You are currently browsing the tag archive for the ‘Digital PLM’ tag.
 Recently, we initiated the Design for Sustainability workgroup, an initiative from two of our PGGA members, Erik Rieger and Matthew Sullivan. You can find a recording of the kick-off here on our YouTube channel.
Recently, we initiated the Design for Sustainability workgroup, an initiative from two of our PGGA members, Erik Rieger and Matthew Sullivan. You can find a recording of the kick-off here on our YouTube channel.
Thanks to the launch of the Design for Sustainability workgroup, we were introduced to Dr. Elvira Rakova, founder and CEO of the startup company Direktin.
Her mission is to build the Digital Ecosystem of engineering tools and simulation for Compressed Air Systems. As typical PLM professionals with a focus on product design, we were curious to learn about developments in the manufacturing space. And it was an interesting discussion, almost a lecture.
Compressed air and Direktin
 Dr. Elvira Rakova has been working with compressed air in manufacturing plants for several years, during which she has observed the inefficiency of how compressed air is utilized in these facilities. It is an available resource for all kinds of machines in the plant, often overdimensioned and a significant source of wasted energy.
Dr. Elvira Rakova has been working with compressed air in manufacturing plants for several years, during which she has observed the inefficiency of how compressed air is utilized in these facilities. It is an available resource for all kinds of machines in the plant, often overdimensioned and a significant source of wasted energy.
To address this waste of energy, linked to CO2 emissions, she started her company to help companies scale, dimension, and analyse their compressed air usage. A mix of software and consultancy to make manufacturing processes using compressed air responsible for less carbon emissions, and for the plant owners, saving significant money related to energy usage.
For us, it was an educational discussion, and we recommend that you watch or listen to the next 36 minutes
What I learned
- The use of compressed air and its energy/environmental impact were like dark matter to me.
I never noticed it when visiting customers as a significant source to become more sustainable. - Although the topic of compressed air seems easy to understand, its usage and impact are all tough to address quickly and easily, due to legacy in plants, lack of visibility on compressed air (energy usage) and needs and standardization among the providers of machinery.
- The need for data analysis is crucial in addressing the reporting challenges of Scope 3 emissions, and it is also increasingly important as part of the Digital Product Passport data to be provided. Companies must invest in the digitalization of their plants to better analyze and improve energy usage, such as in the case of compressed air.
- In the end, we concluded that for sustainability, it is all about digital partnerships connecting the design world and the manufacturing world and for that reason, Elvira is personally motivated to join and support the Design for Sustainability workgroup
Want to learn more?
- Another educational webinar: Design Review Culture and Sustainability
- Explore the Direktin website to learn more
Conclusions
The PLM Green Global Alliance is not only about designing products; we have also seen lifecycle assessments for manufacturing, as discussed with Makersite and aPriori. These companies focused more on traditional operations in a manufacturing plant. Through our lecture/discussion on the use of compressed air in manufacturing plants, we identified a new domain that requires attention.
Last week, my memory was triggered by this LinkedIn post and discussion started by Oleg Shilovitsky: Rethinking the Data vs. Process Debate in the Age of Digital Transformation and AI.

me, 1989
In the past twenty years, the debate in the PLM community has changed a lot. PLM started as a central file repository, combined with processes to ensure the correct status and quality of the information.
Then, digital transformation in the PLM domain became achievable and there was a focus shift towards (meta)data. Now, we are entering the era of artificial intelligence, reshaping how we look at data.
In this technology evolution, there are lessons learned that are still valid for 2025, and I want to share some of my experiences in this post.
 In addition, it was great to read Martin Eigner’s great reflection on the past 40 years of PDM/PLM. Martin shared his experiences and insights, not directly focusing on the data and processes debate, but very complementary and helping to understand the future.
In addition, it was great to read Martin Eigner’s great reflection on the past 40 years of PDM/PLM. Martin shared his experiences and insights, not directly focusing on the data and processes debate, but very complementary and helping to understand the future.
It started with processes (for me 2003-2014)
In the early days when I worked with SmarTeam, one of my main missions was to develop templates on top of the flexible toolkit SmarTeam.
 For those who do not know SmarTeam, it was one of the first Windows PDM/PLM systems, and thanks to its open API (COM-based), companies could easily customize and adapt it. It came with standard data elements and behaviors like Projects, Documents (CAD-specific and Generic), Items and later Products.
For those who do not know SmarTeam, it was one of the first Windows PDM/PLM systems, and thanks to its open API (COM-based), companies could easily customize and adapt it. It came with standard data elements and behaviors like Projects, Documents (CAD-specific and Generic), Items and later Products.
On top of this foundation, almost every customer implemented their business logic (current practices).
And there the problems came …..
 The implementations became too much a highly customized environment, not necessarily thought-through as every customer worked differently based on their (paper) history. Thanks to learning from the discussions in the field supporting stalled implementations, I was also assigned to develop templates (e.g. SmarTeam Design Express) and standard methodology (the FDA toolkit), as the mid-market customers requested. The focus was on standard processes.
The implementations became too much a highly customized environment, not necessarily thought-through as every customer worked differently based on their (paper) history. Thanks to learning from the discussions in the field supporting stalled implementations, I was also assigned to develop templates (e.g. SmarTeam Design Express) and standard methodology (the FDA toolkit), as the mid-market customers requested. The focus was on standard processes.
You can read my 2009 observations here: Can chaos become order through PLM?
The need for standardization?
When developing templates (the right data model and processes), it was also essential to provide template processes for releasing a product and controlling the status and product changes – from Engineering Change Request to Engineering Change Order. Many companies had their processes described in their ISO 900x manual, but were they followed correctly?
 In 2010, I wrote ECR/ECO for Dummies, and it has been my second most-read post over the years. Only the 2019 post The importance of EBOM and MBOM in PLM (reprise) had more readers. These statistics show that many people are, and were, seeking education on general PLM processes and data model principles.
In 2010, I wrote ECR/ECO for Dummies, and it has been my second most-read post over the years. Only the 2019 post The importance of EBOM and MBOM in PLM (reprise) had more readers. These statistics show that many people are, and were, seeking education on general PLM processes and data model principles.
It was also the time when the PLM communities discussed out-of-the-box or flexible processes as Oleg referred to in his post..
You would expect companies to follow these best practices, and many small and medium enterprises that started with PLM did so. However, I discovered there was and still is the challenge with legacy (people and process), particularly in larger enterprises.
The challenge with legacy
 The technology was there, the usability was not there. Many implementations of a PLM system go through a critical stage. Are companies willing to change their methodology and habits to align with common best practices, or do they still want to implement their unique ways of working (from the past)?
The technology was there, the usability was not there. Many implementations of a PLM system go through a critical stage. Are companies willing to change their methodology and habits to align with common best practices, or do they still want to implement their unique ways of working (from the past)?
“The embedded process is limiting our freedom, we need to be flexible”
is an often-heard statement. When every step is micro-managed in the PLM system, you create a bureaucracy detested by the user. In general, when the processes are implemented in a way first focusing on crucial steps with the option to improve later, you will get the best results and acceptance. Nowadays, we could call it an MVP approach.
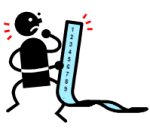 I have seen companies that created a task or issue for every single activity a person should do. Managers loved the (demo) dashboard. It never lead to success as the approach created frustration at the end user level as their To-Do list grew and grew.
I have seen companies that created a task or issue for every single activity a person should do. Managers loved the (demo) dashboard. It never lead to success as the approach created frustration at the end user level as their To-Do list grew and grew.
 Another example of the micro-management mindset is when I worked with a company that had the opposite definition of Version and Revision in their current terminology. Initially, they insisted that the new PLM system should support this, meaning everywhere in the interface where Revisions was mentioned should be Version and the reverse for Version and Revision.
Another example of the micro-management mindset is when I worked with a company that had the opposite definition of Version and Revision in their current terminology. Initially, they insisted that the new PLM system should support this, meaning everywhere in the interface where Revisions was mentioned should be Version and the reverse for Version and Revision.
Can you imagine the cost of implementing and maintaining this legacy per upgrade?
And then came data (for me 2014 – now)
In 2015, during the pivotal PLM Roadmap/PDT conference related to Product Innovation Platforms, it brought the idea of framing digital transformation in the PLM domain in a single sentence: From Coordinated to Connected. See the original image from Marc Halpern here below and those who have read my posts over the years have seen this terminology’s evolution. Now I would say (till 2024): From Coordinated to Coordinated and Connected.
A data-driven approach was not new at that time. Roughly speaking, around 2006 – close to the introduction of the Smartphone – there was already a trend spurred by better global data connectivity at lower cost. Easy connectivity allowed PLM to expand into industries that were not closely connected to 3D CAD systems(CATIA, CREO or NX). Agile PLM, Aras, and SAP PLM became visible – PLM is no longer for design management but also for go-to-market governance in the CPG and apparel industry.
However, a data-driven approach was still rare in mainstream manufacturing companies, where drawings, office documents, email and Excel were the main information carriers next to the dominant ERP system.
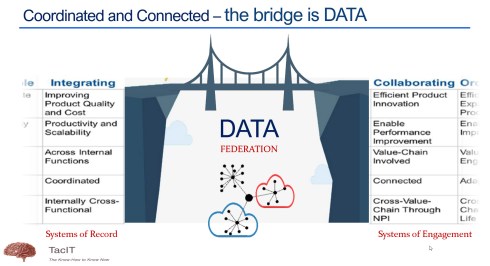
A data-driven approach was a consultant’s dream, and when looking at the impact of digital transformation in other parts of the business, why not for PLM, too? My favorite and still valid 2014 image is the one below from Accenture describing Digital PLM. Here business and PLM come together – the WHY!
Again, the challenge with legacy
 At that time, I saw a few companies linking their digital transformation to implementing a new PLM system. Those were the days the PLM vendors were battling for the big enterprise deals, sometimes motivated by an IT mindset that unifying the existing PDM/PLM systems would fulfill the digital dream. Science was not winning, but emotion. Read the PLM blame game – still actual.
At that time, I saw a few companies linking their digital transformation to implementing a new PLM system. Those were the days the PLM vendors were battling for the big enterprise deals, sometimes motivated by an IT mindset that unifying the existing PDM/PLM systems would fulfill the digital dream. Science was not winning, but emotion. Read the PLM blame game – still actual.
One of my key observations is that companies struggle when they approach PLM transformation with a migration mindset. Moving from Coordinated to Connected isn’t just about technology—it’s about fundamentally changing how we work. Instead of a document-driven approach, organizations must embrace a data-driven, connected way of working.
The PLM community increasingly agrees that PLM isn’t a single system; it’s a strategy that requires a federated approach—whether through SaaS or even beyond it.
 Before AI became a hype, we discussed the digital thread, digital twins, graph databases, ontologies, and data meshes. Legacy – people (skills), processes(rigid) and data(not reliable) – are the elephant in the room. Yet, the biggest challenge remains: many companies see PLM transformation as just buying new tools.
Before AI became a hype, we discussed the digital thread, digital twins, graph databases, ontologies, and data meshes. Legacy – people (skills), processes(rigid) and data(not reliable) – are the elephant in the room. Yet, the biggest challenge remains: many companies see PLM transformation as just buying new tools.
A fundamental transformation requires a hybrid approach—maintaining traditional operations while enabling multidisciplinary, data-driven teams. However, this shift demands new skills and creates the need to learn and adapt, and many organizations hesitate to take that risk.
In his Product Data Plumber Perspective on 2025. Rob Ferrone addressed the challenge to move forward too, and I liked one of his responses in the underlying discussion that says it all – it is hard to get out of your day to day comfort (and data):
Rob Ferrone’s quote:
Transformations are announced, followed by training, then communication fades. Plans shift, initiatives are replaced, and improvements are delayed for the next “fix-all” solution. Meanwhile, employees feel stuck, their future dictated by a distant, ever-changing strategy team.
And then there is Artificial Intelligence (2024 ……)
 In the past two years, I have been reading and digesting much news related to AI, particularly generative AI.
In the past two years, I have been reading and digesting much news related to AI, particularly generative AI.
Initially, I was a little skeptical because of all the hallucinations and hype; however, the progress in this domain is enormous.
I believe that AI has the potential to change our digital thread and digital twin concepts dramatically where the focus was on digital continuity of data.
Now this digital continuity might not be required, reading articles like The End of SaaS (a more and more louder voice), usage of the Fusion Strategy (the importance of AI) and an (academic) example, on a smaller scale, I about learned last year the Swedish Arrowhead™ fPVN project.
I hope that five years from now, there will not be a paragraph with the title Pity there was again legacy.
We should have learned from the past that there is always the first wave of tools – they come with a big hype and promise – think about the Startgate Project but also Deepseek.
 Still remember, the change comes from doing things differently, not from efficiency gains. To do things differently you need an educated, visionary management with the power and skills to take a company in a new direction. If not, legacy will win (again)
Still remember, the change comes from doing things differently, not from efficiency gains. To do things differently you need an educated, visionary management with the power and skills to take a company in a new direction. If not, legacy will win (again)
Conclusion
In my 25 years of working in the data management domain, now known as PLM, I have seen several impressive new developments – from 2D to 3D, from documents to data, from physical prototypes to models and more. All these developments took decades to become mainstream. Whilst the technology was there, the legacy kept us back. Will this ever change? Your thoughts?

