You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Artificial Intelligence’ category.
 In the last two weeks, I had some interesting observations and discussions related to the need to have a (PLM) vision. I placed the word PLM between brackets, as PLM is no longer an isolated topic in an organization. A PLM strategy should align with the business strategy and vision.
In the last two weeks, I had some interesting observations and discussions related to the need to have a (PLM) vision. I placed the word PLM between brackets, as PLM is no longer an isolated topic in an organization. A PLM strategy should align with the business strategy and vision.
To be clear, if you or your company wants to survive in the future, you need a sustainable vision and a matching strategy as the times they are a changing, again!
I love the text: “Don’t criticize what you can’t understand” – a timeless quote.
 First, there was Rob Ferrone’s article: Multi-view. Perspectives that shape PLM – a must-read to understand who to talk to about which dimension of PLM – and it is worth browsing through the comments too – there you will find the discussions, and it helps you to understand the PLM players.
First, there was Rob Ferrone’s article: Multi-view. Perspectives that shape PLM – a must-read to understand who to talk to about which dimension of PLM – and it is worth browsing through the comments too – there you will find the discussions, and it helps you to understand the PLM players.
Note: it is time that AI-generated images become more creative 😉
 Next, there is still the discussion started by Gareth Webb, Digital Thread and the Knowledge Graph, further stirred by Oleg Shilovitsky.
Next, there is still the discussion started by Gareth Webb, Digital Thread and the Knowledge Graph, further stirred by Oleg Shilovitsky.
Based on the likes and comments, it is clearly a topic that creates interaction – people are thinking and talking about it – the Digital Thread as a Service.
One of the remaining points in this debate is still the HOW and WHEN companies decide to implement a Digital Thread, a Knowledge Graph and other modern data concepts.
 So far my impression is that most companies implement their digital enhancements (treads/graphs) in a bottom-up approach, not driven by a management vision but more like band-aids or places where it fits well, without a strategy or vision.
So far my impression is that most companies implement their digital enhancements (treads/graphs) in a bottom-up approach, not driven by a management vision but more like band-aids or places where it fits well, without a strategy or vision.
The same week, we, Beatriz Gonzáles and I, recorded a Share PLM podcast session with Paul Kaiser from MHP Americas as a guest. Paul is the head of the Digital Core & Technology department, where he leads management and IT consulting services focused on end-to-end business transformation.
 During our discussion, Paul mentioned the challenge in engagements when the company has no (PLM) vision. These companies expect external consultants to formulate and implement the vision – a recipe for failure due to wrong expectations.
During our discussion, Paul mentioned the challenge in engagements when the company has no (PLM) vision. These companies expect external consultants to formulate and implement the vision – a recipe for failure due to wrong expectations.
The podcast can be found HERE , and the session inspired me to write this post.
“We just want to be profitable“.
I believe it is a typical characteristic of small and medium enterprises that people are busy with their day-to-day activities. In addition, these companies rarely appoint new top management, which could shake up the company in a positive direction. These companies evolve …..

You often see a stable management team with members who grew up with the company and now monitor and guide it, watching its finances and competition. They know how the current business is running.
 Based on these findings, there will be classical efficiency plans, i.e., cutting costs somewhere, dropping some non-performing products, or investing in new technology that they cannot resist. Still, minor process changes and fundamental organizational changes are not expected.
Based on these findings, there will be classical efficiency plans, i.e., cutting costs somewhere, dropping some non-performing products, or investing in new technology that they cannot resist. Still, minor process changes and fundamental organizational changes are not expected.
Most of the time, the efficiency plans provide single-digit benefits.
 Everyone is happy when the company feels stable and profitable, even if the margins are under pressure. The challenge for this type of company without a vision is that they navigate in the dark when the outside world changes – like nowadays.
Everyone is happy when the company feels stable and profitable, even if the margins are under pressure. The challenge for this type of company without a vision is that they navigate in the dark when the outside world changes – like nowadays.
The world is changing drastically.
Since 2014, I have advocated for digital transformation in the PLM domain and explained it simply using the statement: From Coordinated to Connected, which already implies much complexity.
Moving from document/files to datasets and models, from a linear delivery model to a DevOps model, from waterfall to agile and many other From-To statements.
Moving From-To is a transformational journey, which means you will learn and adapt to new ways of working during the journey. Still, the journey should have a target, directed by a vision.
However, not many companies have started this journey because they just wanted to be profitable.
“Why should we go in an unknown direction?”
With the emergence of sustainability regulations, e.g., GHG and ESG reporting, carbon taxes, material reporting, and the Digital Product Passport, which goes beyond RoHS and REACH and applies to much more industries, there came the realization that there is a need to digitize the product lifecycle processes and data beyond documents. Manual analysis and validation are too expensive and unreliable.
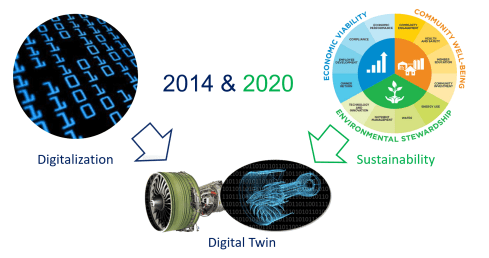
At this stage, there is already a visible shift between companies that have proactively implemented a digitally connected infrastructure and companies that still see compliance with regulations as an additional burden. The first group brings products to the market faster and more sustainably than the second group because sustainability is embedded in their product lifecycle management.
![]() And just when companies felt they could manage the transition from Coordinated to Coordinated and Connected, there was the fundamental disruption of embedded AI in everything, including the PLM domain.
And just when companies felt they could manage the transition from Coordinated to Coordinated and Connected, there was the fundamental disruption of embedded AI in everything, including the PLM domain.
- Large Language Models LLMs can go through all the structured and unstructured data, providing real-time access to information, which would take experts years of learning. Suddenly, everyone can behave experienced.
- The rigidness of traditional databases can be complemented by graph databases, which visualize knowledge that can be added and discovered on the fly without IT experts. Suddenly, an enterprise is no longer a collection of interfaced systems but a digital infrastructure where data flows – some call it Digital Thread as a Service (DTaaS)
- Suddenly, people feel overwhelmed by complexity, leading to fear and doing nothing, a killing attitude.
I cannot predict what will happen in the next 5 to 10 years, but I am sure the current change is one we have never seen before. Be prepared and flexible to act—to be on top of the wave, you need the skills to get there.
Building the vision
The image below might not be new to you, but it illustrates how companies could manage a complex change.
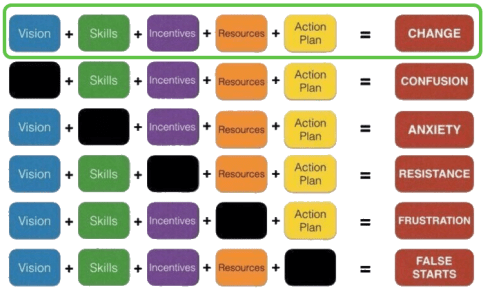
I will focus only on the first two elements, Vision and Skills, as they are the two elements we as individuals can influence. The other elements are partly related to financial and business constraints.
Vision and Skills are closely related because you can have a fantastic vision. Still, to realize the vision, you need a strategy driven by relevant skills to define and implement the vision. With the upcoming AI, traditional knowledge-based skills will suddenly no longer be a guarantee for future jobs.
 AI brings a new dimension for everyone working in a company. To remain relevant, you must develop your unique human skills that make you different from robots or libraries. The importance of human skills might not be new, but now it has become apparent with the explosion of available AI tools.
AI brings a new dimension for everyone working in a company. To remain relevant, you must develop your unique human skills that make you different from robots or libraries. The importance of human skills might not be new, but now it has become apparent with the explosion of available AI tools.
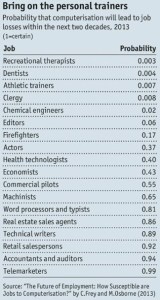
Look at this 2013 table about predicted skills for the future – You can read the details in their paper, The Future of Employment, by Carl Benedikt Frey & Michael Osborne(2013) – click on the image to see the details.
In my 2015 PLM lectures, I joked when showing this image that my job as a PLM coach was secured, because you are a recreational therapist and firefighter combined.
It has become a reality, and many of my coaching engagements nowadays focus on explaining and helping companies formulate and understand their possible path forward. Helping them align and develop a vision of progressing in a volatile world – the technology is there, the skills and the vision are often not yet there.
![]() Combining business strategy with in-depth PLM concepts is a relatively unique approach in our domain. Many of my peers have other primary goals, such as Rob Ferrone’s article: Multi-view. Perspectives that shape PLM explains.
Combining business strategy with in-depth PLM concepts is a relatively unique approach in our domain. Many of my peers have other primary goals, such as Rob Ferrone’s article: Multi-view. Perspectives that shape PLM explains.
And then there is …..
The Share PLM Summit 2025
Modern times need new types of information building and sharing, and therefore, I am eager to participate in the upcoming Share PLM Summit at the end of May in Jerez (Spain).
See the link to the event here: The Share PLM Summit 2025 – with the theme: Where People Take Center Stage to Drive Human-Centric Transformations in PLM and Lead the Future of Digital Innovation.
In my lecture, I will focus on how humans can participate in/anticipate this digital AI-based transformation. But even more, I look forward to the lectures and discussions with other peers, as more people-centric thought leaders and technology leaders will join us:
Quoting Oleg Shilovitsky:
PLM was built to manage data, but too often, it makes people work for the data instead of working the other way around. At Share PLM Summit 2025, I’ll discuss how PLM must evolve from rigid, siloed systems to intelligent, connected, and people-centric data architectures.
We need both, and I hope to see you at the end of May at this unique PLM conference.
Conclusion
We are at a decisive point of the digital transformation as AI will challenge people skills, knowledge and existing ways of working. Combined with a turbulent world order, we need to prepare to be flexible and resilient. Therefore instead of focusing on current best practices we need to prepare for the future – a vision developed by skilled people. How will you or your company work on that? Join us if you have questions or ideas.

 Four years ago, I wrote a series of posts with the common theme: The road to model-based and connected PLM. I discussed the various aspects of model-based and the transition from considering PLM as a system towards considering PLM as a strategy to implement a connected infrastructure.
Four years ago, I wrote a series of posts with the common theme: The road to model-based and connected PLM. I discussed the various aspects of model-based and the transition from considering PLM as a system towards considering PLM as a strategy to implement a connected infrastructure.
Since then, a lot has happened. The terminology of Digital Twin and Digital Thread has become better understood. The difference between Coordinated and Connected ways of working has become more apparent. Spoiler: You need both ways. And at this moment, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a new hype.
 Many current discussions in the PLM domain are about structures and data connectivity, Bills of Materials (BOM), or Bills of Information(BOI) combined with the new term Digital Thread as a Service (DTaaS) introduced by Oleg Shilovitsky and Rob Ferrone. Here, we envision a digitally connected enterprise, based connected services.
Many current discussions in the PLM domain are about structures and data connectivity, Bills of Materials (BOM), or Bills of Information(BOI) combined with the new term Digital Thread as a Service (DTaaS) introduced by Oleg Shilovitsky and Rob Ferrone. Here, we envision a digitally connected enterprise, based connected services.
A lot can be explored in this direction; also relevant Lionel Grealou’s article in Engineering.com: RIP SaaS, long live AI-as-a-service and follow-up discussions related tot his topic. I chimed in with Data, Processes and AI.

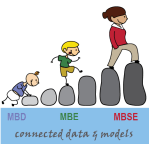
However, we also need to focus on the term model-based or model-driven. When we talk about models currently, Large Language Models (LMM) are the hype, and when you are working in the design space, 3D CAD models might be your first association.
There is still confusion in the PLM domain: what do we mean by model-based, and where are we progressing with working model-based?
A topic I want to explore in this post.
It is not only Model-Based Definition (MBD)
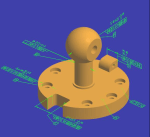
Before I started The Road to Model-Based series, there was already the misunderstanding that model-based means 3D CAD model-based. See my post from that time: Model-Based – the confusion.
Model-Based Definition (MBD) is an excellent first step in understanding information continuity, in this case primarily between engineering and manufacturing, where the annotated model is used as the source for manufacturing.
In this way, there is no need for separate 2D drawings with manufacturing details, reducing the extra need to keep the engineering and manufacturing information in sync and, in addition, reducing the chance of misinterpretations.
 MBD is a common practice in aerospace and particularly in the automotive industry. Other industries are struggling to introduce MBD, either because the OEM is not ready or willing to share information in a different format than 3D + 2D drawings, or their supplier consider MBD too complex for them compared to their current document-driven approach.
MBD is a common practice in aerospace and particularly in the automotive industry. Other industries are struggling to introduce MBD, either because the OEM is not ready or willing to share information in a different format than 3D + 2D drawings, or their supplier consider MBD too complex for them compared to their current document-driven approach.
In its current practice, we must remember that MBD is part of a coordinated approach.
Companies exchange technical data packages based on potential MBD standards (ASME Y14.47 /ISO 16792 but also JT and 3D PDF). It is not yet part of the connected enterprise, but it connects engineering and manufacturing using the 3D Model as the core information carrier.
 As I wrote, learning to work with MBD is a stepping stone in understanding a modern model-based and data-driven enterprise. See my 2022 post: Why Model-based Definition is important for us all.
As I wrote, learning to work with MBD is a stepping stone in understanding a modern model-based and data-driven enterprise. See my 2022 post: Why Model-based Definition is important for us all.
To conclude on MBD, Model-based definition is a crucial practice to improve collaboration between engineering, manufacturing, and suppliers, and it might be parallel to collaborative BOM structures.
And it is transformational as the following benefits are reported through ChatGPT:
- Up to 30% faster in product development cycles due to reduced need for 2D drawings and fewer design iterations. Boeing reported a 50% reduction in engineering change requests by using MBD.

