a significant change as in many automotive companies. Thanks to the modular structure and the well-defined interfaces, creating an electric truck was not a complete change of the truck design.
Another benefit mentioned was that the move to electrification of the vehicle was not such a significant change as in many automotive companies. Thanks to the modular structure and the well-defined interfaces, creating an electric truck was not a complete change of the truck design.
The session with Leif and Karl-Johan could have easily taken longer, giving the interesting question-and-answer dialogue with the curious audience. It was a great learning moment.
Digitization, Sustainability & Modularization
 As a PLM person from the PLM Green Global Alliance, I was allowed to give a speech about the winning combination of Digitization, Sustainability and Modularization. You might have seen my PLM and Sustainability blog post recently; now, a zoom-in on the circular economy and modularity is included.
As a PLM person from the PLM Green Global Alliance, I was allowed to give a speech about the winning combination of Digitization, Sustainability and Modularization. You might have seen my PLM and Sustainability blog post recently; now, a zoom-in on the circular economy and modularity is included.
In this conference, I also focused on Modularity, when implemented based on model-based and data-driven approaches, which is a crucial component of the circular economy (image below) and the lifecycle analysis per module when defined as model-based (Digital Twin).
My entire presentation on SlideShare: Digitization, Sustainability & Modularization.
Conclusion
It was the first time I attended a conference focused on modularity purely, and I realized we are all fighting the same battle. Like the fact that PLM is a strategy and not an engineering system, modularity faces the same challenge. It is a strategy and not an R&D mission. It would be great to see modularity becoming a part of PLM conferences or Circular Economy events as there is so much to learn from each other – and we need them all.
Are you interested in the future of PLM and the meaning of Digital Threads.?
Click on the image to see the agenda and join us for 2 days of discussion & learning.
 During my summer holiday in my “remote” office, I had the chance to digest what I recently read, heard, saw and discussed related to the future of PLM.
During my summer holiday in my “remote” office, I had the chance to digest what I recently read, heard, saw and discussed related to the future of PLM.
I noticed this year/last year that many companies are discussing or working on their future PLM. It is time to make progress after COVID, particularly in digitization.
And as most companies are avoiding the risk of a “big bang”, they are exploring how they can improve their businesses in an evolutionary mode.
PLM is no longer a system
 The most significant change I noticed in my discussions is the growing awareness that PLM is no longer covered by a single system.
The most significant change I noticed in my discussions is the growing awareness that PLM is no longer covered by a single system.
More and more, PLM is considered a strategy, with which I fully agree. Therefore, implementing a PLM strategy requires holistic thinking and an infrastructure of different types of systems, where possible, digitally connected.
This trend is bad news for the PLM vendors as they continuously work on an end-to-end portfolio where every aspect of the PLM lifecycle is covered by one of their systems. The company’s IT department often supports the PLM vendors, as IT does not like a diverse landscape.
 The main question is: “Every PLM Vendor has a rich portfolio on PowerPoint mentioning all phases of the product lifecycle.
The main question is: “Every PLM Vendor has a rich portfolio on PowerPoint mentioning all phases of the product lifecycle.
However, are these capabilities implementable in an economical and user-friendly manner by actual companies or should PLM players need to change their strategy”?
A question I will try to answer in this post
The future of PLM
 I have discussed several observed changes related to the effects of digitization in my recent blog posts, referencing others who have studied these topics in their organizations.
I have discussed several observed changes related to the effects of digitization in my recent blog posts, referencing others who have studied these topics in their organizations.
Some of the posts to refresh your memory are:
- Time to split PLM?
- People, Processes, Data and Tools?
- The rise and the fall of the BOM?
- The new side of PLM? Systems of Engagement!
To summarize what has been discussed in these posts are the following points:
The As Is:
- The traditional PLM systems are examples of a System of Record, not designed to be end-user friendly but designed to have a traceable baseline for manufacturing, service and product compliance.
- The traditional PLM systems are tuned to a mechanical product introduction and release process in a coordinated manner, with a focus on BOM governance.
- The legacy information is stored in BOM structures and related specification files.

System of Record (ENOVIA image 2014)
The To Be:
- We are not talking about a PLM system anymore; a traditional System of Record will be digitally connected to different Systems of Engagement / Domains / Products, which have their own optimized environment for real-time collaboration.
- The BOM structures remain essential for the hardware part; however, overreaching structures are needed to manage software and hardware releases for a product. These structures depend on connected datasets.
- To support digital twins at the various lifecycle stages (design. Manufacturing, operations), product data needs to be based on and consumed by models.
- A future PLM infrastructure is hybrid, based on a Single Source of Change (SSoC) and an Authoritative Source of Truth (ASoT) instead of a Single Source of Truth (SSoT).