The pivotal 2015 PLM Roadmap / PDT conference
 Most times in this PLM and Sustainability series, Klaus Brettschneider and Jos Voskuil from the PLM Green Global Alliance core team speak with PLM related vendors or service partners.
Most times in this PLM and Sustainability series, Klaus Brettschneider and Jos Voskuil from the PLM Green Global Alliance core team speak with PLM related vendors or service partners.
This year we have been speaking with Transition Technologies PSC, Configit, aPriori, Makersite and the PLM Vendors PTC, Siemens and SAP.
Where the first group of companies provided complementary software offerings to support sustainability – “the fourth dimension”– the PLM vendors focused more on the solutions within their portfolio.
This time we spoke with , CIMPA PLM services, a company supporting their customers with PLM and Sustainability challenges, offering an end-to-end support.
What makes them special is that they are also core partner of the PLM Global Green Alliance, where they moderate the Circular Economy theme – read their introduction here: PLM and Circular Economy.
CIMPA PLM services
 We spoke with Pierre DAVID and Mahdi BESBES from CIMPA PLM services. Pierre is an environmental engineer and Mahdi is a consulting manager focusing on parts/components traceability in the context of sustainability and a circular economy. Many of the activities described by Pierre and Mahdi were related to the aerospace industry.
We spoke with Pierre DAVID and Mahdi BESBES from CIMPA PLM services. Pierre is an environmental engineer and Mahdi is a consulting manager focusing on parts/components traceability in the context of sustainability and a circular economy. Many of the activities described by Pierre and Mahdi were related to the aerospace industry.
We had an enjoyable and in-depth discussion of sustainability, as the aerospace industry is well-advanced in traceability during the upstream design processes. Good digital traceability is an excellent foundation to extend for sustainability purposes.
CSRD, LCA, DPP, AI and more
A bunch of abbreviations you will have to learn. We went through the need for a data-driven PLM infrastructure to support sustainability initiatives, like Life Cycle Assessments and more. We zoomed in on the current Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive(CSRD) highlighting the challenges with the CSRD guidelines and how to connect the strategy (why we do the CSRD) to its execution (providing reports and KPIs that make sense to individuals).
In addition, we discussed the importance of using the proper methodology and databases for lifecycle assessments. Looking forward, we discussed the potential of AI and the value of the Digital Product Passport for products in service.
Enjoy the 37 minutes discussion and you are always welcome to comment or start a discussion with us.
What we learned
- Sustainability initiatives are quite mature in the aerospace industry and thanks to its nature of traceability, this industry is leading in methodology and best practices.
- The various challenges with the CSRD directive – standardization, strategy and execution.
- The importance of the right databases when performing lifecycle analysis.
- CIMPA is working on how AI can be used for assessing environmental impacts and the value of the Digital Product Passport for products in service to extend its traceability
Want to learn more?
Here are some links related to the topics discussed in our meeting:
- CIMPA’s theme page on the PLM Green website: PLM and Circular Economy
- CIMPA’s commitments towards A sustainable, human and guiding approach
- Sopra Steria, CIMPA’s parent company: INSIDE #8 magazine
Conclusion
The discussion was insightful, given the advanced environment in which CIMPA consultants operate compared to other manufacturing industries. Our dialogue offered valuable lessons in the aerospace industry, that others can draw on to advance and better understand their sustainability initiatives
 This year, I will celebrate 25 years since I started my company, TacIT, to focus on knowledge management. However, quickly, I was back in the domain of engineering data management, which became a broader topic, which we now call PLM.
This year, I will celebrate 25 years since I started my company, TacIT, to focus on knowledge management. However, quickly, I was back in the domain of engineering data management, which became a broader topic, which we now call PLM.
Looking back, there have been significant changes in these 25 years, from systems to strategy, for documents to data, from linear to iterative. However, in this post, I want to look at my 2024 observations to see where we can progress. This brings me to the first observation.
PLM is human
Despite many academic and marketing arguments describing WHAT and WHY companies need specific business or software capabilities, there is, above all, the need for people to be personally inspired and connected. We want to belong to a successful group of people, teams and companies because we are humans, not resources.
It is all about people, which was also the title of my session during the March 2024 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference in Eindhoven (NL). I led a panel discussion on the importance of people with Dr. Cara Antoine, Daniel Schöpf, and Florens Wolters, each of whom actively led transformational initiatives within their companies.
 Through Dr. Cara Antoine, e at Capgemini and a key voice for women in tech, I learned about her book Make It Personal. The book inspired me and motivated me to continue using a human-centric approach. Give this book to your leadership and read it yourself. It is practical, easy to read, and encouraging
Through Dr. Cara Antoine, e at Capgemini and a key voice for women in tech, I learned about her book Make It Personal. The book inspired me and motivated me to continue using a human-centric approach. Give this book to your leadership and read it yourself. It is practical, easy to read, and encouraging
Recently, in my post “PLM in real life and Gen AI“, I shared insights related to PLM blogs and Gen AI – original content is becoming increasingly the same, and the human touch is disappearing, while generating more and longer blogs.
 I propose keeping Gen AI-generated text for the boring part of PLM and exploring the human side of PLM engagements in blogs. What does this mean? In the post, I also shared the highlights of the Series 2 podcast I did together with Helena Gutierrez from Share PLM. Every recording had its unique human touch and knowledge.
I propose keeping Gen AI-generated text for the boring part of PLM and exploring the human side of PLM engagements in blogs. What does this mean? In the post, I also shared the highlights of the Series 2 podcast I did together with Helena Gutierrez from Share PLM. Every recording had its unique human touch and knowledge.
We are now in full preparation for Series 3—let us know who your hero is and who should be our guest in 2025!
PLM is business
One of the most significant changes I noticed in my PLM-related projects was that many of the activities connected the PLM activities to the company’s business objectives. Not surprisingly, it was mostly a bottom-up activity, explaining to the upper management that a modern, data-driven PLM strategy is crucial to achieving business or sustainability goals.
I wrote two long posts about these experiences. The first one,” PLM – business first,” zooms in on the changing mindset that PLM is not an engineering system anymore but part of a digital infrastructure that supports companies in achieving their business goals. The image below from Dr. Yousef Hooshmand is one of my favorites in this context. The 5 + 1 steps, where the extra step is crucial: Long Executive Commitment.
So, to get an executive commitment, you need to explain and address business challenges.
Executive commitment and participation can be achieved through a Benefits Dependency Network approach, as illustrated in this webinar I did with the Heliple-2 team, where we were justifying the business needs for Federated PLM. More about the Federated PLM part in the next paragraph.
Another point to consider is that when the PLM team is part of the IT organization (the costs side), they have a big challenge in leading or even participating in business discussions. In this context, read (again) Jan Bosch’s post: Structure Eats Strategy.
 The second post, more recent, summarized the experiences I had with several customer engagements. The title says it all: “Don’t use the P**-word! – 5 lessons learned“, with an overlap in content with the first post.
The second post, more recent, summarized the experiences I had with several customer engagements. The title says it all: “Don’t use the P**-word! – 5 lessons learned“, with an overlap in content with the first post.
Conclusion: A successful PLM strategy starts with the business and needs storytelling to align all stakeholders with a shared vision or goal.
PLM is technology
This year has seen the maturation of PLM technology concepts. We are moving away from a monolithic PLM system and exploring federated and connected infrastructures, preferably a mix of Systems of Record (the old PLMs/ERPs) and Systems of Engagement (the new ways of domain collaboration). The Heliple project manifests such an approach, where the vertical layers are Systems of Record, and the horizontal modules could be Systems of Engagement.
I had several discussions with typical System of Engagement vendors, like Colab (“Where traditional PLM fails”) and Partful (“Connected Digital Thread for Lower and Mid-market OEMs“), but I also had broader discussions during the PLM Roadmap PDT Europe conference – see: R-evolutionizing PLM and ERP and Heliple.
 I also follow Dr. Jorg Fischer, who lectures about digital transformation concepts in the manufacturing business domain. Unfortunately, for a broader audience, Jörg published a lot in German, and typically, his references for PLM and ERP are based on SAP and Teamcenter. His blog posts are always interesting to follow – have a look at his recent blog in English: 7 keys to solve PLM & ERP.
I also follow Dr. Jorg Fischer, who lectures about digital transformation concepts in the manufacturing business domain. Unfortunately, for a broader audience, Jörg published a lot in German, and typically, his references for PLM and ERP are based on SAP and Teamcenter. His blog posts are always interesting to follow – have a look at his recent blog in English: 7 keys to solve PLM & ERP.
 Of course, Oleg Shilovitsky’s impressive and continuous flow of posts related to modern PLM concepts is amazing—just browse through his Beyond PLM home page to read about the actual topics happening in his PLM ecosystem or for example, read about modern technology concepts in this recent OpenBOM article.
Of course, Oleg Shilovitsky’s impressive and continuous flow of posts related to modern PLM concepts is amazing—just browse through his Beyond PLM home page to read about the actual topics happening in his PLM ecosystem or for example, read about modern technology concepts in this recent OpenBOM article.
Conceptually, we are making progress. As a commonality, all future concepts focus on data, not so much on managing documents—and here comes the focus on data.
PLM needs accurate data
In a data-driven environment, apps or systems will use a collection of datasets to provide a user with a working environment, either a dashboard or an interactive real-time environment. Below is my AI (Artist Impression) of a digital enterprise.
Of course, it seems logical; the data must be accurate as you no longer have control over access to the data in a data-driven environment. You can be accountable for the data; others can consume the data you created without checking its accuracy by your guidance.
Therefore, data governance and an excellent enterprise architecture are crucial to support the new paradigm:
The nearest source of truth supported by a single source of change
Quote: Yousef Hoohmand
Forget the Single Source of Truth idea, a previous century paradigm.
With data comes Artificial intelligence and algorithms that can play an essential role in your business, providing solutions or insights that support decision-making.
![]() In 2024, most of us have been exploring the benefits of ChatGPT and Generative AI. You can describe examples of where AI could assist in every aspect of the product lifecycle. I saw great examples from Eaton, Ocado, and others at the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference.
In 2024, most of us have been exploring the benefits of ChatGPT and Generative AI. You can describe examples of where AI could assist in every aspect of the product lifecycle. I saw great examples from Eaton, Ocado, and others at the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference.
See my review here: A long week after the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference.
Still, before benefiting from AI in your organization, it remains essential that the AI runs on top of accurate data.
Sustainability needs (digital) PLM
 This paragraph is the only reverse dependency towards PLM and probably the one that is less in people’s minds, perhaps because PLM is already complex enough. In 2024, with the PLM Green Global Alliance, we had good conversations with PLM-related software vendors or service partners (aPriori, Configit, Makersite, PTC, SAP, Siemens and Transition Technologies PSC) where we discussed their solutions and how they are used in the field by companies.
This paragraph is the only reverse dependency towards PLM and probably the one that is less in people’s minds, perhaps because PLM is already complex enough. In 2024, with the PLM Green Global Alliance, we had good conversations with PLM-related software vendors or service partners (aPriori, Configit, Makersite, PTC, SAP, Siemens and Transition Technologies PSC) where we discussed their solutions and how they are used in the field by companies.
We discovered here that most activities are driven by regulations, like ESG reporting, the new CSRD directive for Europe and the implementation of the Digital Product Passport. What is clear from all these activities is that companies need to have a data-driven PLM infrastructure to connect product data to environmental impacts, like carbon emissions equivalents.
Besides complying with regulations, I have been discussing the topic of Product-As-A-Service, or the Product Service System, this year, with excellent feedback from Dave Duncan. You can find a link to his speech: Improving Product Sustainability – PTC with PGGA.
Also, during the PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe conference, I discussed this topic, explaining that achieving a circular economy is a long-term vision, and the starting point is to establish a connected infrastructure within your organizations and with your customers/users in the field.
 Sustainability should be on everyone’s agenda. From the interactions on LinkedIn, you can see that we prefer to discuss terms like PDM/PLM or eBOM/mBOM in the PLM domain. Very few connect PLM to sustainability.
Sustainability should be on everyone’s agenda. From the interactions on LinkedIn, you can see that we prefer to discuss terms like PDM/PLM or eBOM/mBOM in the PLM domain. Very few connect PLM to sustainability.
Sustainability is a long-term mission; however, as we have seen from long-term missions, they can be overwhelmed by the day’s madness and short-term needs.
PLM is Politics
You might not expect this paragraph in my log, as most PLM discussions are about the WHAT and the WHY of a PLM solution or infrastructure. However, the most challenging part of PLM is the HOW, and this is the area that I am still focused on.
In the early days of mediating mainly in SmarTeam implementations, it became clear that the technology was not the issue. A crisis was often due to a lack of (technical) skills or methodology and misplaced expectations.
When the way out became clear, politics often started. Sometimes, there was the HIPPO (HIghest Paid Person’s Opinion) in the company, as Peter Vind explained, or there was the blame game, which I described in my 2019 “The PLM blame game post”.
What makes it even more difficult is that people’s opinions in PLM discussions are often influenced by their friendly relations or history with a particular vendor or implementer from the past, which troubles a proper solution path.
These aspects are challenging to discuss, and nobody wants to discuss them openly. A company (and a country) must promote curiosity instead of adhering to mainstream thinking and working methods. In our latest Share PLM podcast, Brian Berger, a VP at Metso, mentions the importance of diversity within an organization.
“It is a constant element of working in a global business, and the importance cannot be overstated.”
This observation should make us think again when we want to simplify everything and dim the colors.
Conclusion
Initially, I thought this would be a shorter post, but again, it became a long read – therefore, perhaps ideal when closing 2024 and looking forward to activities and focus for 2025. Use this time to read books and educate yourself beyond the social media posts (even my blogs are limited 😉)
In addition, I noticed the build-up of this post was unconsciously influenced by Martijn Dullaart‘s series of messages titled “Configuration Management is ……”. Thanks, Martijn, for your continuous contributions to our joint passion – a digital enterprise where PLM and CM flawlessly interact based on methodology and accurate data.