- Companies using MBD see a 20–50% reduction in manufacturing errors caused by misinterpretations of 2D drawings. Caterpillar reported a 30% improvement in first-pass yield due to better communication between design and manufacturing teams.
- MBD can reduce product launch time by 20–50% by eliminating bottlenecks related to traditional drawings and manual data entry.
- 20–30% reduction in documentation costs by eliminating or reducing 2D drawings. Up to 60% savings on rework and scrap costs by reducing errors and inconsistencies.
Over five years, Lockheed Martin achieved a $300 million cost savings by implementing MBD across parts of its supply chain.
MBSE is not a silo.
For many people, Model-Based Systems Engineering(MBSE) seems to be something not relevant to their business, or it is a discipline for a small group of specialists that are conducting system engineering practices, not in the traditional document-driven V-shape approach but in an iterative process following the V-shape, meanwhile using models to predict and verify assumptions.
And what is the value connected in a PLM environment?
A quick heads up – what is a model
A model is a simplified representation of a system, process, or concept used to understand, predict, or optimize real-world phenomena. Models can be mathematical, computational, or conceptual.
We need models to:
- Simplify Complexity – Break down intricate systems into manageable components and focus on the main components.
- Make Predictions – Forecast outcomes in science, engineering, and economics by simulating behavior – Large Language Models, Machine Learning.
- Optimize Decisions – Improve efficiency in various fields like AI, finance, and logistics by running simulations and find the best virtual solution to apply.
- Test Hypotheses – Evaluate scenarios without real-world risks or costs for example a virtual crash test..
It is important to realize models are as accurate as the data elements they are running on – every modeling practices has a certain need for base data, be it measurements, formulas, statistics.
I watched and listened to the interesting podcast below, where Jonathan Scott and Pat Coulehan discuss this topic: Bridging MBSE and PLM: Overcoming Challenges in Digital Engineering. If you have time – watch it to grasp the challenges.
The challenge in an MBSE environment is that it is not a single tool with a single version of the truth; it is merely a federated environment of shared datasets that are interpreted by modeling applications to understand and define the behavior of a product.
 In addition, an interesting article from Nicolas Figay might help you understand the value for a broader audience. Read his article: MBSE: Beyond Diagrams – Unlocking Model Intelligence for Computer-Aided Engineering.
In addition, an interesting article from Nicolas Figay might help you understand the value for a broader audience. Read his article: MBSE: Beyond Diagrams – Unlocking Model Intelligence for Computer-Aided Engineering.
Ultimately, and this is the agreement I found on many PLM conferences, we agree that MBSE practices are the foundation for downstream processes and operations.
We need a data-driven modeling environment to implement Digital Twins, which can span multiple systems and diagrams.
In this context, I like the Boeing diamond presented by Don Farr at the 2018 PLM Roadmap EMEA conference. It is a model view of a system, where between the virtual and the physical flow, we will have data flowing through a digital thread.
Where this image describes a model-based, data-driven infrastructure to deliver a solution, we can, in addition, apply the DevOp approach to the bigger picture for solutions in operation, as depicted by the PTC image below.
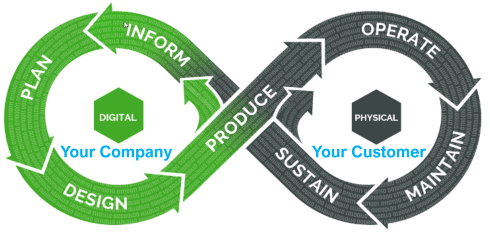
Model-based the foundation of the digital twins
![]() To conclude on MBSE, I hope that it is clear why I am promoting considering MBSE not only as the environment to conceptualize a solution but also as the foundation for a digital enterprise where information is connected through digital threads and AI models (**new**)
To conclude on MBSE, I hope that it is clear why I am promoting considering MBSE not only as the environment to conceptualize a solution but also as the foundation for a digital enterprise where information is connected through digital threads and AI models (**new**)
The data borders between traditional system domains will disappear – the single source of change and the nearest source of truth – paradigm, and this post, The Big Blocks of Future Lifecycle Management, from Prof. Dr. Jörg Fischer, are all about data domains.
However, having accessible data using all kinds of modern data sources and tools are necessary to build digital twins – either to simulate and predict a physical solution or to analyze a physical solution and, based on the analysis, either adjust the solutions or improve your virtual simulations.
Digital Twins at any stage of the product life cycle are crucial to developing and maintaining sustainable solutions, as I discussed in previous lectures. See the image below:

Conclusion
Data quality and architecture are the future of a modern digital enterprise – the building blocks. And there is a lot of discussion related to Artificial Intelligence. This will only work when we master the methodology and practices related to a data-driven and sustainable approach using models. MBD is not new, MBSE perhaps still new, building blocks for a model-based approach. Where are you in your lifecycle?
Last week, my memory was triggered by this LinkedIn post and discussion started by Oleg Shilovitsky: Rethinking the Data vs. Process Debate in the Age of Digital Transformation and AI.

me, 1989
In the past twenty years, the debate in the PLM community has changed a lot. PLM started as a central file repository, combined with processes to ensure the correct status and quality of the information.
Then, digital transformation in the PLM domain became achievable and there was a focus shift towards (meta)data. Now, we are entering the era of artificial intelligence, reshaping how we look at data.
In this technology evolution, there are lessons learned that are still valid for 2025, and I want to share some of my experiences in this post.
 In addition, it was great to read Martin Eigner’s great reflection on the past 40 years of PDM/PLM. Martin shared his experiences and insights, not directly focusing on the data and processes debate, but very complementary and helping to understand the future.
In addition, it was great to read Martin Eigner’s great reflection on the past 40 years of PDM/PLM. Martin shared his experiences and insights, not directly focusing on the data and processes debate, but very complementary and helping to understand the future.
It started with processes (for me 2003-2014)
In the early days when I worked with SmarTeam, one of my main missions was to develop templates on top of the flexible toolkit SmarTeam.
 For those who do not know SmarTeam, it was one of the first Windows PDM/PLM systems, and thanks to its open API (COM-based), companies could easily customize and adapt it. It came with standard data elements and behaviors like Projects, Documents (CAD-specific and Generic), Items and later Products.
For those who do not know SmarTeam, it was one of the first Windows PDM/PLM systems, and thanks to its open API (COM-based), companies could easily customize and adapt it. It came with standard data elements and behaviors like Projects, Documents (CAD-specific and Generic), Items and later Products.
On top of this foundation, almost every customer implemented their business logic (current practices).
And there the problems came …..
 The implementations became too much a highly customized environment, not necessarily thought-through as every customer worked differently based on their (paper) history. Thanks to learning from the discussions in the field supporting stalled implementations, I was also assigned to develop templates (e.g. SmarTeam Design Express) and standard methodology (the FDA toolkit), as the mid-market customers requested. The focus was on standard processes.
The implementations became too much a highly customized environment, not necessarily thought-through as every customer worked differently based on their (paper) history. Thanks to learning from the discussions in the field supporting stalled implementations, I was also assigned to develop templates (e.g. SmarTeam Design Express) and standard methodology (the FDA toolkit), as the mid-market customers requested. The focus was on standard processes.
You can read my 2009 observations here: Can chaos become order through PLM?
The need for standardization?
When developing templates (the right data model and processes), it was also essential to provide template processes for releasing a product and controlling the status and product changes – from Engineering Change Request to Engineering Change Order. Many companies had their processes described in their ISO 900x manual, but were they followed correctly?
 In 2010, I wrote ECR/ECO for Dummies, and it has been my second most-read post over the years. Only the 2019 post The importance of EBOM and MBOM in PLM (reprise) had more readers. These statistics show that many people are, and were, seeking education on general PLM processes and data model principles.
In 2010, I wrote ECR/ECO for Dummies, and it has been my second most-read post over the years. Only the 2019 post The importance of EBOM and MBOM in PLM (reprise) had more readers. These statistics show that many people are, and were, seeking education on general PLM processes and data model principles.
It was also the time when the PLM communities discussed out-of-the-box or flexible processes as Oleg referred to in his post..
You would expect companies to follow these best practices, and many small and medium enterprises that started with PLM did so. However, I discovered there was and still is the challenge with legacy (people and process), particularly in larger enterprises.
The challenge with legacy
 The technology was there, the usability was not there. Many implementations of a PLM system go through a critical stage. Are companies willing to change their methodology and habits to align with common best practices, or do they still want to implement their unique ways of working (from the past)?
The technology was there, the usability was not there. Many implementations of a PLM system go through a critical stage. Are companies willing to change their methodology and habits to align with common best practices, or do they still want to implement their unique ways of working (from the past)?
“The embedded process is limiting our freedom, we need to be flexible”
is an often-heard statement. When every step is micro-managed in the PLM system, you create a bureaucracy detested by the user. In general, when the processes are implemented in a way first focusing on crucial steps with the option to improve later, you will get the best results and acceptance. Nowadays, we could call it an MVP approach.
 I have seen companies that created a task or issue for every single activity a person should do. Managers loved the (demo) dashboard. It never lead to success as the approach created frustration at the end user level as their To-Do list grew and grew.
I have seen companies that created a task or issue for every single activity a person should do. Managers loved the (demo) dashboard. It never lead to success as the approach created frustration at the end user level as their To-Do list grew and grew.
 Another example of the micro-management mindset is when I worked with a company that had the opposite definition of Version and Revision in their current terminology. Initially, they insisted that the new PLM system should support this, meaning everywhere in the interface where Revisions was mentioned should be Version and the reverse for Version and Revision.
Another example of the micro-management mindset is when I worked with a company that had the opposite definition of Version and Revision in their current terminology. Initially, they insisted that the new PLM system should support this, meaning everywhere in the interface where Revisions was mentioned should be Version and the reverse for Version and Revision.
Can you imagine the cost of implementing and maintaining this legacy per upgrade?
And then came data (for me 2014 – now)
In 2015, during the pivotal PLM Roadmap/PDT conference related to Product Innovation Platforms, it brought the idea of framing digital transformation in the PLM domain in a single sentence: From Coordinated to Connected. See the original image from Marc Halpern here below and those who have read my posts over the years have seen this terminology’s evolution. Now I would say (till 2024): From Coordinated to Coordinated and Connected.
A data-driven approach was not new at that time. Roughly speaking, around 2006 – close to the introduction of the Smartphone – there was already a trend spurred by better global data connectivity at lower cost. Easy connectivity allowed PLM to expand into industries that were not closely connected to 3D CAD systems(CATIA, CREO or NX). Agile PLM, Aras, and SAP PLM became visible – PLM is no longer for design management but also for go-to-market governance in the CPG and apparel industry.
However, a data-driven approach was still rare in mainstream manufacturing companies, where drawings, office documents, email and Excel were the main information carriers next to the dominant ERP system.
A data-driven approach was a consultant’s dream, and when looking at the impact of digital transformation in other parts of the business, why not for PLM, too? My favorite and still valid 2014 image is the one below from Accenture describing Digital PLM. Here business and PLM come together – the WHY!
Again, the challenge with legacy
 At that time, I saw a few companies linking their digital transformation to implementing a new PLM system. Those were the days the PLM vendors were battling for the big enterprise deals, sometimes motivated by an IT mindset that unifying the existing PDM/PLM systems would fulfill the digital dream. Science was not winning, but emotion. Read the PLM blame game – still actual.
At that time, I saw a few companies linking their digital transformation to implementing a new PLM system. Those were the days the PLM vendors were battling for the big enterprise deals, sometimes motivated by an IT mindset that unifying the existing PDM/PLM systems would fulfill the digital dream. Science was not winning, but emotion. Read the PLM blame game – still actual.
One of my key observations is that companies struggle when they approach PLM transformation with a migration mindset. Moving from Coordinated to Connected isn’t just about technology—it’s about fundamentally changing how we work. Instead of a document-driven approach, organizations must embrace a data-driven, connected way of working.
The PLM community increasingly agrees that PLM isn’t a single system; it’s a strategy that requires a federated approach—whether through SaaS or even beyond it.
 Before AI became a hype, we discussed the digital thread, digital twins, graph databases, ontologies, and data meshes. Legacy – people (skills), processes(rigid) and data(not reliable) – are the elephant in the room. Yet, the biggest challenge remains: many companies see PLM transformation as just buying new tools.
Before AI became a hype, we discussed the digital thread, digital twins, graph databases, ontologies, and data meshes. Legacy – people (skills), processes(rigid) and data(not reliable) – are the elephant in the room. Yet, the biggest challenge remains: many companies see PLM transformation as just buying new tools.
A fundamental transformation requires a hybrid approach—maintaining traditional operations while enabling multidisciplinary, data-driven teams. However, this shift demands new skills and creates the need to learn and adapt, and many organizations hesitate to take that risk.
In his Product Data Plumber Perspective on 2025. Rob Ferrone addressed the challenge to move forward too, and I liked one of his responses in the underlying discussion that says it all – it is hard to get out of your day to day comfort (and data):
Rob Ferrone’s quote:
Transformations are announced, followed by training, then communication fades. Plans shift, initiatives are replaced, and improvements are delayed for the next “fix-all” solution. Meanwhile, employees feel stuck, their future dictated by a distant, ever-changing strategy team.
And then there is Artificial Intelligence (2024 ……)
 In the past two years, I have been reading and digesting much news related to AI, particularly generative AI.
In the past two years, I have been reading and digesting much news related to AI, particularly generative AI.
Initially, I was a little skeptical because of all the hallucinations and hype; however, the progress in this domain is enormous.
I believe that AI has the potential to change our digital thread and digital twin concepts dramatically where the focus was on digital continuity of data.
Now this digital continuity might not be required, reading articles like The End of SaaS (a more and more louder voice), usage of the Fusion Strategy (the importance of AI) and an (academic) example, on a smaller scale, I about learned last year the Swedish Arrowhead™ fPVN project.
I hope that five years from now, there will not be a paragraph with the title Pity there was again legacy.
We should have learned from the past that there is always the first wave of tools – they come with a big hype and promise – think about the Startgate Project but also Deepseek.
 Still remember, the change comes from doing things differently, not from efficiency gains. To do things differently you need an educated, visionary management with the power and skills to take a company in a new direction. If not, legacy will win (again)
Still remember, the change comes from doing things differently, not from efficiency gains. To do things differently you need an educated, visionary management with the power and skills to take a company in a new direction. If not, legacy will win (again)
Conclusion
In my 25 years of working in the data management domain, now known as PLM, I have seen several impressive new developments – from 2D to 3D, from documents to data, from physical prototypes to models and more. All these developments took decades to become mainstream. Whilst the technology was there, the legacy kept us back. Will this ever change? Your thoughts?

