You are currently browsing the category archive for the ‘Life Cycle Assessment’ category.
 This is a guest post from one of our active members of the PLM Green Global Alliance, Roger L. Franz.
This is a guest post from one of our active members of the PLM Green Global Alliance, Roger L. Franz.
Roger is supporting industry inquiries on regulated substances, sustainable product design and life cycle management, including carbon footprint.
He is a recognized authority on supply chain reporting for compliance with worldwide regulations. Roger brings decades of experience with engineering tools and enterprise IT systems.
Introduction.
More than just unsightly “plastic pollution,” the volume of consumer plastics and lack of closed-loop recovery have created a significant micro- and nano-plastics problem. These invisible plastic particles are found around the world, including in animal and human tissues.
For several reasons, including a much smaller volume of plastic used in electrotechnical products compared to consumer plastics and the generally longer life of hardware compared to the rapid turnover of consumer goods and packaging, the microplastics problem is not typically tagged as a major electronics problem- or at least not yet. Now is the time to be proactive.
 The United Nations Environment Programme has posted summaries of recent discussions on using life cycle assessment (LCA) to address the global problem of plastic pollution. These Life Cycle Initiative areas relate to plastic products, chemicals of concern in plastic products, and plastic product design. The documents are about possible approaches to managing plastics with recommendations but are not detailed prescriptions, methods, or regulations.
The United Nations Environment Programme has posted summaries of recent discussions on using life cycle assessment (LCA) to address the global problem of plastic pollution. These Life Cycle Initiative areas relate to plastic products, chemicals of concern in plastic products, and plastic product design. The documents are about possible approaches to managing plastics with recommendations but are not detailed prescriptions, methods, or regulations.
While the studies did not specifically mention electrotechnical products, this industry will need to accelerate focus on engineering design tools and engineering plastics choices to avoid significantly adding on to the consumer plastic product problems.
Within the UNEP product design discussion, the section on “General considerations on possible approaches to product design, focusing on recyclability and reusability” included the following important point, which bears repeating: Product design approaches should include eco-design and circularity principles.
Product design approaches should include
eco-design and circularity principles.
But what does this mean? In the following discussion, we hope to break these approaches down into more tangible design choices. Even within the electrotechnical product category, there are many product variations, so no claim is made here to cover all of them.
Options for lower carbon footprint plastics already exist to some extent. Except for packaging, electronic components and products are typically made with engineering resins rather than the common consumer plastic “recycling arrow” types. Alternative types of lower carbon footprint engineering resins may be available to use rather than others with higher carbon footprints.
Many plastic manufacturers are currently conducting LCA to quantify the cradle-to-gate carbon footprint of their materials. Different polymer types have inherent differences in carbon footprint due to their different monomeric starting materials and manufacturing processes.
 For many plastics, these flows are detailed by Plastics Europe. Polycarbonate, ABS, and several Polyamides, for example, are included. What is missing in these publicly available sources, as well as LCA inventory databases themselves, are many other engineering plastics; for example, while consumer PET is widely modeled, PBT (Polybutylene terephthalate) is not. These are just some of the data gaps that need to be resolved.
For many plastics, these flows are detailed by Plastics Europe. Polycarbonate, ABS, and several Polyamides, for example, are included. What is missing in these publicly available sources, as well as LCA inventory databases themselves, are many other engineering plastics; for example, while consumer PET is widely modeled, PBT (Polybutylene terephthalate) is not. These are just some of the data gaps that need to be resolved.
More sustainable feedstock is a good option since a given end polymer may be made from different monomeric chemicals, so the more sustainable plastic performs exactly like its classic version because it is the same. One of the growing alternatives includes feedstocks based on renewable, bio-based sources.
 These need some evaluation, again using LCA, to ensure they are free of downsides like increased water use, eutrophication, and chemical pollution due to the use of herbicides, pesticides, fertilizers, and so on. Marketing claims of being a “green material” will need backup data! For guidelines on acceptable environmental benefits claims, refer to the US FTC Green Guides.
These need some evaluation, again using LCA, to ensure they are free of downsides like increased water use, eutrophication, and chemical pollution due to the use of herbicides, pesticides, fertilizers, and so on. Marketing claims of being a “green material” will need backup data! For guidelines on acceptable environmental benefits claims, refer to the US FTC Green Guides.
Reducing the amount of plastic by design is not only a good practice for sustainability, it also saves money. Some designs using parts with enough material to be modeled using generative design may be able to reduce the amount of material while reducing material usage and weight. Reducing factory scrap from injection molding processes leaving sprues in runners and use of captive regrind are other good options.
Choosing manufacturers using renewable fuels– and even benefits like reduction of water use during processing- is another area of choice for sustainability. Local sourcing is also a way to reduce the overall carbon footprint of a material by reducing the contribution of transportation.
Identify large plastic parts. Historical guidelines on eco-design have actually been around for years.