 I am sharing another follow-up interview about PLM and Sustainability with a software vendor or implementer. Last year, in November 2023, Klaus Brettschneider and Jos Voskuil from the PLM Green Global Alliance core team spoke with Transition Technologies PSC about their GreenPLM offering and their first experiences in the field.
I am sharing another follow-up interview about PLM and Sustainability with a software vendor or implementer. Last year, in November 2023, Klaus Brettschneider and Jos Voskuil from the PLM Green Global Alliance core team spoke with Transition Technologies PSC about their GreenPLM offering and their first experiences in the field.
As we noticed with most first interviews, sustainability was a topic of discussion in the PLM domain, but it was still in the early discovery phases for all of us.
![]() Last week, we spoke again with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services. The exciting part of this discussion is that system integrators are usually more directly connected to their customers in the field and, therefore, can be the source of understanding of what is happening.
Last week, we spoke again with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services. The exciting part of this discussion is that system integrators are usually more directly connected to their customers in the field and, therefore, can be the source of understanding of what is happening.
ecoPLM and more
Where Erik is a and he is a long term PLM expert and Rafal is the PLM Practice Lead for Industrial Sustainability. In the interview below they shared their experiences with a first implementation pilot in the field, the value of their _ecoPLM offering in the context of the broader PTC portfolio. And of course we discussed topics closely related to these points and put them into a broader context of sustainably.
Enjoy the 34 minutes discussion and you are always welcome to comment or start a discussion with us.
The slides shown in this presentation and some more can be downloaded HERE.
What I learned
- The GreenPLM offering has changed its name into ecoPLM as TT PSC customers are focusing on developing sustainable products, with currently supporting designer to understand the carbon footprint of their products.
- They are actually in a MVP approach with a Tier 1 automotive supplier to validate and improve their solution and more customers are adding Design for Sustainability to their objective, besides Time to Market, Quality and Cost.
- Erik will provide a keynote speech at the Green PLM conference on November 14th in Berlin – The conference is targeting a German speaking audience although the papers are in English. You can still register and find more info here
- TT PSC is one of the partners completing the PTC sustainability offering and working close with their product management.
- A customer quote: “Sustainability makes PLM sexy again”
Want to learn more?
Here are some links related to the topics discussed in our meeting:
- YouTube: ecoPLM: your roadmap for eco-friendly product development
- ecoPLM – a sustainable product development website
- YouTube: Win the Net-Zero Race with PLM (and PTC)
Conclusions
We are making great progress in the support to design and deliver more sustainable products – sustainability goes beyond marketing as Rafal Witkowski mentioned – the journey has started. What do you see in your company?
 In recent years, I have assisted several companies in defining their PLM strategy. The good news is that these companies are talking first about a PLM strategy and not immediately about a PLM system selection.
In recent years, I have assisted several companies in defining their PLM strategy. The good news is that these companies are talking first about a PLM strategy and not immediately about a PLM system selection.
In addition, a PLM strategy should not be defined in isolation but rather as an integral part of a broader business strategy. One of my favorite one-liners is:
“Are we implementing the past, or are we implementing the future?”
When companies implement the past, it feels like they modernize their current ways of working with new technology and capabilities. The new environment is more straightforward to explain to everybody in the company, and even the topic of migration can be addressed as migration might be manageable.
 Note: Migration should always be considered – the elephant in the room.
Note: Migration should always be considered – the elephant in the room.
I wrote about Migration Migraine in two posts earlier this year, one describing the basics and the second describing the lessons learned and the path to a digital future.
Implementing PLM now should be part of your business strategy.
 Threats coming from different types of competitors, necessary sustainability-related regulations (e.g., CSRD reporting), and, on the positive side, new opportunities are coming (e.g., Product as a Service), all requiring your company to be adaptable to changes in products, services and even business models.
Threats coming from different types of competitors, necessary sustainability-related regulations (e.g., CSRD reporting), and, on the positive side, new opportunities are coming (e.g., Product as a Service), all requiring your company to be adaptable to changes in products, services and even business models.
Suppose your company wants to benefit from concepts like the Digital Twin and AI. In that case, it needs a data-driven infrastructure—
Digital Twins do not run on documents, and algorithms need reliable data.
Digital Transformation in the PLM domain means combining Coordinated and Connected working methods. In other words, you need to build an infrastructure based on Systems of Record and Systems of Engagement. Followers of my blog should be familiar with these terms.
PLM is not an R&D and Engineering solution
(any more)
One of the biggest misconceptions still made is that PLM is implemented by a single system mainly used by R&D and Engineering. These disciplines are considered the traditional creators of product data—a logical assumption at the time when PLM was more of a silo, Managing Projects with CAD and BOM data.
 However, this misconception frames many discussions towards discussions about what is the best system for my discipline, more or less strengthening the silos in an organization. Being able to break the silos is one of the technical capabilities digitization brings.
However, this misconception frames many discussions towards discussions about what is the best system for my discipline, more or less strengthening the silos in an organization. Being able to break the silos is one of the technical capabilities digitization brings.
Business and IT architecture are closely related. Perhaps you have heard about Conway’s law (from 1967):
“Any organization that designs a system (defined broadly) will produce a design whose structure is a copy of the organization’s communication structure.”
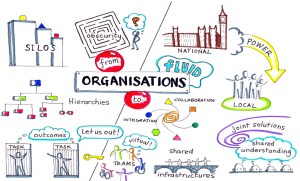 This means that if you plan to implement or improve a PLM infrastructure without considering an organizational change, you will be locked again into your traditional ways of working – the coordinated approach, which is reflected on the left side of the image (click on it to enlarge it).
This means that if you plan to implement or improve a PLM infrastructure without considering an organizational change, you will be locked again into your traditional ways of working – the coordinated approach, which is reflected on the left side of the image (click on it to enlarge it).
An organizational change impacts middle management, a significant category we often neglect. There is the C-level vision and the voice of the end user. Middle management has to connect them and still feel their jobs are not at risk. I wrote about it some years ago: The Middle Management Dilemma.
How do we adapt the business?
The biggest challenge of a business transformation is that it starts with the WHY and should be understood and supported at all organizational levels.
If there is no clear vision for change but a continuous push to be more efficient, your company is at risk!
For over 60 years, companies have been used to working in a coordinated approach, from paper-based to electronic deliverables.
- How do you motivate your organization to move in a relatively unknown direction?
- Who in your organization are the people who can build a digital vision and Strategy?
These two questions are fundamental, and you cannot outsource ownership of it.
 People in the transformation teams need to be digitally skilled (not geeks), communicators (storytellers), and, very importantly, connected to the business.
People in the transformation teams need to be digitally skilled (not geeks), communicators (storytellers), and, very importantly, connected to the business.
Often, the candidates come from the existing business units where they have proven skills. The challenging part is educating them and making them available for this mission.
Digital transformation is not a side job.
Education can come from the outside world. Making people available to work on the new digital infrastructure is a management decision and their sense of priority.
How to get external support?
If you are connected to the PLM world like me, a lot of information is available. In academic papers, projects and in particular on LinkedIn currently, there is an overflow of architectural debates:
Recently, I participated in the discussions below:
- How to Solve PLM & ERP (Oleg Shilovitsky)
- Last week, we finally solved PLM & ERP (Prof. Dr. Jörg W. Fischer / Martin Eigner)
- PLM and MBOM: Supply Chain Debates and Future Solution Architecture (Oleg Shilovitsky)
- Could be a Knowledge Graph resp. the Linked Data technologies the key to …. (Matthias Ahrens)
The challenge with these articles is that they are for insiders and far from shareable with business people. There is always a discussion, as we are all learning to match theory with reality. For example,Prof. Dr. Jörg W. Fischer introduced the Information Architecture as a missing link. You can read his recent post here and the quote below to get interested:
All of these methods focus either on Data Architecture or Business Architecture. And the blind spot? I am convinced that an essential layer between the two is missing. We at STZ-RIM Reshape Information Management call this Information Architecture.
Still, we remain in the expert domain, which a limited group of people understands. We need to connect to the business. Where can we find more education from the business side?
The reaction below in one of the discussions says it all, in my opinion:
Starting from the business
What I have learned from my discussions with the management is:
- Don’t mention PLM – you will be cornered in the R&D / Engineering frame.
- Don’t explain their problems, and tell them that you have the solution (on PowerPoint)
- Create curiosity about topics that are relevant to the business – What if …?
- Use storytelling to imagine a future state – Spare the details.
- Build trust and confidence that you are not selling a product. Let the company discover their needs as it is their transformation.
The diagram below, presented by Yousef Hooshmand during the PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2023 conference in Paris, describes it all:
It will be a continuous iterative process where, starting from business values and objectives, an implementation step is analyzed, how it fits in the PLM landscape and ultimately, how measures and actions guide the implementation of the tools and technology.
It is important to stress that this is not the guidance for a system implementation; it is the guidance for a digital transformation journey. Therefore, the message in the middle of the image is: Long-term Executive Commitment!
 In addition, I want to point to articles and blogs written by Jan Bosch. Jan is an Executive, professor and consultant with more than 20 years of experience in large-scale software R&D management and business.
In addition, I want to point to articles and blogs written by Jan Bosch. Jan is an Executive, professor and consultant with more than 20 years of experience in large-scale software R&D management and business.
Although our worlds do not intersect yet, the management of mechanical products and software is different; his principles fit better and better with a modern data-driven organization. Often, I feel we are fighting the same battle to coach companies in their business transformation.
In the context of this article, I recommend reviewing the BAPO model coming from the software world.
BAPO stands for Business, Architecture, Process and Organization. As the diagram below indicates, you should start from the business, defining the needs for the architecture and then the preferred ways of working. Finally, the organization has to be established in accordance with the processes.
Often, companies use the OPAB approach, which makes them feel more comfortable (Conway’s Law). For further reading in this context, I recommend the following posts from Jan Bosch:
Business and technology
I want to conclude by discussing ways to connect business and technology as you need both.
First, I want to point to an example that we presented in the Federated PLM interest group on LinkedIn. Although the discussion initially focused on technical capabilities, we concluded by connecting them to business transformational needs. The diagram below is our characteristic image used to explain the interaction between Systems of Record (the vertical pillars) and the Systems of Engagement (the horizontal bars – modularity).
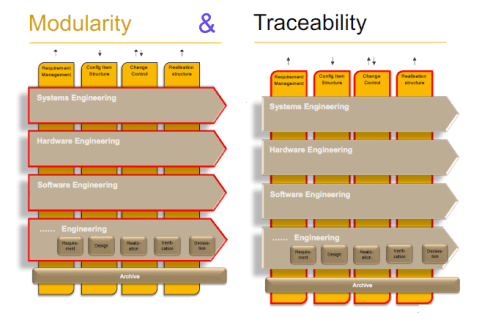
Have a look at the business discussion below:
Next, the diagram below comes from a 2017 McKinsey whitepaper: Toward an integrated technology operating model. Here, the authors describe how a company can move toward an integrated technology operating model using both coordinated and connected technologies.
They do not mention PLM; they have a business focus, and it is important to mention a company can work in different modes. This is an organizational choice, but don’t let people work in two modes,
Conclusion
With this post, I hope I moved the focus from technology and tools to an understandable business focus. Even within my 1500 words, there is much more to say, and this makes our (PLM) mission so complex and interesting. Let me know where you can connect.
 Last week, I participated in the annual 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference, organized by the ENOVIA and NETVIBES brands. With approximately 250 attendees, the 2-day conference on the High-Tech Campus in Eindhoven was fully booked.
Last week, I participated in the annual 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference, organized by the ENOVIA and NETVIBES brands. With approximately 250 attendees, the 2-day conference on the High-Tech Campus in Eindhoven was fully booked.
My PDM/PLM career started in 1990 in Eindhoven.
 First, I spent a significant part of my school life there, and later, I became a physics teacher in Eindhoven. Then, I got infected by CAD and data management, discovering SmarTeam, and the rest is history.
First, I spent a significant part of my school life there, and later, I became a physics teacher in Eindhoven. Then, I got infected by CAD and data management, discovering SmarTeam, and the rest is history.
As I wrote in my last year’s post, the 3DEXPERIENCE conference always feels like a reunion, as I have worked most of my time in the SmarTeam, ENOVIA, and 3DEXPERIENCE Eco-system.
Innovation Drivers in the Generative Economy
Stephane Declee and Morgan Zimmerman kicked off the conference with their keynote, talking about the business theme for 2024: the Generative Economy. Where the initial focus was on the Experience Economy and emotion, the Generative Economy includes Sustainability. It is a clever move as the word Sustainability, like Digital Transformation, has become such a generic term. The Generative Economy clearly explains that the aim is to be sustainable for the planet.
Stephane and Morgan talked about the importance of the virtual twin, which is different from digital twins. A virtual twin typically refers to a broader concept that encompasses not only the physical characteristics and behavior of an object or system but also its environment, interactions, and context within a virtual or simulated world. Virtual Twins are crucial to developing sustainable solutions.
Morgan concluded the session by describing the characteristics of the data-driven 3DEXPERIENCE platform and its AI fundamentals, illustrating all the facets of the mix of a System of Record (traditional PLM) and Systems of Record (MODSIM).
3DEXPERIENCE for All at automation.eXpress
Daniel Schöpf, CEO and founder of automation.eXpress GmbH, gave a passionate story about why, for his business, the 3DEXPERIENCE platform is the only environment for product development, collaboration and sales.
 Automation.eXpress is a young but typical Engineering To Order company building special machinery and services in dedicated projects, which means that every project, from sales to delivery, requires a lot of communication.
Automation.eXpress is a young but typical Engineering To Order company building special machinery and services in dedicated projects, which means that every project, from sales to delivery, requires a lot of communication.
For that reason, Daniel insisted all employees to communicate using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform on the cloud. So, there are no separate emails, chats, or other siloed systems.
Everyone should work connected to the project and the product as they need to deliver projects as efficiently and fast as possible.
Daniel made this decision based on his 20 years of experience in traditional ways of working—the coordinated approach. Now, starting from scratch in a new company without a legacy, Daniel chose the connected approach, an ideal fit for his organization, and using the cloud solution as a scalable solution, an essential criterium for a startup company.
 My conclusion is that this example shows the unique situation of an inspired leader with 20 years of experience in this business who does not choose ways of working from the past but starts a new company in the same industry, but now based on a modern platform approach instead of individual traditional tools.
My conclusion is that this example shows the unique situation of an inspired leader with 20 years of experience in this business who does not choose ways of working from the past but starts a new company in the same industry, but now based on a modern platform approach instead of individual traditional tools.
Augment Me Through Innovative Technology
 Dr. Cara Antoine gave an inspiring keynote based on her own life experience and lessons learned from working in various industries, a major oil & gas company and major high-tech hardware and software brands. Currently, she is an EVP and the Chief Technology, Innovation & Portfolio Officer at Capgemini.
Dr. Cara Antoine gave an inspiring keynote based on her own life experience and lessons learned from working in various industries, a major oil & gas company and major high-tech hardware and software brands. Currently, she is an EVP and the Chief Technology, Innovation & Portfolio Officer at Capgemini.
She explained how a life-threatening infection that caused blindness in one of her eyes inspired her to find ways to augment herself to keep on functioning.
 With that, she drew a parallel with humanity, who continuously have been augmenting themselves from the prehistoric day to now at an ever-increasing speed of change.
With that, she drew a parallel with humanity, who continuously have been augmenting themselves from the prehistoric day to now at an ever-increasing speed of change.
The current augmentation is the digital revolution. Digital technology is coming, and you need to be prepared to survive – it is Innovate of Abdicate.
Dr. Cara continued expressing the need to invest in innovation (me: it was not better in the past 😉 ) – and, of course, with an economic purpose; however, it should go hand in hand with social progress (gender diversity) and creating a sustainable planet (innovation is needed here).
 Besides the focus on innovation drivers, Dr. Cara always connected her message to personal interaction. Her recently published book Make it Personal describes the importance of personal interaction, even if the topics can be very technical or complex.
Besides the focus on innovation drivers, Dr. Cara always connected her message to personal interaction. Her recently published book Make it Personal describes the importance of personal interaction, even if the topics can be very technical or complex.
I read the book with great pleasure, and it was one of the cornerstones of the panel discussion next.
It is all about people…
It might be strange to have a session like this in an ENOVIA/NETVIBES User Conference; however, it is another illustration that we are not just talking about technology and tools.
 I was happy to introduce and moderate this panel discussion,also using the iconic Share PLM image, which is close to my heart.
I was happy to introduce and moderate this panel discussion,also using the iconic Share PLM image, which is close to my heart.
The panelists, Dr. Cara Antoine, Daniel Schöpf, and Florens Wolters, each actively led transformational initiatives with their companies.
We discussed questions related to culture, personal leadership and involvement and concluded with many insights, including “Create chemistry, identify a passion, empower diversity, and make a connection as it could make/break your relationship, were discussed.
And it is about processes.
 Another trend I discovered is that cloud-based business platforms, like the 3DEXERIENCE platform, switch the focus from discussing functions and features in tools to establishing platform-based environments, where the focus is more on data-driven and connected processes.
Another trend I discovered is that cloud-based business platforms, like the 3DEXERIENCE platform, switch the focus from discussing functions and features in tools to establishing platform-based environments, where the focus is more on data-driven and connected processes.
Some examples:
Data Driven Quality at Suzlon Energy Ltd.
 Florens Wolters, who also participated in the panel discussion “It is all about people ..” explained how he took the lead to reimagine the Sulon Energy Quality Management System using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform and ENOVIA from a disconnected, fragmented, document-driven Quality Management System with many findings in 2020 to a fully integrated data-driven management system with zero findings in 2023.
Florens Wolters, who also participated in the panel discussion “It is all about people ..” explained how he took the lead to reimagine the Sulon Energy Quality Management System using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform and ENOVIA from a disconnected, fragmented, document-driven Quality Management System with many findings in 2020 to a fully integrated data-driven management system with zero findings in 2023.
 It is an illustration that a modern data-driven approach in a connected environment brings higher value to the organization as all stakeholders in the addressed solution work within an integrated, real-time environment. No time is wasted to search for related information.
It is an illustration that a modern data-driven approach in a connected environment brings higher value to the organization as all stakeholders in the addressed solution work within an integrated, real-time environment. No time is wasted to search for related information.
 Of course, there is the organizational change management needed to convince people not to work in their favorite siloes system, which might be dedicated to the job, but not designed for a connected future.
Of course, there is the organizational change management needed to convince people not to work in their favorite siloes system, which might be dedicated to the job, but not designed for a connected future.
The image to the left was also a part of the “It is all about people”- session.
Enterprise Virtual Twin at Renault Group
 The presentation of Renault was also an exciting surprise. Last year, they shared the scope of the Renaulution project at the conference (see also my post: The week after the 3DEXPERIENCE conference 2023).
The presentation of Renault was also an exciting surprise. Last year, they shared the scope of the Renaulution project at the conference (see also my post: The week after the 3DEXPERIENCE conference 2023).
Here, Renault mentioned that they would start using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform as an enterprise business platform instead of a traditional engineering tool.
Their presentation today, which was related to their Engineering Virtual Twin, was an example of that. Instead of using their document-based SCR (Système de Conception Renault – the Renault Design System) with over 1000 documents describing processes connected to over a hundred KPI, they have been modeling their whole business architecture and processes in UAF using a Systems of System Approach.
The image above shows Franck Gana, Renault’s engineering – transformation chief officer, explaining the approach. We could write an entire article about the details of how, again, the 3DEXPERIENCE platform can be used to provide a real-time virtual twin of the actual business processes, ensuring everyone is working on the same referential.
Bringing Business Collaboration to the Next Level with Business Experiences
To conclude this section about the shifting focus toward people and processes instead of system features, Alizée Meissonnier Aubin and Antoine Gravot introduced a new offering from 3DS, the marketplace for Business Experiences.