The pivotal 2015 PLM Roadmap / PDT conference
 In my general 2025 outlook for PLM, My 2025 focus, I mentioned Sustainability at the end, as I believe it is a topic on its own, worth an entire blog post.
In my general 2025 outlook for PLM, My 2025 focus, I mentioned Sustainability at the end, as I believe it is a topic on its own, worth an entire blog post.
After our 2025 PLM Global Green Alliance core team kick-off last week, I felt the importance of sharing our thoughts, observations, and personal thoughts/focus.
 The PGGA core team consists of Rich McFall – Climate Change, Klaus Brettschneider Life Cycle Assessment, Mark Reisig Sustainability and Green Energy, Evgeniya Burimskaya Circular Economy, Erik Reiger Design for Sustainability and me Talking about Sustainability.
The PGGA core team consists of Rich McFall – Climate Change, Klaus Brettschneider Life Cycle Assessment, Mark Reisig Sustainability and Green Energy, Evgeniya Burimskaya Circular Economy, Erik Reiger Design for Sustainability and me Talking about Sustainability.
Some interesting observations:
- Evgenia mentioned that in job interviews for CIMPA, it is motivating to see that new employees want to contribute to sustainability activities and the education of companies. Sustainability is part of their WHY (I will come back to that later)
- We have more and more PGGA members from Asia, while percentage of US members is declining. Where the US has the loudest voice against human-caused climate change and Sustainability, there are a lot of hidden and positive success stories from Asia, and we are looking for spokespeople from that region.
Regulations
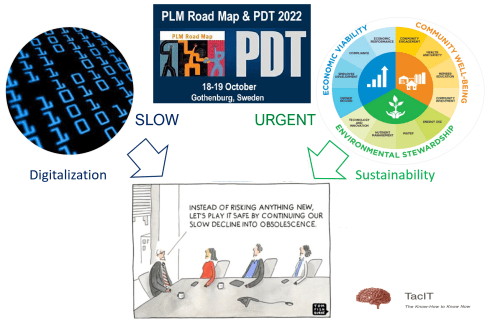
In many lectures, I explained that digitization in PLM was going slow because this is a complex topic for many companies, and current business performance might be challenging but not too bad. So why would we go on an unknown and potentially risky transformation journey?
 Due to sustainability regulations, digital transformation has gotten a push in the right direction. GHG (Greenhouse Gas) reporting, ESG (Environmental Social Governance) reporting, CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), and the DPP (Digital Product Passport) have all created the need for companies to create digital threads for information that historically did not exist or was locked in documents.
Due to sustainability regulations, digital transformation has gotten a push in the right direction. GHG (Greenhouse Gas) reporting, ESG (Environmental Social Governance) reporting, CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), and the DPP (Digital Product Passport) have all created the need for companies to create digital threads for information that historically did not exist or was locked in documents.
 Therefore, it is interesting to read Oleg Shilovitsky’ s blog, Reimagining PLM for 2025: Key Strategic Trends, in which he also sees the importance of Sustainability and the Circular Economy.
Therefore, it is interesting to read Oleg Shilovitsky’ s blog, Reimagining PLM for 2025: Key Strategic Trends, in which he also sees the importance of Sustainability and the Circular Economy.
Quoting Oleg:
Sustainability cannot be ignored and, therefore I expect more interest to environmental considerations in PLM strategies. Companies are incorporating sustainability metrics into product design and lifecycle assessment, aligning with Industry 5.0 and Engineering 5.0 principles. It is impossible without digital thread and data connectivity and, therefore will continue to support business strategies.
 The challenge of regulations is that they limit someone’s freedom. Regulations are there to create an equal playing field for all and ensure society makes progress. Be it traffic regulations, business regulations or environmental regulations. The challenge is not to over-regulate and create a Kafkaesque society. Whereas if you are alone in the world or are the only important person in the world, you do not need regulations as you do not care.
The challenge of regulations is that they limit someone’s freedom. Regulations are there to create an equal playing field for all and ensure society makes progress. Be it traffic regulations, business regulations or environmental regulations. The challenge is not to over-regulate and create a Kafkaesque society. Whereas if you are alone in the world or are the only important person in the world, you do not need regulations as you do not care.
Now the challenge comes of how we deal with regulations.
The WHY!
 I have learned to always look at the WHY. Why are companies doing business in a certain manner, why are people behaving in a certain manner even against common logic?
I have learned to always look at the WHY. Why are companies doing business in a certain manner, why are people behaving in a certain manner even against common logic?
There is the difference between the long-term WHY (strategy) and the short-term WHY(emotion). For most individuals the short-term WHY prevails, for companies and governments the long term WHY should lead their decisions.
Unfortunately short term decisions (money, food, comfort, legacy habits) get a higher priority by humans instead of long term goals (transformations and transitions).
 Daniel Kahneman, Nobel prize winner writing about this in his book Thinking Fast and Slow. We see this dilemma, fast based on gut-feeling or slow based on a real analysis in companies, we see it in our society .
Daniel Kahneman, Nobel prize winner writing about this in his book Thinking Fast and Slow. We see this dilemma, fast based on gut-feeling or slow based on a real analysis in companies, we see it in our society .
- How many companies have a 10-years sustainable strategy and consistent roadmap?
- How many countries have a 10-years sustainable strategy and consistent roadmap?
Jan Bosch also mentioned the importance of the WHY in his Digital Reflection #15: Why do you get out of bed in the morning? Did you ask yourself this question?
Sustainability, like digitization in PLM, requires a behavioral change. From traditional linear coordinated ways of working we need to learn to work in a more complex and advanced environment with real-time data. Luckily if the data is accurate AI will help us to manage the complexity.
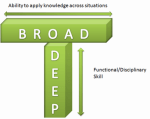 Still it is a transformational change in the way you work and this is a challenge for an existing workforce. They reached their status by being an expert in a certain discipline, by mastering specific skills. Now the needed expertise is changing (from Expert to T-shape) and new skills are needed. Are you able to acquire those new skills or do you give up and complain about the future?
Still it is a transformational change in the way you work and this is a challenge for an existing workforce. They reached their status by being an expert in a certain discipline, by mastering specific skills. Now the needed expertise is changing (from Expert to T-shape) and new skills are needed. Are you able to acquire those new skills or do you give up and complain about the future?
The same challenges happen related to sustainability. Our current (western) habits are draining the planet and only behavioral changes can stop or reduce the damage. Most of us are aware that the planet is limited in resources and we need an energy transition in the long term. But are you able to learn those new behaviors or do you give up and hold on to the good old past?
 Note: It’s important to understand that individual actions are not the primary cause of the climate crisis, nor can they alone resolve it. This idea is often promoted by industries. The bigger question is whether our societies can change—consider where financial resources are being allocated.
Note: It’s important to understand that individual actions are not the primary cause of the climate crisis, nor can they alone resolve it. This idea is often promoted by industries. The bigger question is whether our societies can change—consider where financial resources are being allocated.
Sustainability and Systems Thinking
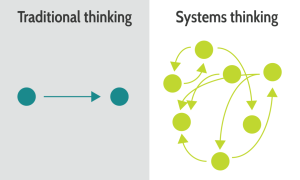 We cannot just produce product or consume like crazy if we care about future generations. It is not longer only about the money, it is about next generations and the environment – if you care. This complexity pushes us toward Systems Thinking – many topics are connected – addressing a single topic does not solve the rest.
We cannot just produce product or consume like crazy if we care about future generations. It is not longer only about the money, it is about next generations and the environment – if you care. This complexity pushes us toward Systems Thinking – many topics are connected – addressing a single topic does not solve the rest.
I wrote two posts in 2022 about Systems Thinking t: SYSTEMS THINKING – a must-have skill in the 21st century and as a follow-up based on interactions Systems Thinking: a second thought. The challenge with Systems Thinking is that the solution is not black or white and requires brain power.
Sustainability and Political Leadership
With what is happening currently in our societies you can see that sustainability is strongly connected to its country’s political system. The bad news for long term issues democracy is probably the worst. Let me share some observations.
Europe
 Historically Europe has been a stable democracy since the second world war and the European Union has been able to establish quite a unified voice step by step. Of course the European Union was heavily influenced by the Automotive and Agricultural lobby. Still the European Green Deal was established with great consensus in the middle instead of focusing on the extremes. A multi-party parliament guarantees a balanced outcome. However type of democracy is still very sensitive for influences from lobbyist and external forces.
Historically Europe has been a stable democracy since the second world war and the European Union has been able to establish quite a unified voice step by step. Of course the European Union was heavily influenced by the Automotive and Agricultural lobby. Still the European Green Deal was established with great consensus in the middle instead of focusing on the extremes. A multi-party parliament guarantees a balanced outcome. However type of democracy is still very sensitive for influences from lobbyist and external forces.
There are so many Dunning-Kruger experts roaring down the common sense debates – mainly in democratic countries. It would be great if people started from the WHY. WHY is someone acting – is it a short-term gain/fear to loose or is there a long-term strategy.
As long as Europe can maintain its consensus culture there is hope for the long-term.
US
 The US has been leading the world in polarization. With two major parties fighting always for the 51 % majority vote, there is no place for consensus. The winner takes it all. And although we call it a democracy, you need to have a lot of money to be elected and money is the driving power behind the elections. The WHY in most cases in the US is about short term money making, although I found an interesting point related to Elon Musk.
The US has been leading the world in polarization. With two major parties fighting always for the 51 % majority vote, there is no place for consensus. The winner takes it all. And although we call it a democracy, you need to have a lot of money to be elected and money is the driving power behind the elections. The WHY in most cases in the US is about short term money making, although I found an interesting point related to Elon Musk.
 In his 2022 interview he shares his vision that the future is in solar energy and batteries with nuclear needed for the transition. Also he is no fan of longevity – quote from the video (5:30)
In his 2022 interview he shares his vision that the future is in solar energy and batteries with nuclear needed for the transition. Also he is no fan of longevity – quote from the video (5:30)
Most people don’t change their mind, they just die. And if they don’t die we will be stuck with old ideas and society won’t advance.
It is a great example of “If you cannot beat them – join them” and then use them to fund your missions. A narcistic president becomes your helper to achieve your long-term strategy.
Saudi Arabia
 Here we are not talking about a democracy anymore and they might seem the biggest enemy for the climate. However they have a long-term strategy. While keeping the world addicted to fossil fuels, they invest heavily in solar and hydrogen and once the western world understands the energy transition is needed, they are far ahead in experience and remain a main energy supplier.
Here we are not talking about a democracy anymore and they might seem the biggest enemy for the climate. However they have a long-term strategy. While keeping the world addicted to fossil fuels, they invest heavily in solar and hydrogen and once the western world understands the energy transition is needed, they are far ahead in experience and remain a main energy supplier.
China
 With 1.4 billion inhabitants and not a democracy either, China has a different mission. Initially as the manufacturing hub for the planet they needed huge amount of energy and therefore they are listed as the most polluting country in the world.
With 1.4 billion inhabitants and not a democracy either, China has a different mission. Initially as the manufacturing hub for the planet they needed huge amount of energy and therefore they are listed as the most polluting country in the world.
However their energy transition towards solar, water, wind and even nuclear goes so much faster than committed in the Paris agreements, as China has a long-term strategy to be energy independent and to be the major supplier in the energy transition. The long-term WHY is clear.
Russia
 It is a pity to mention Russia as with their war-economy and reliance on fossil fuels, they are on a path towards oblivion. Even if they would win a few other wars, innovation is gone and fossil is ending. It will be a blessing for humanity. I hope they will find a new long-term strategy.
It is a pity to mention Russia as with their war-economy and reliance on fossil fuels, they are on a path towards oblivion. Even if they would win a few other wars, innovation is gone and fossil is ending. It will be a blessing for humanity. I hope they will find a new long-term strategy.
Conclusion
PLM and Sustainability are important for the long-term, despite the throw-back you might see on the short term due to politics and lobbies. In addition we need courage to keep on focusing on the long-term as our journey has just started.
Feel free to share your thoughts with compassion and respect for other opinions.