Various Systems of Engagement
Related podcasts
I relistened two podcasts before writing this post, and I think they are a must to listen to.
 The Peer Check podcast from Colab episode 17 — The State of PLM in 2022 w/Oleg Shilovitsky. Adam and Oleg have a great discussion about the future of PLM.
The Peer Check podcast from Colab episode 17 — The State of PLM in 2022 w/Oleg Shilovitsky. Adam and Oleg have a great discussion about the future of PLM.
Highlights: From System to Platform – the new norman. A Single Source of Truth doesn’t work anymore – it is about value streams. People in big companies fear making wrong PLM decisions, which is seen as a significant risk for your career.
There is no immediate need to change the current status quo.
 The Share PLM Podcast – Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights from Yousef Hooshmand. Yousef talked with Helena and me about proven ways to migrate an old PLM landscape to a modern PLM/Business landscape.
The Share PLM Podcast – Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights from Yousef Hooshmand. Yousef talked with Helena and me about proven ways to migrate an old PLM landscape to a modern PLM/Business landscape.
Highlights: The term Single Source of Change and the existing concepts of a hybrid PLM infrastructure based on his experiences at Daimler and now at NIO. Yousef stresses the importance of having the vision and the executive support to execute.
![]() The time of “big bangs” is over, and Yousef provided links to relevant content, which you can find here in the comments.
The time of “big bangs” is over, and Yousef provided links to relevant content, which you can find here in the comments.
In addition, I want to point to the experiences provided by Erik Herzog in the Heliple project using OSLC interfaces as the “glue” to connect (in my terminology) the Systems of Engagement and the Systems of Record.
If you are interested in these concepts and want to learn and discuss them with your peers, more can be learned during the upcoming CIMdata PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference.
In particular, look at the agenda for day two if you are interested in this topic.
The future for the PLM vendors
 If you look at the messaging of the current PLM Vendors, none of them is talking about this federated concept.
If you look at the messaging of the current PLM Vendors, none of them is talking about this federated concept.
They are more focused with their messaging on the transition from on-premise to the cloud, providing a SaaS offering with their portfolio.
I was slightly disappointed when I saw this article on Engineering.com provided by Autodesk: 5 PLM Best Practices from the Experiences of Autodesk and Its Customers.
The article is tool-centric, with statements that make sense and could be written by any PLM Vendor. However, Best Practice #1 Central Source of Truth Improves Productivity and Collaboration was the message that struck me. Collaboration comes from connecting people, not from the Single Source of Truth utopia.
I don’t believe PLM Vendors have to be afraid of losing their installed base rapidly with companies using their PLM as a System or Record. There is so much legacy stored in these systems that might still be relevant. The existence of legacy information, often documents, makes a migration or swap to another vendor almost impossible and unaffordable.