According to the HBR article, workers switch an average of 1200 times per day between applications, leading to 9 % of their time reorienting themselves after toggling.
1200 is a high number and a plea for working in a collaboration platform instead of siloed systems (the Systems of Engagement, in my terminology – data-driven, real-time connected). The story has been told before by Daniel Schöpf, Florens Wolters and Franck Gana, who shared the benefits of working in a connected collaboration environment.
The announced marketplace will be a place where customers can download Business Experiences.
There is was more ….
There were several engaging presentations and workshops during the conference. But, as we reach 1500 words, I will mention just two of them, which I hope to come back to in a later post with more detail.
- Delivering Sustainable & Eco Design with the 3DS LCA Solution
 Valentin Tofana from Comau, an Italian multinational company in the automation and committed to more sustainable products. In the last context Valentin shared his experiences and lessons learned starting to use the 3DS LifeCycle Assessment tools on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
Valentin Tofana from Comau, an Italian multinational company in the automation and committed to more sustainable products. In the last context Valentin shared his experiences and lessons learned starting to use the 3DS LifeCycle Assessment tools on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
This session gave such a clear overview that we will come back with the PLM Green Global Alliance in a separate interview. - Beyond PLM. Productivity is the Key to Sustainable Business
 Neerav MEHTA from L&T Energy Hydrocarbon demonstrated how they currently have implemented a virtual twin of the plant, allowing everyone to navigate, collaborate and explore all activities related to the plant.I was promoting this concept in 2013 also for Oil & Gas EPC companies, at that time, an immense performance and integration challenge. (PLM for all industries) Now, ten years later, thanks to the capabilities of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, it has become a workable reality. Impressive.
Neerav MEHTA from L&T Energy Hydrocarbon demonstrated how they currently have implemented a virtual twin of the plant, allowing everyone to navigate, collaborate and explore all activities related to the plant.I was promoting this concept in 2013 also for Oil & Gas EPC companies, at that time, an immense performance and integration challenge. (PLM for all industries) Now, ten years later, thanks to the capabilities of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, it has become a workable reality. Impressive.
Conclusion
Again, I learned a lot during these days, seeing the architecture of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform growing (image below). In addition, more and more companies are shifting their focus to real-time collaboration processes in the cloud on a connected platform. Their testimonies illustrate that to be sustainable in business, you have to augment yourself with digital.
Note: Dassault Systemes did not cover any of the cost for me attending this conference. I picked the topics close to my heart and got encouraged by all the conversations I had.
 Last week, I shared my first impressions from my favorite conference, in the post: The weekend after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2023, where most impressions could be classified as traditional PLM and model-based.
Last week, I shared my first impressions from my favorite conference, in the post: The weekend after PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe 2023, where most impressions could be classified as traditional PLM and model-based.
There is nothing wrong with conventional PLM, as there is still much to do within this scope. A model-based approach for MBSE (Model-Based Systems Engineering) and MBD (Model-Based Definition) and efficient supplier collaboration are not topics you solve by implementing a new system.
 Ultimately, to have a business-sustainable PLM infrastructure, you need to structure your company internally and connect to the outside world with a focus on standards to avoid a vendor lock-in or a dead end.
Ultimately, to have a business-sustainable PLM infrastructure, you need to structure your company internally and connect to the outside world with a focus on standards to avoid a vendor lock-in or a dead end.
In short, this is what I described so far in The weekend after ….part 1.
Now, let’s look at the relatively new topics for this audience.
Enabling the Marketing, Engineering & Manufacturing Digital Thread
 Cyril Bouillard, the PLM & CAD Tools Referent at the Mersen Electrical Protection (EP) business unit, shared his experience implementing an end-to-end digital backbone from marketing through engineering and manufacturing.
Cyril Bouillard, the PLM & CAD Tools Referent at the Mersen Electrical Protection (EP) business unit, shared his experience implementing an end-to-end digital backbone from marketing through engineering and manufacturing.
Cyril showed the benefits of a modern PLM infrastructure that is not CAD-centric and focused on engineering only. The advantages of this approach are a seamless integrated flow of PLM and PIM (Product Information Management).