 First, I wish you all a prosperous 2025 and hope you will take the time to digest information beyond headlines.
First, I wish you all a prosperous 2025 and hope you will take the time to digest information beyond headlines.
Taking time to digest information is my number one principle now, which means you will see fewer blog posts from my side and potentially more podcast recordings.
My theme for 2025 : “It is all about people, data,
a sustainable business and a smooth digital transformation”.
Fewer blog posts
Fewer blog posts, as although AI might be a blessing for content writers, it becomes as exciting as Wikipedia pages. Here, I think differently than Oleg Shilovitsky, whose posts brought innovative thoughts to our PLM community – “Just my thoughts”.
![]() Now Oleg endorses AI, as you can read in his post: PLM in 2025: A new chapter of blogging transformation. I asked ChatGPT to summarize my post in 50 words, and this is the answer I got – it saves you reading the rest:
Now Oleg endorses AI, as you can read in his post: PLM in 2025: A new chapter of blogging transformation. I asked ChatGPT to summarize my post in 50 words, and this is the answer I got – it saves you reading the rest:
The author’s 2025 focus emphasizes digesting information deeply, reducing blog posts, and increasing podcast recordings exploring real-life PLM applications. They stress balancing people and data-centric strategies, sustainable digital transformation, AI’s transformative role, and forward-looking concepts like Fusion Strategy. Success requires prioritizing business needs, people, and accurate data to harness AI’s potential.
![]() Summarizing blog posts with AI saves you time. Thinking about AI-generated content, I understand that when you work in marketing, you want to create visibility for your brand or offer.
Summarizing blog posts with AI saves you time. Thinking about AI-generated content, I understand that when you work in marketing, you want to create visibility for your brand or offer.
Do we need a blogging transformation? I am used to browsing through marketing content and then looking for the reality beyond it – facts and figures. Now it will be harder to discover innovative thoughts in this AI-generated domain.
Am I old fashioned? Time will tell.
More podcast recordings
 As I wrote in a recent post, “PLM in real life and Gen AI“, I believe we can learn much from exploring real-life examples. You can always find the theory somewhere and many of the articles make sense and address common points. Some random examples:
As I wrote in a recent post, “PLM in real life and Gen AI“, I believe we can learn much from exploring real-life examples. You can always find the theory somewhere and many of the articles make sense and address common points. Some random examples:
- Top 4 Reasons Why PLM Implementations Fail
- 13 Common PLM Implementation Problems And How to Avoid Them
- 10 steps to a Successful PLM implementation
- 11 Essential Product Lifecycle Management Best Practices for Success
 Similar recommendations exist for topics like ERP, MES, CRM or Digital Transformation (one of the most hyped terms).
Similar recommendations exist for topics like ERP, MES, CRM or Digital Transformation (one of the most hyped terms).
They all describe WHAT to do or not to do. The challenge however is: HOW to apply this knowledge in your unique environment, considering people, skills, politics and culture.
With the focus on the HOW, I worked with Helena Gutierrez last year on the Share PLM podcast series 2. In this series, we interviewed successful individuals from various organizations to explore HOW they approached PLM within their companies. Our goal was to gain insights from their experiences, particularly those moments when things didn’t go as planned, as these are often the most valuable learning opportunities.
 I am excited to announce that the podcast will continue this year with Series 3! Joining me this season will be Beatriz Gonzales, Share PLM’s co-founder and new CEO. For Series 3, we’ve decided to broaden the scope of our interviews. In addition to featuring professionals working within companies, we’ll also speak with external experts, such as coaches and implementation partners, who support organizations in their PLM journey.
I am excited to announce that the podcast will continue this year with Series 3! Joining me this season will be Beatriz Gonzales, Share PLM’s co-founder and new CEO. For Series 3, we’ve decided to broaden the scope of our interviews. In addition to featuring professionals working within companies, we’ll also speak with external experts, such as coaches and implementation partners, who support organizations in their PLM journey.
Our goal is to uncover not only best practices from these experts but also insights into emerging “next practices.”
Stay tuned for series 3!
#datacentric or #peoplecentric ?
 The title of the paragraph covers topics from the previous paragraphs and it was also the theme from a recent post shared through LinkedIn from Lionel Grealou: Driving Transformation: Data or People First?
The title of the paragraph covers topics from the previous paragraphs and it was also the theme from a recent post shared through LinkedIn from Lionel Grealou: Driving Transformation: Data or People First?
We all agree here that it is not either one or the other, and as the discussion related to the post further clarifies, it is about a business strategy that leads to both of these aspects.
This is the challenge with strategies. A strategy can be excellent – on paper – the success comes from the execution.
This discussion reminds me of the lecture Yousef Hooshmand gave at the PLM platform in the Netherlands last year – two of his images that could cover the whole debate:
Whatever you implement starts from the user experience, giving the data-centric approach the highest priority and designing the solution for change, meaning avoiding embedded hard-coded ways of working.
![]() While companies strive to standardize processes to provide efficiency and traceability, the processes should be reconfigurable or adaptable when needed, reconfigured on reliable data sources.
While companies strive to standardize processes to provide efficiency and traceability, the processes should be reconfigurable or adaptable when needed, reconfigured on reliable data sources.
Jan Bosch shared this last thought too in his Digital Reflection #5: Cog in the Machine. My favorite quote from this refection
“However, in a world where change is accelerating, we need to organize ourselves in ways that make it easy to incorporate change and not ulcer-inducing hard. How do we get there?”
Of course, before we reach tools and technology, the other image Yousef Hooshmand shared below gives a guiding principle that I believe everyone should follow in their context.
It starts with having a C-level long-term commitment when you want to perform a business transformation, and then, in an MVP approach, you start from the business, which will ultimately lead you to the tools and technologies.
 The challenge seen in this discussion is that:
The challenge seen in this discussion is that:
most manufacturing companies are still too focused on investing in what they are good at now and do not explore the future enough.
This behavior is why Industry 4.0 is still far from being implemented, and the current German manufacturing industry is in a crisis.
It requires an organization that understands the big picture and has a (fusion) strategy.
Fusion Strategy ?
 Is the Fusion Strategy the next step, as Steef Klein often mentions in our PLM discussions? The Fusion Strategy, introduced by world-renowned innovation guru Vijay Govindarajan (The Three Box Solution) and digital strategy expert Venkat Venkatraman (Fusion Strategy), offers a roadmap that will help industrial companies combine what they do best – creating physical products – with what digital technology companies do best – capturing and analyzing data through algorithms and AI.
Is the Fusion Strategy the next step, as Steef Klein often mentions in our PLM discussions? The Fusion Strategy, introduced by world-renowned innovation guru Vijay Govindarajan (The Three Box Solution) and digital strategy expert Venkat Venkatraman (Fusion Strategy), offers a roadmap that will help industrial companies combine what they do best – creating physical products – with what digital technology companies do best – capturing and analyzing data through algorithms and AI.
 It is a topic I want to explore this year and see how to connect it to companies in my ecosystem. It is an unknown phenomenon as most of them struggle with a data-driven foundation and skills and focus on the right AI applications.
It is a topic I want to explore this year and see how to connect it to companies in my ecosystem. It is an unknown phenomenon as most of them struggle with a data-driven foundation and skills and focus on the right AI applications.
The End of SaaS?
 A potential interesting trend als related to AI I want to clarify further is the modern enterprise architecture . Over the past two years, we have seen a growing understanding that we should not think in systems connected through interfaces but towards a digitally connected infrastructure where APIs, low-code platforms or standardized interfaces will be responsible for real-time collaboration.
A potential interesting trend als related to AI I want to clarify further is the modern enterprise architecture . Over the past two years, we have seen a growing understanding that we should not think in systems connected through interfaces but towards a digitally connected infrastructure where APIs, low-code platforms or standardized interfaces will be responsible for real-time collaboration.
I wrote about these concepts in my PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe review. Look at the section: R-evolutionizing PLM and ERP and Heliple. At that time, I shared the picture below, which illustrates the digital enterprise.
The five depicted platforms in the image ( IIoT, CRM, PLM, ERP, MES) are not necessarily a single system. They can be an ecosystem of applications and services providing capabilities in that domain. In modern ways of thinking, each platform could be built upon a SaaS portfolio, ensuring optimal and scalable collaboration based on the company’s needs.
Implementing such an enterprise based on a combination of SaaS offerings might be a strategy for companies to eliminate IT overhead.
However, known forward-thinking experts like Vijay Govindarajan and Venkat Venkatraman with their Fusion Strategy. Also, Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, imagines instead of connected platforms a future with an AI layer taking care of the context of the information – the Microsoft Copilot message. Some of his statements:
This transformation is poised to disrupt traditional tools and workflows, paving the way for a new generation of applications.
The business logic is all going to these AI agents. They’re not going to discriminate between what the backend is — they’ll update multiple databases, and all the logic will be in the AI tier.
Software as a Business Weapon?
Interesting thoughts to follow and to combine with this Forbes article, The End Of The SaaS Era: Rethinking Software’s Role In Business by Josipa Majic Predin. She introduces the New Paradigm: Software as a Business Weapon.
Quote:
Instead of focusing solely on selling software subscriptions, innovative companies are using software to enhance and transform existing businesses. The goal is to leverage technology to make certain businesses significantly more valuable, efficient, and competitive.
This approach involves developing software that can improve the operations of “real world” businesses by 20-30% or more. By creating such powerful tools, technology companies can position themselves to acquire or partner with the businesses they’ve enhanced, thereby capturing a larger share of the value they’ve created.
 It is interesting to see these thoughts popping up, usually 10 to 20 years ahead before companies adopt them. However, I believe with AI’s unleashed power, this is where we should be active and learn. It is an exciting area where terms like eBOM or mBOM sound hackneyed.
It is interesting to see these thoughts popping up, usually 10 to 20 years ahead before companies adopt them. However, I believe with AI’s unleashed power, this is where we should be active and learn. It is an exciting area where terms like eBOM or mBOM sound hackneyed.
Sustainability?
As a PLM Green Global Alliance member, I will continue to explore topics related to PLM and how they can serve Sustainability. They are connected as the image from the 2022 PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe indicates:

I will keep on focusing on separate areas within my PGGA network.
Conclusion
I believe 2025 will be the year to focus on understanding the practical applications of AI. Amid the hype and noise, there lies significant potential to re-imagine our PLM landscape and vision. However, success begins with prioritizing the business, empowering people, and ensuring accurate data.

 This year, I will celebrate 25 years since I started my company, TacIT, to focus on knowledge management. However, quickly, I was back in the domain of engineering data management, which became a broader topic, which we now call PLM.
This year, I will celebrate 25 years since I started my company, TacIT, to focus on knowledge management. However, quickly, I was back in the domain of engineering data management, which became a broader topic, which we now call PLM.
Looking back, there have been significant changes in these 25 years, from systems to strategy, for documents to data, from linear to iterative. However, in this post, I want to look at my 2024 observations to see where we can progress. This brings me to the first observation.
PLM is human
Despite many academic and marketing arguments describing WHAT and WHY companies need specific business or software capabilities, there is, above all, the need for people to be personally inspired and connected. We want to belong to a successful group of people, teams and companies because we are humans, not resources.
It is all about people, which was also the title of my session during the March 2024 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference in Eindhoven (NL). I led a panel discussion on the importance of people with Dr. Cara Antoine, Daniel Schöpf, and Florens Wolters, each of whom actively led transformational initiatives within their companies.
 Through Dr. Cara Antoine, e at Capgemini and a key voice for women in tech, I learned about her book Make It Personal. The book inspired me and motivated me to continue using a human-centric approach. Give this book to your leadership and read it yourself. It is practical, easy to read, and encouraging
Through Dr. Cara Antoine, e at Capgemini and a key voice for women in tech, I learned about her book Make It Personal. The book inspired me and motivated me to continue using a human-centric approach. Give this book to your leadership and read it yourself. It is practical, easy to read, and encouraging
Recently, in my post “PLM in real life and Gen AI“, I shared insights related to PLM blogs and Gen AI – original content is becoming increasingly the same, and the human touch is disappearing, while generating more and longer blogs.
 I propose keeping Gen AI-generated text for the boring part of PLM and exploring the human side of PLM engagements in blogs. What does this mean? In the post, I also shared the highlights of the Series 2 podcast I did together with Helena Gutierrez from Share PLM. Every recording had its unique human touch and knowledge.
I propose keeping Gen AI-generated text for the boring part of PLM and exploring the human side of PLM engagements in blogs. What does this mean? In the post, I also shared the highlights of the Series 2 podcast I did together with Helena Gutierrez from Share PLM. Every recording had its unique human touch and knowledge.
We are now in full preparation for Series 3—let us know who your hero is and who should be our guest in 2025!
PLM is business
One of the most significant changes I noticed in my PLM-related projects was that many of the activities connected the PLM activities to the company’s business objectives. Not surprisingly, it was mostly a bottom-up activity, explaining to the upper management that a modern, data-driven PLM strategy is crucial to achieving business or sustainability goals.
I wrote two long posts about these experiences. The first one,” PLM – business first,” zooms in on the changing mindset that PLM is not an engineering system anymore but part of a digital infrastructure that supports companies in achieving their business goals. The image below from Dr. Yousef Hooshmand is one of my favorites in this context. The 5 + 1 steps, where the extra step is crucial: Long Executive Commitment.
So, to get an executive commitment, you need to explain and address business challenges.
Executive commitment and participation can be achieved through a Benefits Dependency Network approach, as illustrated in this webinar I did with the Heliple-2 team, where we were justifying the business needs for Federated PLM. More about the Federated PLM part in the next paragraph.
Another point to consider is that when the PLM team is part of the IT organization (the costs side), they have a big challenge in leading or even participating in business discussions. In this context, read (again) Jan Bosch’s post: Structure Eats Strategy.
 The second post, more recent, summarized the experiences I had with several customer engagements. The title says it all: “Don’t use the P**-word! – 5 lessons learned“, with an overlap in content with the first post.
The second post, more recent, summarized the experiences I had with several customer engagements. The title says it all: “Don’t use the P**-word! – 5 lessons learned“, with an overlap in content with the first post.
Conclusion: A successful PLM strategy starts with the business and needs storytelling to align all stakeholders with a shared vision or goal.
PLM is technology
This year has seen the maturation of PLM technology concepts. We are moving away from a monolithic PLM system and exploring federated and connected infrastructures, preferably a mix of Systems of Record (the old PLMs/ERPs) and Systems of Engagement (the new ways of domain collaboration). The Heliple project manifests such an approach, where the vertical layers are Systems of Record, and the horizontal modules could be Systems of Engagement.
I had several discussions with typical System of Engagement vendors, like Colab (“Where traditional PLM fails”) and Partful (“Connected Digital Thread for Lower and Mid-market OEMs“), but I also had broader discussions during the PLM Roadmap PDT Europe conference – see: R-evolutionizing PLM and ERP and Heliple.
 I also follow Dr. Jorg Fischer, who lectures about digital transformation concepts in the manufacturing business domain. Unfortunately, for a broader audience, Jörg published a lot in German, and typically, his references for PLM and ERP are based on SAP and Teamcenter. His blog posts are always interesting to follow – have a look at his recent blog in English: 7 keys to solve PLM & ERP.
I also follow Dr. Jorg Fischer, who lectures about digital transformation concepts in the manufacturing business domain. Unfortunately, for a broader audience, Jörg published a lot in German, and typically, his references for PLM and ERP are based on SAP and Teamcenter. His blog posts are always interesting to follow – have a look at his recent blog in English: 7 keys to solve PLM & ERP.
 Of course, Oleg Shilovitsky’s impressive and continuous flow of posts related to modern PLM concepts is amazing—just browse through his Beyond PLM home page to read about the actual topics happening in his PLM ecosystem or for example, read about modern technology concepts in this recent OpenBOM article.
Of course, Oleg Shilovitsky’s impressive and continuous flow of posts related to modern PLM concepts is amazing—just browse through his Beyond PLM home page to read about the actual topics happening in his PLM ecosystem or for example, read about modern technology concepts in this recent OpenBOM article.
Conceptually, we are making progress. As a commonality, all future concepts focus on data, not so much on managing documents—and here comes the focus on data.
PLM needs accurate data
In a data-driven environment, apps or systems will use a collection of datasets to provide a user with a working environment, either a dashboard or an interactive real-time environment. Below is my AI (Artist Impression) of a digital enterprise.
Of course, it seems logical; the data must be accurate as you no longer have control over access to the data in a data-driven environment. You can be accountable for the data; others can consume the data you created without checking its accuracy by your guidance.
Therefore, data governance and an excellent enterprise architecture are crucial to support the new paradigm:
The nearest source of truth supported by a single source of change
Quote: Yousef Hoohmand
Forget the Single Source of Truth idea, a previous century paradigm.
With data comes Artificial intelligence and algorithms that can play an essential role in your business, providing solutions or insights that support decision-making.
![]() In 2024, most of us have been exploring the benefits of ChatGPT and Generative AI. You can describe examples of where AI could assist in every aspect of the product lifecycle. I saw great examples from Eaton, Ocado, and others at the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference.
In 2024, most of us have been exploring the benefits of ChatGPT and Generative AI. You can describe examples of where AI could assist in every aspect of the product lifecycle. I saw great examples from Eaton, Ocado, and others at the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference.
See my review here: A long week after the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference.
Still, before benefiting from AI in your organization, it remains essential that the AI runs on top of accurate data.
Sustainability needs (digital) PLM
 This paragraph is the only reverse dependency towards PLM and probably the one that is less in people’s minds, perhaps because PLM is already complex enough. In 2024, with the PLM Green Global Alliance, we had good conversations with PLM-related software vendors or service partners (aPriori, Configit, Makersite, PTC, SAP, Siemens and Transition Technologies PSC) where we discussed their solutions and how they are used in the field by companies.
This paragraph is the only reverse dependency towards PLM and probably the one that is less in people’s minds, perhaps because PLM is already complex enough. In 2024, with the PLM Green Global Alliance, we had good conversations with PLM-related software vendors or service partners (aPriori, Configit, Makersite, PTC, SAP, Siemens and Transition Technologies PSC) where we discussed their solutions and how they are used in the field by companies.
We discovered here that most activities are driven by regulations, like ESG reporting, the new CSRD directive for Europe and the implementation of the Digital Product Passport. What is clear from all these activities is that companies need to have a data-driven PLM infrastructure to connect product data to environmental impacts, like carbon emissions equivalents.
Besides complying with regulations, I have been discussing the topic of Product-As-A-Service, or the Product Service System, this year, with excellent feedback from Dave Duncan. You can find a link to his speech: Improving Product Sustainability – PTC with PGGA.
Also, during the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, I discussed this topic, explaining that achieving a circular economy is a long-term vision, and the starting point is to establish a connected infrastructure within your organizations and with your customers/users in the field.
 Sustainability should be on everyone’s agenda. From the interactions on LinkedIn, you can see that we prefer to discuss terms like PDM/PLM or eBOM/mBOM in the PLM domain. Very few connect PLM to sustainability.
Sustainability should be on everyone’s agenda. From the interactions on LinkedIn, you can see that we prefer to discuss terms like PDM/PLM or eBOM/mBOM in the PLM domain. Very few connect PLM to sustainability.
Sustainability is a long-term mission; however, as we have seen from long-term missions, they can be overwhelmed by the day’s madness and short-term needs.
PLM is Politics
You might not expect this paragraph in my log, as most PLM discussions are about the WHAT and the WHY of a PLM solution or infrastructure. However, the most challenging part of PLM is the HOW, and this is the area that I am still focused on.
In the early days of mediating mainly in SmarTeam implementations, it became clear that the technology was not the issue. A crisis was often due to a lack of (technical) skills or methodology and misplaced expectations.
When the way out became clear, politics often started. Sometimes, there was the HIPPO (HIghest Paid Person’s Opinion) in the company, as Peter Vind explained, or there was the blame game, which I described in my 2019 “The PLM blame game post”.
What makes it even more difficult is that people’s opinions in PLM discussions are often influenced by their friendly relations or history with a particular vendor or implementer from the past, which troubles a proper solution path.
These aspects are challenging to discuss, and nobody wants to discuss them openly. A company (and a country) must promote curiosity instead of adhering to mainstream thinking and working methods. In our latest Share PLM podcast, Brian Berger, a VP at Metso, mentions the importance of diversity within an organization.
“It is a constant element of working in a global business, and the importance cannot be overstated.”
This observation should make us think again when we want to simplify everything and dim the colors.
Conclusion
Initially, I thought this would be a shorter post, but again, it became a long read – therefore, perhaps ideal when closing 2024 and looking forward to activities and focus for 2025. Use this time to read books and educate yourself beyond the social media posts (even my blogs are limited 😉)
In addition, I noticed the build-up of this post was unconsciously influenced by Martijn Dullaart‘s series of messages titled “Configuration Management is ……”. Thanks, Martijn, for your continuous contributions to our joint passion – a digital enterprise where PLM and CM flawlessly interact based on methodology and accurate data.