 One good example is the ECMA 341 Standard, “Environmental Design Considerations for ICT & CE Products (4th Edition / December 2010), which says, “All plastic parts weighing 25 g or more and with a flat area of 200 mm2 or more are marked with the type of polymer, copolymer, polymer blends or alloys in conformance with ISO 11469.” This practice enables the identification of plastic types of large parts, while in practice, the ability to sort becomes less useful when a variety of goods are mixed in a production recycling facility. Success here depends either on manual sorting or more sophisticated methods like infrared spectroscopy to be effective. Some equipment recyclers have such capability.
One good example is the ECMA 341 Standard, “Environmental Design Considerations for ICT & CE Products (4th Edition / December 2010), which says, “All plastic parts weighing 25 g or more and with a flat area of 200 mm2 or more are marked with the type of polymer, copolymer, polymer blends or alloys in conformance with ISO 11469.” This practice enables the identification of plastic types of large parts, while in practice, the ability to sort becomes less useful when a variety of goods are mixed in a production recycling facility. Success here depends either on manual sorting or more sophisticated methods like infrared spectroscopy to be effective. Some equipment recyclers have such capability.
Keep it clean. More useful guidance from ECMA 341 is to avoid the following: non-recyclable composites; coatings and surface finishes on plastic parts; adhesive-backed stickers or foams on plastic parts; if stickers are required, they should be separable; and metal inserts in plastic parts unless easily removable with common tools. These are common sense from a clean recycling stream perspective and should not be difficult to implement.
Closing the end-of-life loop. Recycling is imperfect, and as far as this author has seen, is rarely in place for engineering plastics.
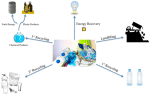 Processes under development to decompose plastics back to new monomer feedstocks, called chemical recycling or tertiary recycling. This approach is achieving some success with a limited number of materials, mostly for high-volume consumer plastics rather than engineering types.
Processes under development to decompose plastics back to new monomer feedstocks, called chemical recycling or tertiary recycling. This approach is achieving some success with a limited number of materials, mostly for high-volume consumer plastics rather than engineering types.
LCA is needed to validate that achieving plastic circularity this way with the necessary processing energy and chemicals will have a net environmental benefit. The obvious problem with all approaches is that plastics were never designed for the environment in the first place.
Selecting More Sustainable Additives is another area where product engineers have some choices. There are thousands of possible additives used in plastic, usually specified for a given grade and end application. These include flame retardants, processing aids, fillers, colorants, ultraviolet stabilizers, plasticizers for flexibility, and so on and on. While these choices are primarily the responsibility of the resin manufacturer, pressure from regulators and industry demand can influence the use of more sustainable additives.
Whenever possible, new products should avoid regulated substances by design, which may include Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) as defined by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and, more recently, polyfluorinated substances called PFAS. This is easier said than done but definitely belongs on the checklist of ecodesign considerations.
Besides plastics? While the present discussion is about plastics, choices of using altogether different materials may be possible in some cases.
 High-volume hardware is probably unable to use alternative materials like wood, glass, bamboo, etc. Historically, though, until the rise of both solid-state and plastic technology in the 1950s, radios and televisions featured wooden cases and consoles. Miniaturization in the solid-state era brought in mostly plastic housings. One recent example that the author worked on was an audio teleconferencing system that featured either oak or walnut to blend with the executive conference room.
High-volume hardware is probably unable to use alternative materials like wood, glass, bamboo, etc. Historically, though, until the rise of both solid-state and plastic technology in the 1950s, radios and televisions featured wooden cases and consoles. Miniaturization in the solid-state era brought in mostly plastic housings. One recent example that the author worked on was an audio teleconferencing system that featured either oak or walnut to blend with the executive conference room.
While the intent was not specifically to avoid using plastic, it is an interesting example to think outside the plastic box. Wood avoids many of the issues with plastics, but of course, the plastics in the circuitry content remain to be addressed.
Other large household electrical/electronic goods are likely to use recyclable steel and/or stainless steel cabinets. And if you consider an automobile to be an electronic product, these metals come into play in high volume in automobile shredder residue. Using metal rather than plastic housings may be possible for some products; for example, aluminum may be used for personal communications and IT devices, bringing a tradeoff between initial cost and the potential advantage of aluminum being more highly recyclable for use in new equipment than any plastic.
Only LCA can quantify the tradeoffs. We should also mention toys, which increasingly incorporate some electronics and use colored plastics extensively.
New material technology. One of the many emerging material technologies is Engineered Wood. The cited research hardly suggests that a wood-based material could be a drop-in, for example, injection molded thermoplastics, but the possibility is most intriguing. However, just having a material of natural origins is not automatically a panacea for replacing plastics. Quite the contrary, significant cautions remain; for example,
“Chemical and thermal modifications are usually applied to adapt the wood structure and impart necessary functionalities. Most of these treatments use substantial amounts of chemicals, energy, and water. They also innocently incorporate unwanted chemically bonded structures into the wood and generate a large amount of waste products which are harmful to the environment. This brings a dilemma where an entirely sustainable and green material is converted to a non-environmentally friendly material”
(El Akban et. al, Green Chemistry, 2021).