I wrote about this topic in 2019: PLM and PIM – the complementary value in a digital enterprise. Combining the concepts of PLM and PIM in an integrated, connected environment could also provide a serious benefit when collaborating with external parties.
 Another benefit Cyril demonstrated was the integration of RoHS compliance to the BOM as an integrated environment. In my session, I also addressed integrated RoHS compliance as a stepping stone to efficiency in future compliance needs.
Another benefit Cyril demonstrated was the integration of RoHS compliance to the BOM as an integrated environment. In my session, I also addressed integrated RoHS compliance as a stepping stone to efficiency in future compliance needs.
Read more later or in this post: Material Compliance – as a stepping-stone towards Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Cyril concluded with some lessons learned.
Data quality is essential in such an environment, and there are significant time savings implementing the connected Digital Thread.
Meeting the Challenges of Sustainability in Critical Transport Infrastructures
 Etienne Pansart, head of digital engineering for construction at SYSTRA, explained how they address digital continuity with PLM throughout the built assets’ lifecycle.
Etienne Pansart, head of digital engineering for construction at SYSTRA, explained how they address digital continuity with PLM throughout the built assets’ lifecycle.
Etienne’s story was related to the complexity of managing a railway infrastructure, which is a linear and vertical distribution at multiple scales; it needs to be predictable and under constant monitoring; it is a typical system of systems network, and on top of that, maintenance and operational conditions need to be continued up to date.
Regarding railway assets – a railway needs renewal every two years, bridges are designed to last a hundred years, and train stations should support everyday use.
When complaining about disturbances, you might have a little more respect now (depending on your country). However, on top of these challenges, Etienne also talked about the additional difficulties expected due to climate change: floods, fire, earth movements, and droughts, all of which will influence the availability of the rail infrastructure.
In that context, Etienne talked about the MINERVE project – see image below:
As you can see from the main challenges, there is an effort of digitalization for both the assets and a need to provide digital continuity over the entire asset lifecycle. This is not typically done in an environment with many different partners and suppliers delivering a part of the information.
Etienne explained in more detail how they aim to establish digital twins and MBSE practices to build and maintain a data-driven, model-based environment.
Having digital twins allows much more granular monitoring and making accurate design decisions, mainly related to sustainability, without the need to study the physical world.
His presentation was again a proof point that through digitalization and digital twins, the traditional worlds of Product Lifecycle Management and Asset Information Management become part of the same infrastructure.
 And it may be clear that in such a collaboration environment, standards are crucial to connect the various stakeholder’s data sources – Etienne mentioned ISO 16739 (IFC), IFC Rail, and ISO 19650 (BIM) as obvious standards but also ISO 10303 (PLCS) to support the digital thread leveraged by OSLC.
And it may be clear that in such a collaboration environment, standards are crucial to connect the various stakeholder’s data sources – Etienne mentioned ISO 16739 (IFC), IFC Rail, and ISO 19650 (BIM) as obvious standards but also ISO 10303 (PLCS) to support the digital thread leveraged by OSLC.
I am curious to learn more about the progress of such a challenging project – having worked with the high-speed railway project in the Netherlands in 1995 – no standards at that time (BIM did not exist) – mainly a location reference structure with documents. Nothing digital.
The connected Digital Thread
The theme of the conference was The Digital Thread in a Heterogeneous, Extended Enterprise Reality, and in the next section, I will zoom in on some of the inspiring sessions for the future, where collaboration or information sharing is all based on a connected Digital Thread – a term I will explain in more depth in my next blog post.
Transforming the PLM Landscape:
The Gateway to Business Transformation
 Yousef Hooshmand‘s presentation was the highlight of this conference for me.
Yousef Hooshmand‘s presentation was the highlight of this conference for me.
Yousef is the PLM Architect and Lead for the Modernization of the PLM Landscape at NIO, and he has been active before in the IT-landscape transformation at Daimler, on which he published the paper: From a monolithic PLM landscape to a federated domain and data mesh.
 If you read my blog or follow Share PLM, you might seen the reference to Yousef’s work before, or recently, you can hear the full story at the Share PLM Podcast: Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights.
If you read my blog or follow Share PLM, you might seen the reference to Yousef’s work before, or recently, you can hear the full story at the Share PLM Podcast: Episode 6: Revolutionizing PLM: Insights.
It was the first time I met Yousef in 3D after several virtual meetings, and his passion for the topic made it hard to fit in the assigned 30 minutes.
There is so much to share on this topic, and part of it we already did before the conference in a half-day workshop related to Federated PLM (more on this in the following review).
First, Yousef started with the five steps of the business transformation at NIO, where long-term executive commitment is a must.
His statement: “If you don’t report directly to the board, your project is not important”, caused some discomfort in the audience.
As the image shows, a business transformation should start with a systematic description and analysis of which business values and objectives should be targeted, where they fit in the business and IT landscape, what are the measures and how they can be tracked or assessed and ultimately, what we need as tools and technology.
In his paper From a Monolithic PLM Landscape to a Federated Domain and Data Mesh, Yousef described the targeted federated landscape in the image below.
And now some vendors might say, we have all these domains in our product portfolio (or we have slides for that) – so buy our software, and you are good.
And here Yousef added his essential message, illustrated by the image below.
Start by delivering the best user-centric solutions (in an MVP manner – days/weeks – not months/years). Next, be data-centric in all your choices and ultimately build an environment ready for change. As Yousef mentioned: “Make sure you own the data – people and tools can leave!”
And to conclude reporting about his passionate plea for Federated PLM:
“Stop talking about the Single Source of Truth, start Thinking of the Nearest Source of Truth based on the Single Source of Change”.
Heliple-2 PLM Federation:
A Call for Action & Contributions
 A great follow-up on Yousef’s session was Erik Herzog‘s presentation about the final findings of the Heliple 2 project, where SAAB Aeronautics, together with Volvo, Eurostep, KTH, IBM and Lynxwork, are investigating a new way of federated PLM, by using an OSLC-based, heterogeneous linked product lifecycle environment.
A great follow-up on Yousef’s session was Erik Herzog‘s presentation about the final findings of the Heliple 2 project, where SAAB Aeronautics, together with Volvo, Eurostep, KTH, IBM and Lynxwork, are investigating a new way of federated PLM, by using an OSLC-based, heterogeneous linked product lifecycle environment.
Heliple stands for HEterogeneous LInked Product Lifecycle Environment
The image below, which I shared several times before, illustrates the mindset of the project.
Last year, during the previous conference in Gothenburg, Erik introduced the concept of federated PLM – read more in my post: The week after PLM Roadmap / PDT Europe 2022, mentioning two open issues to be investigated: Operational feasibility (is it maintainable over time) and Realisation effectivity (is it affordable and maintainable at a reasonable cost)
As you can see from the slide below, the results were positive and encouraged SAAB to continue on this path.
One of the points to mention was that during this project, Lynxwork was used to speed up the development of the OSLC adapter, reducing costs, time and needed skills.
 After this successful effort, Erik and several others who joined us at the pre-conference workshop agreed that this initiative is valid to be tested, discussed and exposed outside Sweden.
After this successful effort, Erik and several others who joined us at the pre-conference workshop agreed that this initiative is valid to be tested, discussed and exposed outside Sweden.
Therefore, the Federated PLM Interest Group was launched to join people worldwide who want to contribute to this concept with their experiences and tools.
A first webinar from the group is already scheduled for December 12th at 4 PM CET – you can join and register here.
More to come
Given the length of this blog post, I want to stop here.
 Topics to share in the next post are related to my contribution at the conference The Need for a Governance Digital Thread, where I addressed the need for federated PLM capabilities with the upcoming regulations and practices related to sustainability, which require a connected Digital.
Topics to share in the next post are related to my contribution at the conference The Need for a Governance Digital Thread, where I addressed the need for federated PLM capabilities with the upcoming regulations and practices related to sustainability, which require a connected Digital.
 I want to combine this post with the findings that Mattias Johansson, CEO of Eurostep, shared in his session: Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense, goes beyond manufacturing, and should be standards-based.
I want to combine this post with the findings that Mattias Johansson, CEO of Eurostep, shared in his session: Why a Digital Thread makes a lot of sense, goes beyond manufacturing, and should be standards-based.
There are some interesting findings in these two presentations.
 And there was the introduction of AI at the conference, with some experts’ talks and thoughts. Perhaps at this stage, it is too high on Gartner’s hype cycle to go into details. It will surely be THE topic of discussion or interest you must have noticed.
And there was the introduction of AI at the conference, with some experts’ talks and thoughts. Perhaps at this stage, it is too high on Gartner’s hype cycle to go into details. It will surely be THE topic of discussion or interest you must have noticed.
The recent turmoil at OpenAI is an example of that. More to come for sure in the future.
Conclusion
The PLM Roadmap/PDT Europe conference was significant for me because I discovered that companies are working on concepts for a data-driven infrastructure for PLM and are (working on) implementing them. The end of monolithic PLM is visible, and companies need to learn to master data using ontologies, standards and connected digital threads.
 It might have been silent in the series of PLM and Sustainability … interviews where we as PLM Green Global Alliance core team members, talk with software vendors, implementers and consultants and their relation to PLM and sustainability. The interviews are still in a stage of exploring what is happening at this moment. More details per vendor or service provider next year.
It might have been silent in the series of PLM and Sustainability … interviews where we as PLM Green Global Alliance core team members, talk with software vendors, implementers and consultants and their relation to PLM and sustainability. The interviews are still in a stage of exploring what is happening at this moment. More details per vendor or service provider next year.
Our last interview was in April this year when we spoke with Mark Reisig, Green Energy Practice Director & Executive Consultant at CIMdata. You can find the interview here, and at that time, I mentioned the good news is that sustainability is no longer a software discussion.
As companies are planning or pushed by regulations to implement sustainable strategies, it becomes clear that education and guidance are needed beyond the tools.
This trend is also noticeable in our PLM Green Global Alliance community, which has grown significantly in the past half year. While writing this post, we have 862 members, not all as active as we hoped. Still, there is more good news related to dedicated contributors and more to come in the next PGGA update.
 This time, we want to share the interview with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services.
This time, we want to share the interview with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services.
I met them during the LiveWorx conference in Boston in May – you can read more about the conference in my post: The weekend after LiveWorx 2023. Here we decided to follow-up on GreenPLM/
GreenPLM
![]() The label “GreenPLM” is always challenging as it could be considered green-washing. However, in this case, GreenPLM is an additional software offering that can be implemented on top of a PLM system, enabling people to make scientifically informed decisions for a more sustainable, greener product.
The label “GreenPLM” is always challenging as it could be considered green-washing. However, in this case, GreenPLM is an additional software offering that can be implemented on top of a PLM system, enabling people to make scientifically informed decisions for a more sustainable, greener product.
For GreenPLM, Rafal’s and Erik’s experiences are based on implementing GreenPLM on top of the PTC Windchill suite. Listen for the next 34 minutes to an educative session and learn.
You can download the slides shown in the recording here.
What I learned
- It was more a general educative session related to the relation PLM and Sustainability, focusing on the importance of design decisions – the 80 % impact number.
- Erik considers sustainability not a disruption for designers; they already work within cost, quality and time parameters. Now, sustainability is the fourth dimension to consider.
- Erik’s opinion is also reflected in the pragmatic approach of GreenPLM as an additional extension of Windchill using PTC Navigate and OSLC standards.
- GreenPLM is more design-oriented than Mendix-based Sustaira, a sustainability platform we discussed in this series – you can find the recording here.
Want to learn more?
Here are some links related to the topics discussed in our meeting:
Conclusions
With GreenPLM, it is clear that the focus of design for sustainability is changing from a vision (led by software vendors and environmental regulations) towards implementations in the field. Pragmatic and an extension of the current PLM infrastructure. System integrators like Transition Technologies are the required bridge between vision and realization. We are looking for more examples from the field.
Two more weeks to go – don’t miss this opportunity when you are in Europe
Click on the image to see the full and interesting agenda/
 During May and June, I wrote a guest chapter for the next edition of John Stark’s book Product Lifecycle Management (Volume 2): The Devil is in the Details.
During May and June, I wrote a guest chapter for the next edition of John Stark’s book Product Lifecycle Management (Volume 2): The Devil is in the Details.
The book is considered a standard in the academic world when studying aspects of PLM.
Looking into the table of contents through the above link, it shows that understanding PLM in its full scope is broad. I wrote about it recently: PLM is Complex (and we have to accept it?), and Roger Tempest and others are still fighting to get the job as PLM Professional recognized Associate Yourself With Professional PLM.
 To make the scope broader, John invited me to write a chapter about PLM and Sustainability, which is an actual topic in many organizations. As sustainability is my dedicated topic in the PLM Global Green Alliance (PGGA) core team, I was happy to accept this challenge.
To make the scope broader, John invited me to write a chapter about PLM and Sustainability, which is an actual topic in many organizations. As sustainability is my dedicated topic in the PLM Global Green Alliance (PGGA) core team, I was happy to accept this challenge.
This activity is challenging because writing a chapter on a current topic might make it outdated soon. For the same reason, I never wanted to write a PLM book as I wrote in my 2014 post: Did you notice PLM is changing?
 The book, with the additional chapter, will be available later this year. I want to share with you in this post the topics I addressed in this chapter. Perhaps relevant for your organization or personal interests. Also, I am looking forward to learning if I missed any topics.
The book, with the additional chapter, will be available later this year. I want to share with you in this post the topics I addressed in this chapter. Perhaps relevant for your organization or personal interests. Also, I am looking forward to learning if I missed any topics.
Introduction
The chapter starts with defining the context. PLM is considered a strategy supported by a connected IT infrastructure, and for the definition of sustainability, I refer to the relevant SDGs as described on our PGGA theme page: PLM and Sustainability