 Congratulations if you have shown you can resist the psychological and emotional pressure and did not purchase anything in the context of Black Friday. However, we must not forget that another big part of the world cannot afford this behavior, as they do not have the means to do so – ultimate Black Friday might be their dream and a fast track to more enormous challenges.
Congratulations if you have shown you can resist the psychological and emotional pressure and did not purchase anything in the context of Black Friday. However, we must not forget that another big part of the world cannot afford this behavior, as they do not have the means to do so – ultimate Black Friday might be their dream and a fast track to more enormous challenges.
The difference between our societies, all living on the same planet, is illustrated in the image below, illustrating the unfairness of this situation
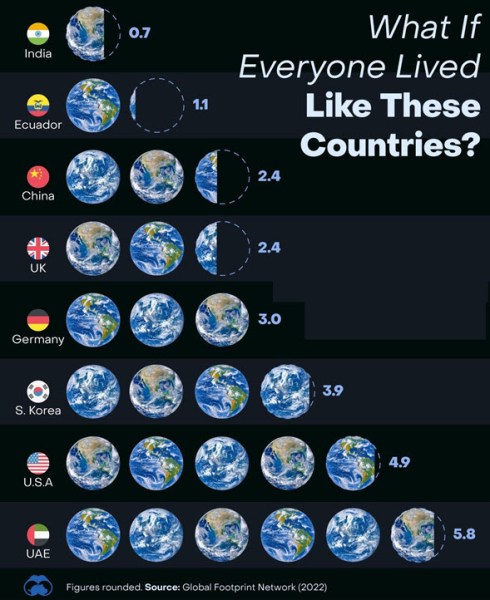
What the image also shows is a warning that we all have to act, as step by step, we will reach planet boundaries for resources.
 Or we need more planets, and I understand a brilliant guy is already working on it. Let’s go to Mars and enjoy life there.
Or we need more planets, and I understand a brilliant guy is already working on it. Let’s go to Mars and enjoy life there.
For those generations staying on this planet, there is only one option: we need to change our economy of unlimited growth and reconsider how we use our natural resources.
The circular economy?
You are probably familiar with the butterfly diagram from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, where we see the linear process: Take-Make-Use-Waste in the middle.
This approach should be replaced by more advanced regeneration loops on the left side and the five R’s on the right: Reduce, Repair, Reuse, Refurbish and Recycle as the ultimate goal is the minimum leakage of Earth resources.
Closely related to the Circular Economy concept is the complementary Cradle-To-Cradle design approach. In this case, while designing our products, we also consider the end of life of a product as the start for other products to be created based on the materials used.
The CE butterfly diagram’s right side is where product design plays a significant role and where we, as a PLM community, should be active. Each loop has its own characteristics, and the SHARE loop is the one I focused on during the recent PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference in Gothenburg.
As you can see, the Maintain, Reuse, Refurbish and Recycle loops depend on product design strategies, in particular, modularity and, of course, depending on material choices.
 It is important to note that the recycle loop is the most overestimated loop, where we might contribute to recycling (glass, paper, plastic) in our daily lives; however, other materials, like composites often with embedded electronics, have a much more significant impact.
It is important to note that the recycle loop is the most overestimated loop, where we might contribute to recycling (glass, paper, plastic) in our daily lives; however, other materials, like composites often with embedded electronics, have a much more significant impact.
Watch the funny meme in this post: “We did everything we could– we brought our own bags.”
![]() The title of my presentation was: Products as a Service – The Ultimate Sustainable Economy?
The title of my presentation was: Products as a Service – The Ultimate Sustainable Economy?
You can find my presentation on SlideShare here.
Let’s focus on the remainder of the presentation’s topic: Product As A Service.
The Product Service System
 Where Product As A Service might be the ultimate dream for an almost wasteless society, Ida Auken, a Danish member of the parliament, gave a thought-provoking lecture in that context at the 2016 World Economic Forum. Her lecture was summarized afterward as
Where Product As A Service might be the ultimate dream for an almost wasteless society, Ida Auken, a Danish member of the parliament, gave a thought-provoking lecture in that context at the 2016 World Economic Forum. Her lecture was summarized afterward as
“In the future, you will own nothing and be happy.”
A theme also picked up by conspiracy thinkers during the COVID pandemic, claiming “they” are making us economic slaves and consumers. With Black Friday in mind, I do not think there is a conspiracy; it is the opposite.
Closer to implementing everywhere Product as a Service for our whole economy, we might be going into Product Service Systems.
As the image shows, a product service system is a combination of providing a product with related services to create value for the customer.
In the ultimate format, the manufacturer owns the products and provides the services, keeping full control of the performance and materials during the product lifecycle. The benefits for the customer are that they pay only for the usage of the product and, therefore, do not need to invest upfront in the solution (CAPEX), but they only pay when using the solution (OPEX).
 A great example of this concept is Spotify or other streaming services. You do not pay for the disc/box anymore; you pay for the usage, and the model is a win-win for consumers (many titles) and producers (massive reach).
A great example of this concept is Spotify or other streaming services. You do not pay for the disc/box anymore; you pay for the usage, and the model is a win-win for consumers (many titles) and producers (massive reach).
Although the Product Service System will probably reach consumers later, the most significant potential is currently in the B2B business model, e.g., transportation as a service and special equipment usage as a service. Examples are popping up in various industries.
 My presentation focused on three steps that manufacturing companies need to consider now and in the future when moving to a Product Service System.
My presentation focused on three steps that manufacturing companies need to consider now and in the future when moving to a Product Service System.
Step 1: Get (digital) connected to your Product and customer
A foundational step companies must take is to create a digital infrastructure to support all stakeholders in the product service offering. Currently, many companies have a siloed approach where each discipline Marketing/Sales, R&D, Engineering, Manufacturing and Sales will have their own systems.
Digital Transformation in the PLM domain is needed here – where are you on this level?
But it is not only the technical silos that impede the end-to-end visibility of information. If there are no business targets to create and maintain the end-to-end information sharing, you can not expect it to happen.
Therefore, companies should invest in the digitalization of their ways of working, implementing an end-to-end digital thread AND changing their linear New Product Development process into a customer-driven DevOp approach. The PTC image below shows the way to imagine a end-to-end connected environment