The System of Record is incompatible with data-driven PLM capabilities
I would like to see more clear developments of the PLM Vendors, creating a plug-and-play infrastructure for Systems of Engagement. Plug-and-play solutions could be based on a neutral partner collaboration hub like ShareAspace or the Systems of Engagement I discussed recently in my post and interview: The new side of PLM? Systems of Engagement!
 Plug-and-play systems of engagement require interface standards, and PLM Vendors will only move in this direction if customers are pushing for that, and this is the chicken-and-egg discussion. And probably, their initiatives are too fragmented at the moment to come to a standard. However, don’t give up; keep building MVPs to learn and share.
Plug-and-play systems of engagement require interface standards, and PLM Vendors will only move in this direction if customers are pushing for that, and this is the chicken-and-egg discussion. And probably, their initiatives are too fragmented at the moment to come to a standard. However, don’t give up; keep building MVPs to learn and share.
Some people believe AI, with the examples we have seen with ChatGPT, will be the future direction without needing interface standards.
I am curious about your thoughts and experiences in that area and am willing to learn.
Talking about learning?
 Besides reading posts and listening to podcasts, I also read an excellent book this summer. Martijn Dullaart, often participating in PLM and CM discussions, had decided to write a book based on the various discussions related to part (re-)identification (numbering, revisioning).
Besides reading posts and listening to podcasts, I also read an excellent book this summer. Martijn Dullaart, often participating in PLM and CM discussions, had decided to write a book based on the various discussions related to part (re-)identification (numbering, revisioning).
As Martijn starts in the preface:
“I decided to write this book because, in my search for more knowledge on the topics of Part Re-Identification, Interchangeability, and Traceability, I could only find bits and pieces but not a comprehensive work that helps fundamentally understand these topics”.
 I believe the book should become standard literature for engineering schools that deal with PLM and CM, for software vendors and implementers and last but not least companies that want to improve or better clarify their change processes.
I believe the book should become standard literature for engineering schools that deal with PLM and CM, for software vendors and implementers and last but not least companies that want to improve or better clarify their change processes.
Martijn writes in an easily readable style and uses step-by-step examples to discuss the various options. There are even exercises at the end to use in a classroom or for your team to digest the content.
The good news is that the book is not about the past. You might also know Martijn for our joint discussion, The Future of Configuration Management, together with Maxime Gravel and Lisa Fenwick, on the impact of a model-based and data-driven approach to CM.
 I plan to come back with a more dedicated discussion at some point with Martijn soon. Meanwhile, start reading the book. Get your free chapter if needed by following the link at the bottom of this article.
I plan to come back with a more dedicated discussion at some point with Martijn soon. Meanwhile, start reading the book. Get your free chapter if needed by following the link at the bottom of this article.
I recommend buying the book as a paperback so you can navigate easily between the diagrams and the text.
Conclusion
The trend for federated PLM is becoming more and more visible as companies start implementing these concepts. The end of monolithic PLM is a threat and an opportunity for the existing PLM Vendors. Will they work towards an open plug-and-play future, or will they keep their portfolios closed? What do you think?














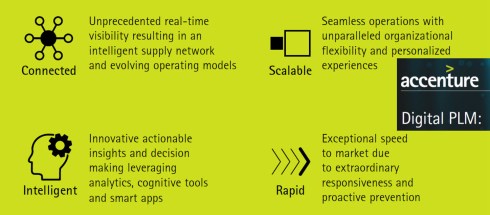

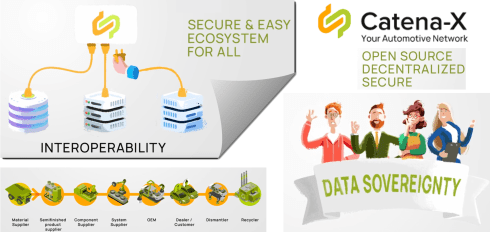
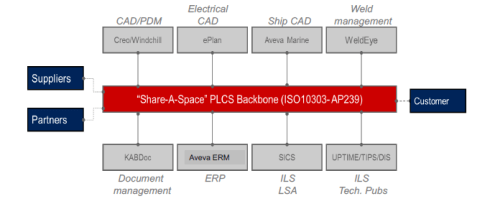
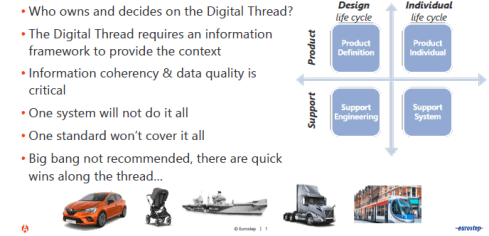
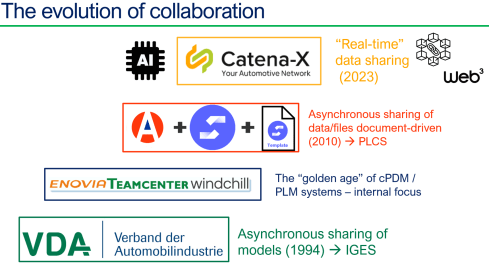





















[…] (The following post from PLM Green Global Alliance cofounder Jos Voskuil first appeared in his European PLM-focused blog HERE.) […]
[…] recent discussions in the PLM ecosystem, including PSC Transition Technologies (EcoPLM), CIMPA PLM services (LCA), and the Design for…
Jos, all interesting and relevant. There are additional elements to be mentioned and Ontologies seem to be one of the…
Jos, as usual, you've provided a buffet of "food for thought". Where do you see AI being trained by a…
Hi Jos. Thanks for getting back to posting! Is is an interesting and ongoing struggle, federation vs one vendor approach.…