Next, I discuss two major concepts indissoluble connected with sustainability.
The Circular Economy
On a planet with limited resources and still a growing consumption of raw materials, we need to follow the concepts of the circular economy in our businesses and lives. The circular economy section addresses mainly the hardware side of the butterfly as, here, PLM practices have the most significant impact.
The circular economy requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including businesses, governments and consumers. It involves rethinking production processes and establishing new consumption patterns. Policies and regulations will push for circular economy patterns, as seen in the following paragraphs.
Systems Thinking
A significant change in bringing products to the market will be the need to change how we look at our development processes. Historically, many of these processes were linear and only focused on time to market, cost and quality. Now, we have to look into other dimensions, like environmental impact, usage and impact on the planet. As I wrote in the past Systems Thinking – a must-have skill in the 21st century?
Systems Thinking is a cognitive approach that emphasizes understanding complex problems by considering interconnections, feedback loops, and emergent properties. It provides a holistic perspective and explores multiple viewpoints.
Systems Thinking guides problem-solving and decision-making and requires you to treat a solution with a mindset of a system interacting with other systems.
Regulations
More sustainable products and services will be driven primarily by existing and upcoming regulations. In this section, I refer to the success of the CFC (ChloroFluorCarbon) emission reduction, leading to slowly fixing the hole in the Ozon layer. Current regulations like WEEE, RoHS and REACH are already relevant for many companies, and compliance with these regulations is a good exercise for more stringent regulations related to Carbon emissions and upcoming related to the Digital Product Passport.