In a Product Service System, the customer is the solution user, and the solution provider is responsible for the uptime and improvement of the solution over time.
 As an upcoming bonus and a must, companies need to use AI to run their Product Service System as it will improve customer knowledge and trends. Don’t forget that AI (and Digital Twins) runs best on reliable data.
As an upcoming bonus and a must, companies need to use AI to run their Product Service System as it will improve customer knowledge and trends. Don’t forget that AI (and Digital Twins) runs best on reliable data.
Step 2 From Product to Experience
A Product Service System is not business as usual by providing products with some additional services. Besides concepts such as Digital Thread and Digital Twins of the solution, there is also the need to change the company’s business model.
 In the old way, customers buy the product; in the Product Service System, the customer becomes a user. We should align the company and business to become user-centric and keep the user inspired by the experience of the Product Service System.
In the old way, customers buy the product; in the Product Service System, the customer becomes a user. We should align the company and business to become user-centric and keep the user inspired by the experience of the Product Service System.
In this context, there are two interesting articles to read:
- Jan Bosch: From Agile to Radical: Business Model
- Chris Seiler: How to escape the vicious circle in times of transformation?
The change in business model means that companies should think about a circular customer journey.
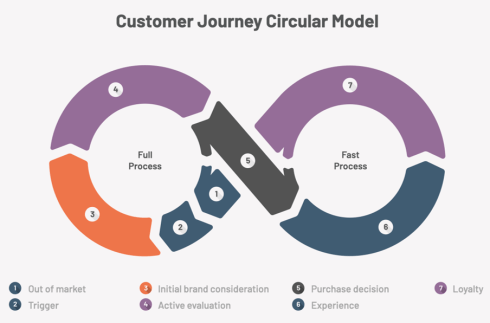
As the company will remain the product owner, it is crucial to understand what happens when the customers stop using the service or how to ensure maintenance and upgrades.
In addition, to keep the customer satisfied, it remains vital to discover the customer KPIs and how additional services could potentially improve the relationship. Again, AI can help find relationships that are not yet digitally established.
 Step 2: From product to experience can already significantly impact organizations. The traditional salesperson’s role will disappear and be replaced by excellence in marketing, services and product management.
Step 2: From product to experience can already significantly impact organizations. The traditional salesperson’s role will disappear and be replaced by excellence in marketing, services and product management.
This will not happen quickly as, besides the vision, there needs to be an evolutionary path to the new business model.
Therefore, companies must analyze their portfolio and start experimenting with a small product, converting it into a product service system. Starting simple allows companies to learn and be prepared for scaling up.
A Product Service System also influences a company’s cash flow as revenue streams will change.
 When scaling up slowly, the company might be able to finance this transition themselves. Another option, already happening, is for a third party to finance the Product Service System – think about car leasing, power by the hour, or some industrial equipment vendors.
When scaling up slowly, the company might be able to finance this transition themselves. Another option, already happening, is for a third party to finance the Product Service System – think about car leasing, power by the hour, or some industrial equipment vendors.
Step 3 Towards a doughnut economy?
The last step is probably a giant step or even a journey. An economic mindset shift is needed from the ever-growing linear economy towards an economy flourishing for everyone within economic, environmental and social boundaries.
Unlimited growth is the biggest misconception on a planet reaching its borders. Either we need more planets, or we need to adjust our society.
In that context, I read the book “The Doughnut Economy” by Kate Raworth, a recognized thought leader who explains how a future economic model can flourish, including a circular economy, and you will be happy.
 But we must abandon the old business models and habits – there will be a lot of resistance to change before people are forced to change. This change can take generations as the outside world will not change without a reason, and the established ones will fight for their privileges.
But we must abandon the old business models and habits – there will be a lot of resistance to change before people are forced to change. This change can take generations as the outside world will not change without a reason, and the established ones will fight for their privileges.
It is a logical process where people and boundaries will learn to find a new balance. Will it be in a Doughnut Economy, or did we overlook some bright other concepts?
Conclusion
The week after Black Friday and hopefully the month after all the Christmas presents, it is time to formulate your good intentions for 2025. As humans, we should consume less; as companies, we should direct our future to a sustainable future by exploring the potential of the Product Service System and beyond.
 Recently, I noticed I reduced my blogging activities as many topics have already been discussed and repeatably published without new content.
Recently, I noticed I reduced my blogging activities as many topics have already been discussed and repeatably published without new content.
With the upcoming of Gen AI and ChatGPT, I believe my PLM feeds are flooded by AI-generated blog posts.
The ChatGPT option
 Most companies are not frontrunners in using extremely modern PLM concepts, so you can type risk-free questions and get common-sense answers.
Most companies are not frontrunners in using extremely modern PLM concepts, so you can type risk-free questions and get common-sense answers.
I just tried these five questions:
- Why do we need an MBOM in PLM, and which industries benefit the most?
- What is the difference between a PLM system and a PLM strategy?
- Why do so many PLM projects fail?
- Why do so many ERP projects fail?
- What are the changes and benefits of a model-based approach to product lifecycle management?
![]() Note: Questions 3 and 4 have almost similar causes and impacts, although slightly different, which is to be expected given the scope of the domain.
Note: Questions 3 and 4 have almost similar causes and impacts, although slightly different, which is to be expected given the scope of the domain.
All these questions provided enough information for a blog post based on the answer. This illustrates that if you are writing about what are current best practices in the field – stop writing – the knowledge is there.
PLM in the real life
Recently, I had several discussions about which skills a PLM expert should have or which topics a PLM project should address.
PLM for the individual
 For the individual, there are often certifications to obtain. Roger Tempest has been fighting for PLM professional recognition through certification – a challenge due to the broad scope and possibilities. Read more about Roger’s work in this post: PLM is complex (and we have to accept it?)
For the individual, there are often certifications to obtain. Roger Tempest has been fighting for PLM professional recognition through certification – a challenge due to the broad scope and possibilities. Read more about Roger’s work in this post: PLM is complex (and we have to accept it?)
PLM vendors and system integrators often certify their staff or resellers to guarantee the quality of their solution delivery. Potential topics will be missed as they do not fulfill the vendor’s or integrator’s business purpose.
Asking ChatGPT about the required skills for a PLM expert, these were the top 5 answers:
- Technical skills
- Domain Knowledge
- Analytical and Problem-Solving Skills
- Interpersonal and Management Skills
- Strategic Thinking
 It was interesting to see the order proposed by ChatGPT. Fist the tools (technology), then the processes (domain knowledge / analytical thinking), and last the people and business (strategy and interpersonal and management skills) It is hard to find individuals with all these skills in a single person.
It was interesting to see the order proposed by ChatGPT. Fist the tools (technology), then the processes (domain knowledge / analytical thinking), and last the people and business (strategy and interpersonal and management skills) It is hard to find individuals with all these skills in a single person.
Although we want people to be that broad in their skills, job offerings are mainly looking for the expert in one domain, be it strategy, communication, industry or technology. To get an impression of the skills read my PLM and Education concluding blog post.
Now, let’s see what it means for an organization.
PLM for the organization
In this area, one of the most consistent frameworks I have seen over time is CIMdata‘s Critical Dozen. Although they refer less to skills and more to trends and enablers, a company should invest in – educate people & build skills – to support a successful digital transformation in the PLM domain.
 Oleg Shilovitsky’s recent blog post, The 12 “P” s of PLM Explained by Role: How to Make PLM More Than Just a Buzzword describes in an AI manner the various aspects of the term PLM, using 12 P**-words, reacting to Lionel Grealou’ s post: Making PLM Great Again
Oleg Shilovitsky’s recent blog post, The 12 “P” s of PLM Explained by Role: How to Make PLM More Than Just a Buzzword describes in an AI manner the various aspects of the term PLM, using 12 P**-words, reacting to Lionel Grealou’ s post: Making PLM Great Again
The challenge I see with these types of posts is: “OK, what to do now? Where to start?”
I believe where to start at the first place is a commonly agreed topic.
Everything starts from having a purpose and a vision. And this vision should be supported by a motivating story about the WHY that inspires everyone.
 It is teamwork to define such a strategy, communicate it through a compelling story and make it personal. An excellent book to read is Make it personal from Dr. Cara Antoine – click on the image to discover the content and find my review why I believe this book is so compelling.
It is teamwork to define such a strategy, communicate it through a compelling story and make it personal. An excellent book to read is Make it personal from Dr. Cara Antoine – click on the image to discover the content and find my review why I believe this book is so compelling.
An important reason why we have to make transformations personal is because we are dealing first of all with human beings. And human beings are driven by emotions first even before ratio kicks in. We see it everywhere and unfortunately also in politics.
The HOW from real-life
 This question cannot be answered by external PLM vendors, consultants or system integrators. Forget the Out-of-the-Box templates or the industry best practices (from the past), but start from your company’s culture and vision, introducing step-by-step new technologies, ways of working and business models to move towards the company’s vision target.
This question cannot be answered by external PLM vendors, consultants or system integrators. Forget the Out-of-the-Box templates or the industry best practices (from the past), but start from your company’s culture and vision, introducing step-by-step new technologies, ways of working and business models to move towards the company’s vision target.
Building the HOW is not an easy journey, and to illustrate the variety of skills needed to be successful, I worked with Share PLM on their Series 2 podcast. You can find the complete overview here. There is one more to come to conclude this year.
 Our focus was to speak only with PLM experts from the field, understanding their day-to-day challenges with a focus on HOW they did it and WHAT they learned.
Our focus was to speak only with PLM experts from the field, understanding their day-to-day challenges with a focus on HOW they did it and WHAT they learned.
And this is what we learned:
Unveiling FLSmidth’s Industrial Equipment PLM Transformation: From Projects to Products
 It was our first episode of Series 2, and we spoke with Johan Mikkelä, Head of the PLM Solution Architecture at FLSmidth.
It was our first episode of Series 2, and we spoke with Johan Mikkelä, Head of the PLM Solution Architecture at FLSmidth.
FLSmidth provides the global mining and cement industries with equipment and services, which is very much an ETO business moving towards CTO.
We discussed their Industrial Equipment PLM Transformation and the impact it has made.
Start With People: ABB’s Engineering Approach to Digital Transformation
 We spoke with Issam Darraj, who shared his thoughts on human-centric digitalization. Issam talks us through ABB’s engineering perspective on driving transformation and discusses the importance of focusing on your people. Our favorite quote:
We spoke with Issam Darraj, who shared his thoughts on human-centric digitalization. Issam talks us through ABB’s engineering perspective on driving transformation and discusses the importance of focusing on your people. Our favorite quote:
To grow, you need to focus on your people. If your people are happy, you will automatically grow. If your people are unhappy, they will leave you or work against you.
Enabling change: Exploring the human side of digital transformations
 We spoke with Antonio Casaschi as he shared his thoughts on the human side of digital transformation. When discussing the PLM expert, he agrees it is difficult. Our favorite part here:
We spoke with Antonio Casaschi as he shared his thoughts on the human side of digital transformation. When discussing the PLM expert, he agrees it is difficult. Our favorite part here:
“I see a PLM expert as someone with a lot of experience in organizational change management. Of course, maybe people with a different background can see a PLM expert with someone with a lot of knowledge of how you develop products, all the best practices around products, etc. We first need to agree on what a PLM expert is, and then we can agree on how you become an expert in such a domain.”
Revolutionizing PLM: Insights from Yousef Hooshmand
 With Dr. Yousef Hooshmand, writer of the paper: From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and
With Dr. Yousef Hooshmand, writer of the paper: From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and
Data Mesh, with over 15 years of experience in the PLM domain, currently PLM Lead at NIO, we discussed the complexity of digital transformation in the PLM domain and How to deal with legacy, meanwhile implementing a user-centric, data-driven future.
My favorite quote: The End of Single Source of Truth, now it is about The nearest Source of Truth and Single Source of Change.
Steadfast Consistency: Delving into Configuration Management with Martijn Dullaart
 Martijn Dullaart, who is the man behind the blog MDUX: The Future of CM and author of the book The Essential Guide to Part Re-Identification: Unleash the Power of Interchangeability and Traceability, has been active both in the PLM and CM domain and with Martijn the similarities and differences between PLM and CM and why organizations need to be educated on the topic of CM
Martijn Dullaart, who is the man behind the blog MDUX: The Future of CM and author of the book The Essential Guide to Part Re-Identification: Unleash the Power of Interchangeability and Traceability, has been active both in the PLM and CM domain and with Martijn the similarities and differences between PLM and CM and why organizations need to be educated on the topic of CM
The ROI of Digitalization: A Deep Dive into Business Value with Susanna Maëntausta
 With Susanna Maëntausta, we discussed how to implement PLM in non-traditional manufacturing industries, such as the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
With Susanna Maëntausta, we discussed how to implement PLM in non-traditional manufacturing industries, such as the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Susanna teaches us to ensure PLM projects are value-driven, connecting business objectives and KPIs to the implementation and execution steps in the field. Susanna is highly skilled in connecting people at any level of the organization.
Narratives of Change: Grundfos Transformation Tales with Björn Axling
 As Head of PLM and part of the Group Innovation management team at Grundfos, Bjorn Axling aims to drive a Group-wide, cross-functional transformation into more innovative, more efficient, and data-driven ways of working through the product lifecycle from ideation to end-of-life.
As Head of PLM and part of the Group Innovation management team at Grundfos, Bjorn Axling aims to drive a Group-wide, cross-functional transformation into more innovative, more efficient, and data-driven ways of working through the product lifecycle from ideation to end-of-life.
In this episode, you will learn all the various aspects that come together when leading such a transformation in terms of culture, people, communication, and modern technology.
The Next Lane: Marel and the Digital Product Highway with Roger Kabo
 With Roger Kabo, we discussed the steps needed to replace a legacy PLM environment and be open to a modern, federated, and data-driven future.
With Roger Kabo, we discussed the steps needed to replace a legacy PLM environment and be open to a modern, federated, and data-driven future.
Step 1: Start with the end in mind. Every successful business starts with a clear and compelling vision. Your vision should be specific, inspiring, and something your team can rally behind.
Next, build on value and do it step by step.
How do you manage technology and data when you have a diverse product portfolio?
 We talked with Jim van Oss, the former CIO of Moog Inc., for a deep dive into the fascinating world of technology transformations.
We talked with Jim van Oss, the former CIO of Moog Inc., for a deep dive into the fascinating world of technology transformations.
Key Takeaway: Evolving technology requires a clear strategy!
Jim underscores the importance of having a north star to guide your technological advancements, ensuring you remain focused and adaptable in an ever-changing landscape.
Diverse Products, Unified Systems: MBSE Insights with Max Gravel from Moog
 We discussed the future of the Model-Based approaches with Max Gravel – MBD at Gulfstream and MBSE at Moog.
We discussed the future of the Model-Based approaches with Max Gravel – MBD at Gulfstream and MBSE at Moog.
Max Gravel, Manager of Model-Based Engineering at Moog Inc., who is also active in modern CM, emphasizes that understanding your company’s goals with MBD is crucial.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution: it’s about tailoring the strategy to drive real value for your business. The tools are available, but the key lies in addressing the right questions and focusing on what matters most. A great, motivating story containing all the aspects of digital transformation in the PLM domain/
Customer-First PLM: Insights on Digital Transformation and Leadership
 With Helene Arlander, who has been involved in big transformation projects in the telecom industry. Starting from a complex legacy environment, implementing new data-driven approaches. We discussed the importance of managing product portfolios end-to-end and the leadership strategies needed for engaging people in charge.
With Helene Arlander, who has been involved in big transformation projects in the telecom industry. Starting from a complex legacy environment, implementing new data-driven approaches. We discussed the importance of managing product portfolios end-to-end and the leadership strategies needed for engaging people in charge.
We also discussed the role of AI in shaping the future of PLM and the importance of vision, diverse skill sets, and teamwork in transformations.
Conclusion
I believe the time of traditional blogging is over – current PLM concepts and issues can be easily queried by using ChatGPT-like solutions. The fundamental understanding of what you can do now comes from learning and listening to people, not as fast as a TikTok video or Insta message. For me, a podcast is a comfortable method of holistic learning.
Let us know what you think and who should be in Season 3
And for my friends in the United States – Happy Thanksgiving and think about the day after ……..

 Due to other activities, I could not immediately share the second part of the review related to the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, held on 23-24 October in Gothenburg. You can read my first post, mainly about Day 1, here: The weekend after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2024.
Due to other activities, I could not immediately share the second part of the review related to the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, held on 23-24 October in Gothenburg. You can read my first post, mainly about Day 1, here: The weekend after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2024.
There were several interesting sessions which I will not mention here as I want to focus on forward-looking topics with a mix of (federated) data-driven PLM environments and the applicability of AI, staying around 1500 words.
R-evolutionizing PLM and ERP and Heliple
Cristina Paniagua from the Luleå University of Technology closed the first day of the conference, giving us food for thought to discuss over dinner. Her session, describing the Arrowhead fPTN project, fitted nicely with the concepts of the Federated PLM Heliple project presented by Erik Herzog also on Day 2.
They are both research products related to the future state of a digital enterprise. Therefore, it makes sense to treat them together.
Cristina’s session started with sharing the challenges of traditional PLM and ERP systems:
These statements align with the drivers of the Heliple project. The PLM and ERP systems—Systems of Record—provide baselines and traceability. However, Systems of Record have not historically been designed to support real-time collaboration or to create an attractive user experience.
The Heliple project focuses on connecting various modules—the horizontal bars—for systems engineering, hardware engineering, etc., as real-time collaboration environments that can be highly customized and replaceable if needed. The Heliple project explored the usage of OSLC to connect these modules, the Systems of Engagement, with the Systems of Record.
![]() By using Lynxwork as a low-code wrapper to develop the OSLC connections and map them to the needed business scenarios, the team concluded that this approach is affordable for businesses.
By using Lynxwork as a low-code wrapper to develop the OSLC connections and map them to the needed business scenarios, the team concluded that this approach is affordable for businesses.
Now, the Heliple team is aiming to expand their research with industry scale validation through the Demoiple project (Validate that the Heliple-2 technology can be implemented and accredited in Saab Aeronautics’ operational IT) combined with the Nextiple project, where they will investigate the role of heterogeneous information models/ontologies for heterogeneous analysis.
![]() If you are interested in participating in Nextiple, don’t hesitate to contact Erik Herzog.
If you are interested in participating in Nextiple, don’t hesitate to contact Erik Herzog.
 Christina’s Arrowhead flexible Production Value Network(fPVN) project aims to provide autonomous and evolvable information interoperability through machine-interpretable content for fPVN stakeholders. In less academic words, building a digital data-driven infrastructure.
Christina’s Arrowhead flexible Production Value Network(fPVN) project aims to provide autonomous and evolvable information interoperability through machine-interpretable content for fPVN stakeholders. In less academic words, building a digital data-driven infrastructure.
The resulting technology is projected to impact manufacturing productivity and flexibility substantially.