Making regulatory compliance a part of the concept phase ensures no late changes are needed to become compliant, saving time and costs. In addition, making regulatory compliance as much as possible with a data-driven approach reduces the overhead required to prove regulatory compliance. Both topics are part of a PLM strategy.
![]() In this context, see Lionel Grealou’s article 5 Brand Value Benefits at the Intersection of Sustainability and Product Compliance. The article has also been shared in our PGGA LinkedIn group.
In this context, see Lionel Grealou’s article 5 Brand Value Benefits at the Intersection of Sustainability and Product Compliance. The article has also been shared in our PGGA LinkedIn group.
Business
On the business side, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol is explained. How companies will have to report their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions and, ultimately, Scope 3 – see the image below for the details.
GHG reporting will support companies, investors and consumers to decide where to prioritize and put their money.
Ultimately, companies have to be profitable to survive in their business. The ESG framework is relevant in this context as it will allow investors to put their money not only based on short-term gains (as expected) but also on Environmental or Social parameters. There are a lot of discussions related to the ESG framework, as you might have read in Vincent de la Mar’s monthly newsletter, Sustainability & ESG Insights, which is also published in our PGGA group – a link below..
Besides ESG guidelines, there is also the drive by governments and consumers to push for a Product as a Service economy. Instead of owning products, consumers would pay for the usage of these products.
The concept is not new when considering lease cars, EV scooters, or streaming services like Spotify and Netflix. In the CIMdata PLM Roadmap/PDT Fall 2021 conference, we heard Kenn Webster explaining: In the future, you will own nothing & you will be happy.
Changing the business to a Product as a Service is not something done overnight. It requires repairable, upgradeable products. And business related, it requires a connected ecosystem of all stakeholders – the manufacturer, the finance company, and the operating entities.
Digital Transformation
All the subjects discussed before require real-time reporting and analysis combined with data access to compliance-related databases. More in the section related to Life Cycle Assessment. As I discussed last year in several conferences, a sustainability initiative starts with data-driven and model-based approaches during the concept phase, but when manufacturing and operating (connected) products in the field. You can read the entire story here: Sustainability and Data-Driven PLM – the Perfect Storm.

Life Cycle Analysis
Special attention is given in this chapter to Life Cycle Analysis, which seems to be a popular topic among PLM vendors. Here, they can provide tools to make a lifecycle assessment, and you can read an impression of these tools in a guest blog from Roger L. Franz titled PLM Tools to Design for Sustainability – PLM Green Global Alliance.
However, Lifecycle Analysis is not as simple. Looking at the ISO 14040 framework, which describes – having the right goals and scope in mind, allows you to do an LCA where the Product Category Rules (PCS) will enable companies to compare their products with others.
PCRs include the description of the product category, the goal of the LCA, functional units, system boundaries, cut-off criteria, allocation rules, impact categories, information on the use phase, units, calculation procedures, requirements for data quality, and other information on the lifecycle Inventory Phase.
So be aware there is more to do than installing a tool.
Digital Twin
 This section describes the importance of implementing a digital twin for the design phase, allowing companies to develop, test and analyze their products and services first virtually. Trade-off studies on virtual products are much cheaper, and when they are done in a data-driven, model-based environment, it will be the most efficient environment. In my terminology, setting up such a collaboration environment might be considered a System of Engagement.
This section describes the importance of implementing a digital twin for the design phase, allowing companies to develop, test and analyze their products and services first virtually. Trade-off studies on virtual products are much cheaper, and when they are done in a data-driven, model-based environment, it will be the most efficient environment. In my terminology, setting up such a collaboration environment might be considered a System of Engagement.
The second crucial digital twin mentioned is the digital twin from a product in operation where performance can be monitored and usage can be optimized for a minimal environmental impact. Suppose a company is able to create a feedback loop between its products in the field and its product innovation platform. In that case, it can benchmark its design models and update the product behavior for better performance.

The manufacturing digital twin is also discussed in the context of environmental impact, as choosing the right processes and resources can significantly affect scope 3 emissions.
The chapter finishes with the story of a fictive company, WePack, where we can follow the impact and implementations of the topics described in this chapter.
Conclusion
As I described in the introduction, the topic of PLM and Sustainability is relatively new and constantly evolving. What do you think? Did I miss any dimensions?
Feel free to contribute to our PLM Global Green Alliance LinkedIn group.



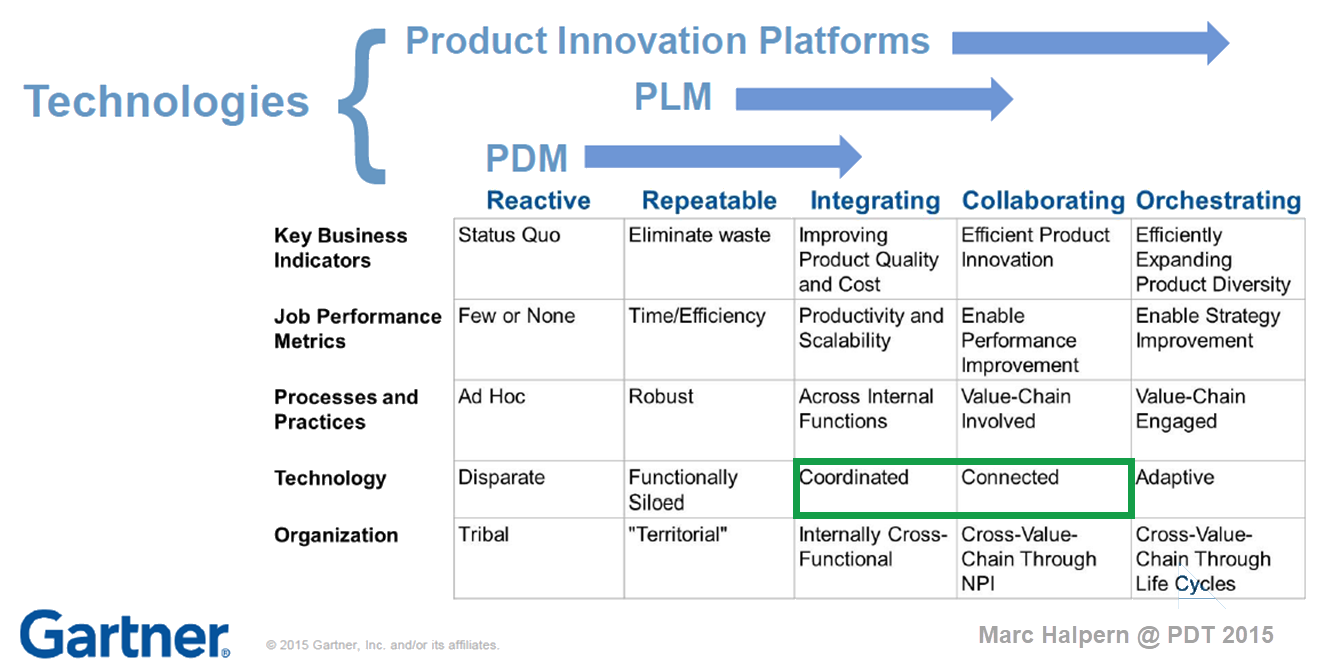

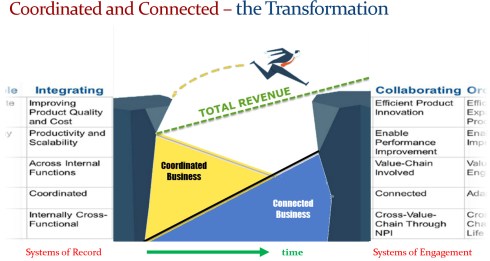
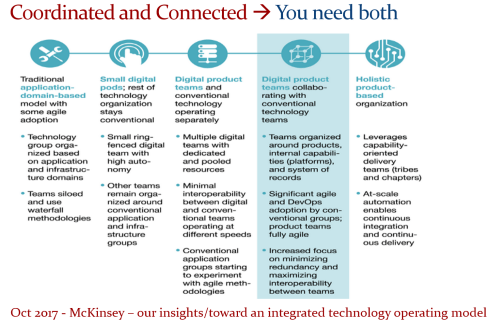


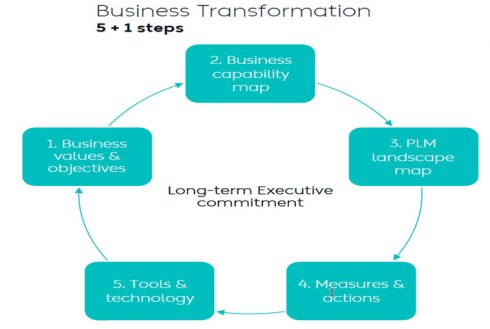

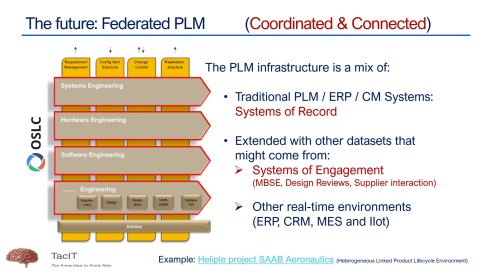

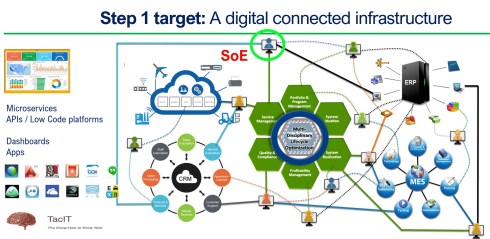
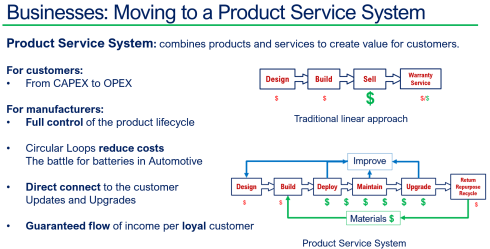
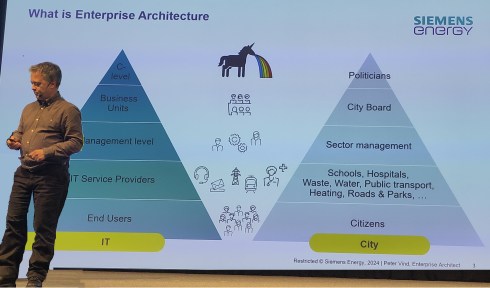

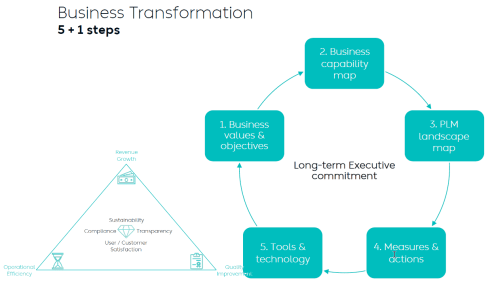
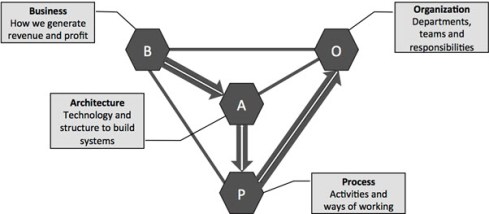






















[…] (The following post from PLM Green Global Alliance cofounder Jos Voskuil first appeared in his European PLM-focused blog HERE.) […]
[…] recent discussions in the PLM ecosystem, including PSC Transition Technologies (EcoPLM), CIMPA PLM services (LCA), and the Design for…
Jos, all interesting and relevant. There are additional elements to be mentioned and Ontologies seem to be one of the…
Jos, as usual, you've provided a buffet of "food for thought". Where do you see AI being trained by a…
Hi Jos. Thanks for getting back to posting! Is is an interesting and ongoing struggle, federation vs one vendor approach.…