The exciting starting point of the Arrowhead project is that it wants to use existing standards and systems as a foundation and, on top of that, create a business and user-oriented layer, using modern technologies such as micro-services to support real-time processing and semantic technologies, ontologies, system modeling, and AI for data translations and learning—a much broader and ambitious scope than the Heliple project.
 I believe that in our PLM domain, this resonates with actual discussions you will find on LinkedIn, too. @Oleg Shilovitsky, @Dr. Yousef Hooshmand, @Prof. Dr. Jörg W. Fischer and Martin Eigner are a few of them steering these discussions. I consider it a perfect match for one of the images I shared about the future the digital enterprise.
I believe that in our PLM domain, this resonates with actual discussions you will find on LinkedIn, too. @Oleg Shilovitsky, @Dr. Yousef Hooshmand, @Prof. Dr. Jörg W. Fischer and Martin Eigner are a few of them steering these discussions. I consider it a perfect match for one of the images I shared about the future the digital enterprise.
Potentially, there are five platforms with their own internal ways of working, a mix of systems of record and systems of engagement, supported by an overlay of several Systems of Engagement environments.
![]() I previously described these dedicated environments, e.g., OpenBOM, Colab, Partful, and Authentise. These solutions could also be dedicated apps supporting a specific ecosystem role.
I previously described these dedicated environments, e.g., OpenBOM, Colab, Partful, and Authentise. These solutions could also be dedicated apps supporting a specific ecosystem role.
See below my artist’s impression of how a Service Engineer would work in its app connected to CRM, PLM and ERP platform datasets:
The exciting part of the Arrowhead fPVN project is that it wants to explore the interactions between systems and user roles based on existing mature standards instead of leaving the connections to software developers.
Christina mentioned some of these standards below:
I greatly support this approach as, historically, much knowledge and effort has been put into developing standards to support interoperability. Maybe not in real-time, but the embedded knowledge in these standards will speed up the broader usage. Therefore, I concur with the concluding slide:
A final comment: Industrial users must push for these standards if they do not want a future vendor lock-in. Vendors will do what the majority of their customers ask for but will also keep their customers’ data in proprietary formats to prevent them from switching to another system.
Accelerated Product Development Enabled by Digitalization
![]() The keynote session on Day 2, delivered by Uyiosa Abusomwan, Ph.D., Senior Global Technology Manager – Digital Engineering at Eaton, was a visionary story about the future of engineering.
The keynote session on Day 2, delivered by Uyiosa Abusomwan, Ph.D., Senior Global Technology Manager – Digital Engineering at Eaton, was a visionary story about the future of engineering.
With its broad range of products, Eaton is exploring new, innovative ways to accelerate product design by modeling the design process and applying AI to narrow design decisions and customer-specific engineering work. The picture below shows the areas of attention needed to model the design processes. Uyiosa mentioned the significant beneficial results that have already been reached.
Together with generative design, Eaton works towards modern digital engineering processes built on models and knowledge. His session was complementary to the Heliple and Arrowhead story. To reach such a contemporary design engineering environment, it must be data-driven and built upon open PLM and software components to fully use AI and automation.
Next Gen” Life Cycle Management in Next-Gen Nuclear Power and LTO Legacy Plants
Kent Freeland‘s presentation was a trip into memory land when he discussed the issues with Long Term Operations of legacy nuclear plants.
 I spent several years in Ringhals (Sweden) discussing and piloting the setup of a PLM front-end next to the MRO (Maintenance Repair Overhaul) system. As nuclear plants developed in the sixties, they required a longer than anticipated lifecycle, with access to the right design and operational data; maintenance and upgrade changes in the plant needed to be planned and controlled. The design data is often lacking; it resides at the EPC or has been stored in a document management system with limited retrieval capabilities.
I spent several years in Ringhals (Sweden) discussing and piloting the setup of a PLM front-end next to the MRO (Maintenance Repair Overhaul) system. As nuclear plants developed in the sixties, they required a longer than anticipated lifecycle, with access to the right design and operational data; maintenance and upgrade changes in the plant needed to be planned and controlled. The design data is often lacking; it resides at the EPC or has been stored in a document management system with limited retrieval capabilities.
See also my 2019 post: How PLM, ALM, and BIM converge thanks to the digital twin.
Kent described these experienced challenges – we must have worked in parallel universes – that now, for the future, we need a digitally connected infrastructure for both plant design and maintenance artifacts, as envisioned below:
 The solution reminded me of a lecture I saw at the PI PLMx 2019 conference, where the Swedish ESS facility demonstrated its Asset Lifecycle Data Management solution based on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
The solution reminded me of a lecture I saw at the PI PLMx 2019 conference, where the Swedish ESS facility demonstrated its Asset Lifecycle Data Management solution based on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
You can still find the presentation here: Henrik Lindblad Ola Nanzell ESS – Enabling Predictive Maintenance Through PLM & IIOT.
Also, Kent focused on the relevant standards to support a “Single Source of Truth” concept, where I would say after all the federated PLM discussions, I would go for:
“The nearest source of truth and a single source of Change”
assuming this makes more sense in a digitally connected enterprise.
Why do you need to be SMART when contracting for information?
 Rob Bodington‘s presentation was complementary to Kent Freeland’s presentation. Ron, a technical fellow at Eurostep, described the challenge of information acquisition when working with large assets that require access to the correct data once the asset is in operation. The large asset could be a nuclear plant or an aircraft carrier.
Rob Bodington‘s presentation was complementary to Kent Freeland’s presentation. Ron, a technical fellow at Eurostep, described the challenge of information acquisition when working with large assets that require access to the correct data once the asset is in operation. The large asset could be a nuclear plant or an aircraft carrier.
In the ideal world, the asset owner wants to have a digital twin of the asset fed by different data sources through a digital thread. Of course, this environment will only be reliable when accurate data is used and presented.
Getting accurate data starts with the information acquisition process, and Rob explained that this needed to be done SMARTly – see the image below:
 Rob zoomed in on the SMART keywords and the challenge the various standards provide to make the information SMARTly accessible, like the ISO 10303 / PLCS standard, the CFIHOS exchange standard and more. And then there is the ISO 8000 standard about data quality.
Rob zoomed in on the SMART keywords and the challenge the various standards provide to make the information SMARTly accessible, like the ISO 10303 / PLCS standard, the CFIHOS exchange standard and more. And then there is the ISO 8000 standard about data quality.
Click on the image to get smart.
Rob believes that AI might be the silver bullet as it might help understand the data quality, ontology and context of the data and even improve contracting, generating data clauses for contracting….
And there was a lot of AI ….
![]() There was a dazzling presentation from Gary Langridge, engineering manager at Ocado, explaining their Ocado Smart Platform (OSP), which leverages AI, robotics, and automation to tackle the challenges of online grocery and allow their clients to excel in performance and customer responsiveness.
There was a dazzling presentation from Gary Langridge, engineering manager at Ocado, explaining their Ocado Smart Platform (OSP), which leverages AI, robotics, and automation to tackle the challenges of online grocery and allow their clients to excel in performance and customer responsiveness.
There was a significant AI component in his presentation, and if you are tired of reading, watch this video
![]() But here was more AI – from the 25 sessions in this conference, 19 of them mentioned the potential or usage of AI somewhere in their speech – this is more than 75 %!
But here was more AI – from the 25 sessions in this conference, 19 of them mentioned the potential or usage of AI somewhere in their speech – this is more than 75 %!
There was a dedicated closing panel discussion related to the real business value of Artificial Intelligence in the PLM domain, moderated by Peter Bilello and answered by selected speakers from the conference, Sandeep Natu (CIMdata), Lars Fossum (SAP), Diana Goenage (Dassault Systemes) and Uyiosa Abusomwan (Eaton).
The discussion was realistic and helpful for the audience. It is clear that to reap the benefits, companies must explore the technology and use it to create valuable business scenarios. One could argue that many AI tools are already available, but the challenge remains that they have to run on reliable data. The data foundation is crucial for a successful outcome.
 An interesting point in the discussion was the statement from Diane Goenage, who repeatedly warned that using LLM-based solutions has an environmental impact due to the amount of energy they consume.
An interesting point in the discussion was the statement from Diane Goenage, who repeatedly warned that using LLM-based solutions has an environmental impact due to the amount of energy they consume.
We have a similar debate in the Netherlands – do we want the wind energy consumed by data centers (the big tech companies with a minimum workforce in the Netherlands), or should the Dutch citizens benefit from renewable energy resources?
Conclusion
There were even more interesting presentations during these two days, and you might have noticed that I did not advertise my content. This is because I have already reached 1600 words, but I also want to spend more time on the content separately.
It was about PLM and Sustainability, a topic often covered in this conference. Unfortunately, only 25 % of the presentations touched on sustainability, and AI over-hypes the topic.
Hopefully, it is not a sign of the time?

 It was a great pleasure to attend my favorite vendor-neutral PLM conference this year in Gothenburg—approximately 150 attendees, where most have expertise in the PLM domain.
It was a great pleasure to attend my favorite vendor-neutral PLM conference this year in Gothenburg—approximately 150 attendees, where most have expertise in the PLM domain.
We had the opportunity to learn new trends, discuss reality, and meet our peers.
The theme of the conference was:Value Drivers for Digitalization of the Product Lifecycle, a topic I have been discussing in my recent blog posts, as we need help and educate companies to understand the importance of digitalization for their business.
 The two-day conference covered various lectures – view the agenda here – and of course the topic of AI was part of half of the lectures, giving the attendees a touch of reality.
The two-day conference covered various lectures – view the agenda here – and of course the topic of AI was part of half of the lectures, giving the attendees a touch of reality.
In this first post, I will cover the main highlight of Day 1.
Value Drivers for Digitalization of the Product Lifecycle
 As usual, the conference started with Peter Bilello, president & CEO of CIMdata, stressing again that when implementing a PLM strategy, the maximum result comes from a holistic approach, meaning look at the big picture, don’t just focus on one topic.
As usual, the conference started with Peter Bilello, president & CEO of CIMdata, stressing again that when implementing a PLM strategy, the maximum result comes from a holistic approach, meaning look at the big picture, don’t just focus on one topic.
It was interesting to see again the classic graph (below) explaining the benefits of the end-to-end approach – I believe it is still valid for most companies; however, as I shared in my session the next day, implementing concepts of a Products Service System will require more a DevOp type of graph (more next week).
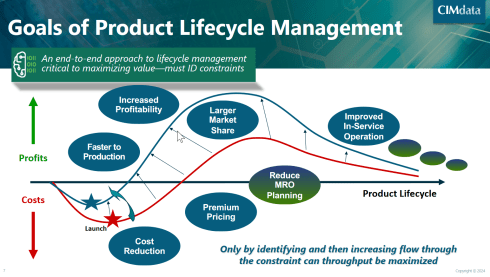
Next, Peter went through the CIMdata’s critical dozen with some updates. You can look at the updated 2024 image here.
 Some of the changes: Digital Thread and Digital Twin are merged– as Digital Twins do not run on documents. And instead of focusing on Artificial Intelligence only, CIMdata introduced Augmented Intelligence as we should also consider solutions that augment human activities, not just replace them.
Some of the changes: Digital Thread and Digital Twin are merged– as Digital Twins do not run on documents. And instead of focusing on Artificial Intelligence only, CIMdata introduced Augmented Intelligence as we should also consider solutions that augment human activities, not just replace them.
Peter also shared the results of a recent PLM survey where companies were asked about their main motivation for PLM investments. I found the result a little discouraging for several reasons:
The number one topic is still faster, cheaper and better – almost 65 % of the respondents see this as their priority. This number one topic illustrates that Sustainability has not reached the level of urgency, and perhaps the topic can be found in standards compliance.
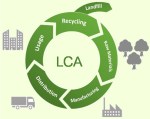 Many of the companies with Sustainability in their mission should understand that a digital PLM infrastructure is the foundation for most initiatives, like Lifecycle Analysis (LCA). Sustainability is more than part of standards compliance, if it was mentioned anyway.
Many of the companies with Sustainability in their mission should understand that a digital PLM infrastructure is the foundation for most initiatives, like Lifecycle Analysis (LCA). Sustainability is more than part of standards compliance, if it was mentioned anyway.
The second disappointing observation for the understanding of PLM is that customer support is mentioned only by 15 % of the companies. Again, connecting your products to your customers is the first step to a DevOp approach, and you need to be able to optimize your product offering to what the customer really wants.
Digital Transformation of the Value Chain in Pharma
The second keynote was from Anders Romare, Chief Digital and Information Officer at Novo Nordisk. Anders has been participating in the PDT conference in the past. See my 2016 PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe post, where Anders presented on behalf of Airbus: Digital Transformation through an e2e PLM backbone.
Anders started by sharing some of the main characteristics of the companies he has been working for. Volvo, Airbus and now Novo Nordisk. It is interesting to compare these characteristics as they say a lot about the industry’s focus. See below:
Anders is now responsible for digital transformation in Novo Nordisk, which is a challenge in a heavily regulated industry.
 One of the focus areas for Novo Nordisk in 2024 is also Artificial Intelligence, as you can see from the image to the left (click on it for the details).
One of the focus areas for Novo Nordisk in 2024 is also Artificial Intelligence, as you can see from the image to the left (click on it for the details).
As many others in this conference, Anders mentioned AI can only be applicable when it runs on top of accurate data.
Understanding the potential of AI, they identified 59 areas where AI can create value for the business, and it is interesting to compare the traditional PLM curve Peter shared in his session with the potential AI-enabled drug-development curve as presented by Anders below:
Next, Anders shared some of the example cases of this exploration, and if you are interested in the details, visit their tech.life site.
When talking about the engineering framing of PLM, it was interesting to learn from Anders, who had a long history in PLM before Novo Nordisk, when he replied to a question from the audience that he would never talk about PLM at the management level. It’s very much aligned with my Don’t mention the P** word post.
A Strategy for the Management of Large Enterprise PLM Platforms
One of the highlights for me on Day 1 was Jorgen Dahl‘s presentation. Jorgen, a senior PLM director at GE Aerospace, shared their story towards a single PLM approach needed due to changes in businesses. And addressing the need for a digital thread also comes with an increased need for uptime.
I like his strategy to execution approach, as shown in the image below, as it contains the most important topics. The business vision and understanding, the imagination of the end status and What must be True?
In my experience, the three blocks are iteratively connected. When describing the strategy, you might not be able to identify the required capabilities and management systems yet.
But then, when you start to imagine the ideal end state, you will have to consider them. And for companies, it is essential to be ambitious – or, as Jorgen stated, uncomfortable ambitious. Go for the 75 % to almost 100 % to be true. Also, asking What must be True is an excellent way to allow people to be involved and creatively explore the next steps.
Note: This approach does not provide all the details, as it will be a multiyear journey of learning and adjusting towards the future. Therefore, the strategy must be aligned with the culture to avoid continuous top-down governance of the details. In that context, Jorgen stated:
“Culture is what happens when you leave the room.”
It is a more positive statement than the famous Peter Drucker’s quote: “Culture eats strategy for breakfast.”
Jorgen’s concluding slide mentions potential common knowledge, although I believe the way Jorgen used the right easy-to-digest points will be helpful for all organizations to step back, look at their initiatives, and compare where they can improve.
How a Business Capability Model and Application Portfolio Management Support Through Changing Times
Peter Vind‘s presentation was nicely connected to the presentation from Jorgen Dahl. Peter, who is an enterprise architect at Siemens Energy, started by explaining where the enterprise architect fits in an organization and comparing it to a city.
In his entertaining session, he mentioned he has to deal with the unicorns at the C-level, who, like politicians in a city, sometimes have the most “innovative” ideas – can they be realized?
Peter explained how they used Business Capability Modeling when Siemens Energy went through various business stages. First, the carve-out from Siemens AG and later the merger with Siemens Gamesa. Their challenge is to understand which capabilities remain, which are new or overlapping, both during the carve-out and merging process.
The business capability modeling leads to a classification of the applications used at different levels of the organization, such as customer-facing, operational, or supporting business capabilities.
Next, for the lifecycle of the applications, the TIME approach was used, meaning that each application was mapped to business fitness and technical fitness. Click on the diagram to see the details.
The result could look like the mapping shown below – a comprehensive overview of where the action is
It is a rational approach; however, Peter mentioned that we also should be aware of the HIPPOs in an organization. If there is a HiPPO (Highest Paid Person’s Opinion) in play, you might face a political battle too.
It was a great educational session illustrating the need for an Enterprise Architect, the value of business capabilities modeling and the TIME concept.
And some more …
There were several other exciting presentations during day 1; however, as not all presentations are publicly available, I cannot discuss them in detail; I just looked at my notes.
Driving Trade Compliance and Efficiency
 Peter Sandeck, Director of Project Management at TE Connectivity shared what they did to motivate engineers to endorse their Jurisdiction and Classification Assessment (JCA) process. Peter showed how, through a Minimal Viable Product (MVP) approach and listening to the end-users, they reached a higher Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) score after several iterations of the solution developed for the JCA process.
Peter Sandeck, Director of Project Management at TE Connectivity shared what they did to motivate engineers to endorse their Jurisdiction and Classification Assessment (JCA) process. Peter showed how, through a Minimal Viable Product (MVP) approach and listening to the end-users, they reached a higher Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) score after several iterations of the solution developed for the JCA process.
This approach is an excellent example of an agile method in which engineers are involved. My remaining question is still – are the same engineers in the short term also pushed to make lifecycle assessments? More work; however, I believe if you make it personal, the same MVP approach could work again.
Value of Model-Based Product Architecture
 Jussi Sippola, Chief Expert, Product Architecture Management & Modularity at Wärtsilä, presented an excellent story related to the advantages of a more modular product architecture. Where historically, products were delivered based on customer requirements through the order fulfillment process, now there is in parallel the portfolio management process, defining the platform of modules, features and options.
Jussi Sippola, Chief Expert, Product Architecture Management & Modularity at Wärtsilä, presented an excellent story related to the advantages of a more modular product architecture. Where historically, products were delivered based on customer requirements through the order fulfillment process, now there is in parallel the portfolio management process, defining the platform of modules, features and options.
Jussi mentioned that they were able to reduce the number of parts by 50 % while still maintaining the same level of customer capabilities. In addition, thanks to modularity, they were able to reduce the production lead time by 40 % – essential numbers if you want to remain competitive.
Conclusion
Day 1 was a day where we learned a lot as an audience, and in addition, the networking time and dinner in the evening were precious for me and, I assume, also for many of the participants. In my next post, we will see more about new ways of working, the AI dream and Sustainability.

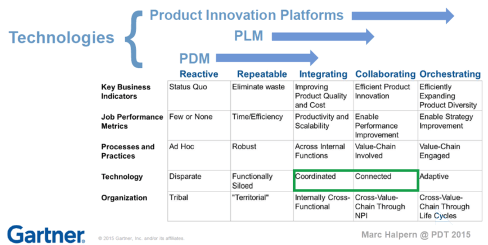


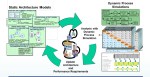
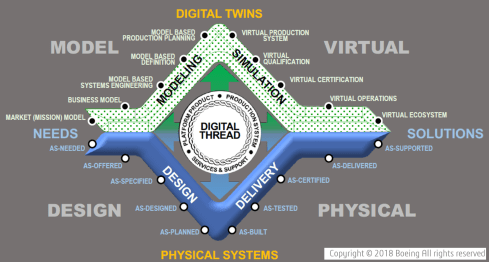

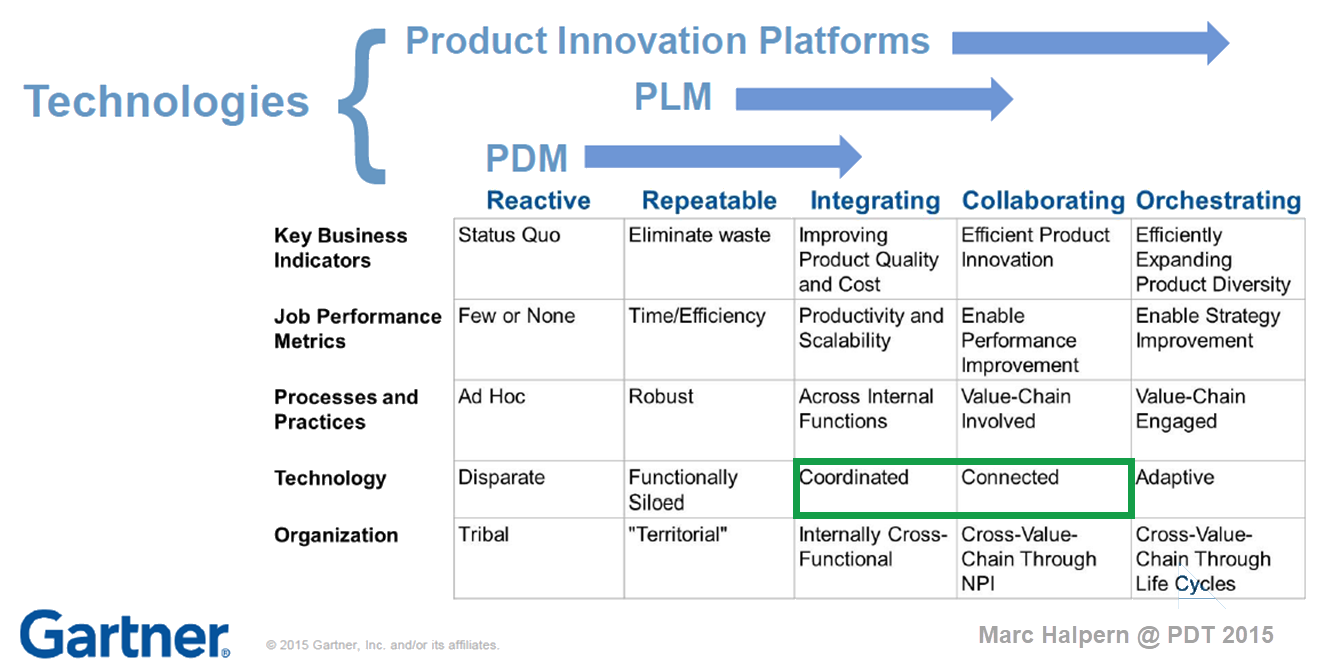

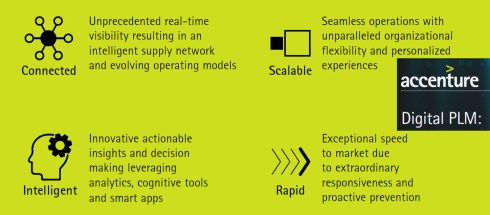
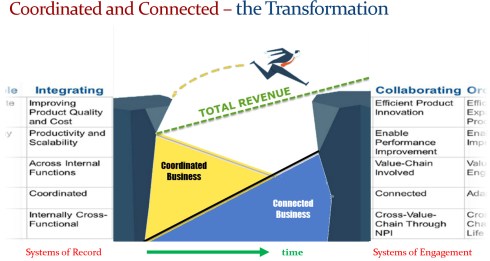
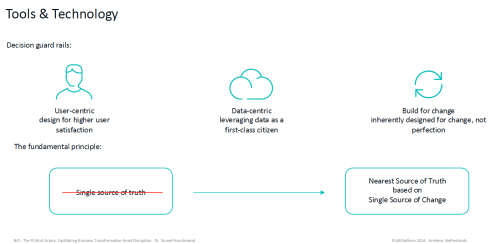
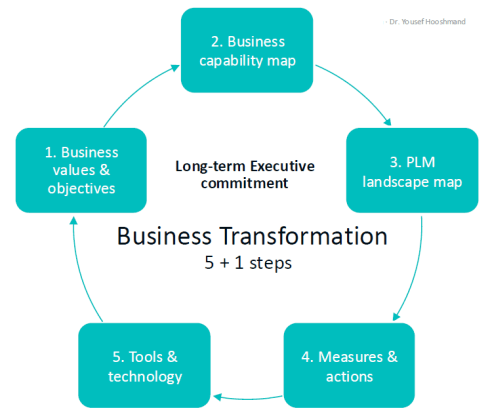
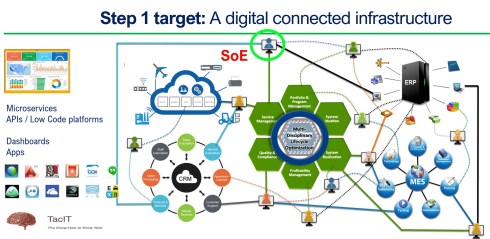

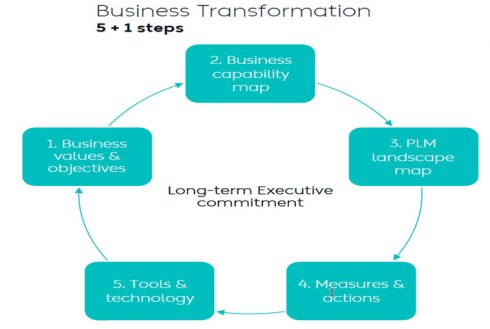

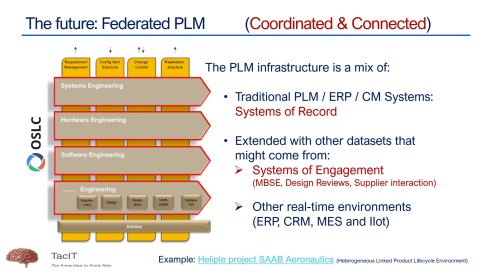

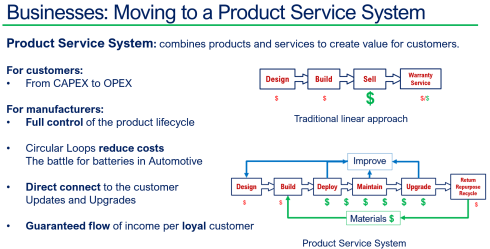
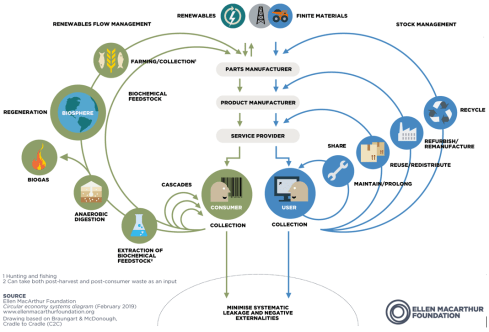
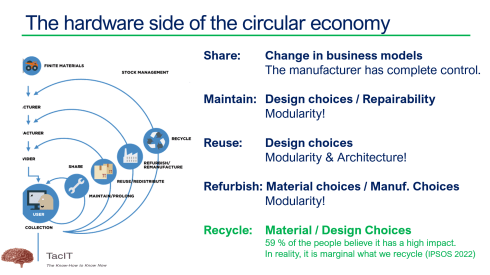
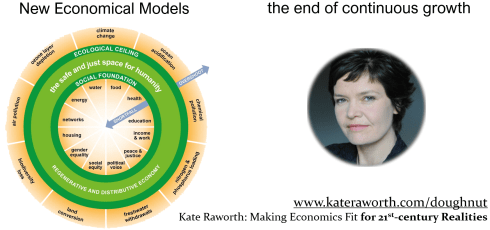

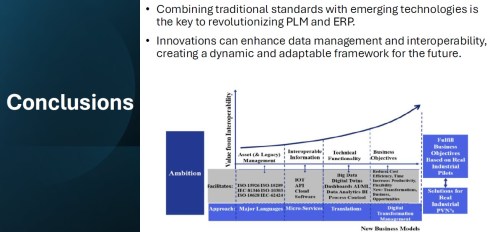
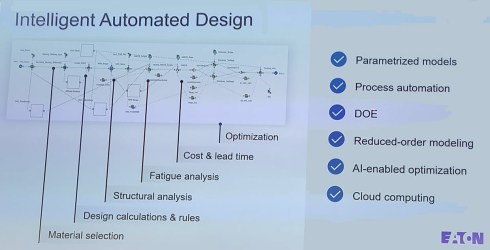

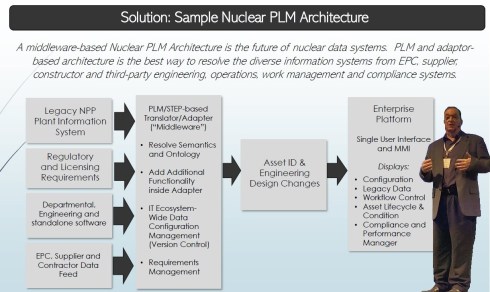


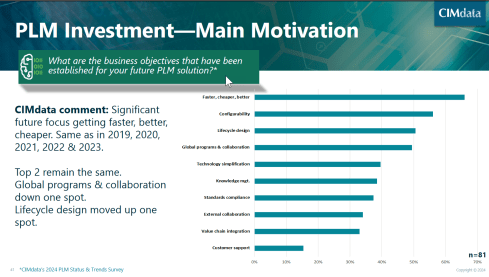
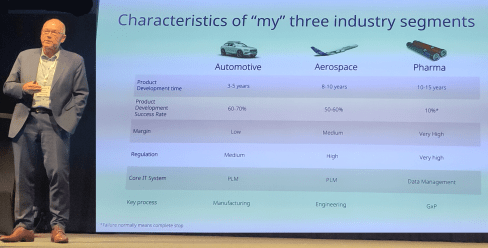
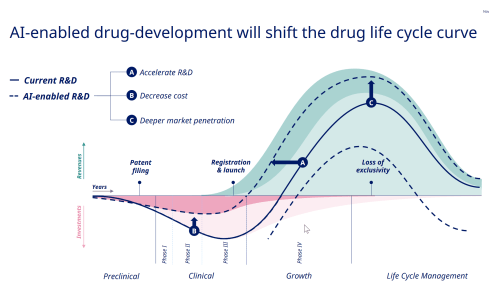
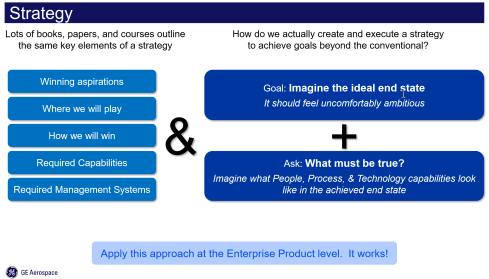

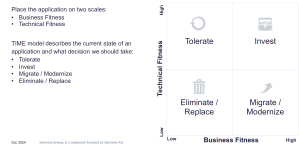

[…] (The following post from PLM Green Global Alliance cofounder Jos Voskuil first appeared in his European PLM-focused blog HERE.) […]
[…] recent discussions in the PLM ecosystem, including PSC Transition Technologies (EcoPLM), CIMPA PLM services (LCA), and the Design for…
Jos, all interesting and relevant. There are additional elements to be mentioned and Ontologies seem to be one of the…
Jos, as usual, you've provided a buffet of "food for thought". Where do you see AI being trained by a…
Hi Jos. Thanks for getting back to posting! Is is an interesting and ongoing struggle, federation vs one vendor approach.…