For now, the point is that reconsidering classical synthetic polymers in the light of more natural and renewable materials may have an interesting future.
Modularity. The ease of disassembly into “modules” is often listed as an eco-design practice that improves circularity, but the present author is skeptical about providing practical details. More specific guidance requires each manufacturer to know how its products can be disassembled at their end of life and where such disassembly would lead in terms of reuse, remanufacturing, or material recovery. In the context of plastics, a large plastic housing that can be easily disassembled into a single clean material is more likely to be sent to a recycler rather than reused as a “module” in other products.
It is unfortunate that software tools to make early design choices for disassembly began to be developed 25 years ago but have gone by the wayside since. The author had personal experience with such a “Green Design Advisor” tool that modeled a product assembly from its raw materials and showed how disassembly into environmentally and economically viable recovery fractions could be optimized.
One example that is probably still true today is that an epoxy circuit board and its components would be a “module” to be submitted to size a reduction, separation, and metal recovery process. Such a tool could also model the choice of a plastic housing vs. a metal alloy and the impacts of circular recovery of the material choices. Disassembly modeling tools for product designers is an area that needs significant development now, while software using artificial intelligence (AI) claims to be the answer. We shall see.
In conclusion, it must be recognized that most plastics were never designed for the environment in the first place. While there is currently no 100% perfect alternative, engineers do have options to improve the life cycle sustainability of tomorrow’s products.
- Select lower PCF plastics and avoid regulated additives.
- Reduce the amount of plastics if possible and keep larger parts free of different materials.
- Consider materials other than plastics.
- Be aware of new developments in both sources of plastic and end-of-life options.
Roger L. Franz / RogerLFranz@gmail.com – Sept. 2024
 Our recent interviews this year with aPriori and SAP were with companies that had less of a focus on the traditional product design process and more of a focus on the (circular) manufacturing process. In these interviews the importance of working with connected data was discussed in a shared (digital) thread.
Our recent interviews this year with aPriori and SAP were with companies that had less of a focus on the traditional product design process and more of a focus on the (circular) manufacturing process. In these interviews the importance of working with connected data was discussed in a shared (digital) thread.
This time, we, Mark Reisig and Jos Voskuil, were excited to talk with Siemens, not only a well-known PLM vendor but also a manufacturer of products and, therefore, having a close understanding of what is needed and can be achieved with their software solutions.
Siemens
![]() As Siemens is such a broad enterprise; we were happy to speak with Ryan R. Rochelle, who focuses on Sustainable Production, Sustainable Manufacturing and Sustainable Industry within Siemens . In the interview we discussed the importance of digital twins and the feedback loops between design and manufacturing. Despite some flaws in the network connection, we are happy to share an informative interview.
As Siemens is such a broad enterprise; we were happy to speak with Ryan R. Rochelle, who focuses on Sustainable Production, Sustainable Manufacturing and Sustainable Industry within Siemens . In the interview we discussed the importance of digital twins and the feedback loops between design and manufacturing. Despite some flaws in the network connection, we are happy to share an informative interview.
Enjoy listening and watching the next 33 minutes, talking with Ryan Rochelle.
You can download the images shown during the interview HERE
What I have learned
- Like all PLM vendors in this domain, Siemens talks about the importance of a circular economy and the need for digital threads and digital twins, confirming the need for all of us to invest in the digitization of the product lifecycle.

- Siemens is in a unique position as both the industrial user and software provider of its PLM suite, therefore having a unique feedback loop on the usability and applicability of its software in its industry.
- In the area of sustainability, they learn from both customers and internal customers. They are customer zero. Here, they observe shifting in engineering activities to the left” to optimize processes, supply chain and manufacturing earlier . (<<PGGA>>: which aligns with our aPriori and Makersite interviews).
- Siemens, SiGreen’s solution is an example of this unique position, being be able to track the carbon footprint of products across the supply chain.
Want to learn more
- There is the Siemens Sustainable industries website
- How the Digital Enterprise helps attain sustainability
- The Journey to a Sustainability Lighthouse awarded by the World Economic Forum
Conclusion
We have been discussing the relationship between PLM and sustainability with relevant software vendors for over two years now. As we saw initially in 2022, a few companies were exploring the possibilities.
Now, with further regulations and advanced software capabilities, companies are starting to implement new capabilities to make their product development process and products more sustainable. Siemens, as a software provider and an industrial user of its tools, is leading this journey—is it time for your company to step up, too?
 Last week, I participated in the annual 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference, organized by the ENOVIA and NETVIBES brands. With approximately 250 attendees, the 2-day conference on the High-Tech Campus in Eindhoven was fully booked.
Last week, I participated in the annual 3DEXPERIENCE User Conference, organized by the ENOVIA and NETVIBES brands. With approximately 250 attendees, the 2-day conference on the High-Tech Campus in Eindhoven was fully booked.
My PDM/PLM career started in 1990 in Eindhoven.
 First, I spent a significant part of my school life there, and later, I became a physics teacher in Eindhoven. Then, I got infected by CAD and data management, discovering SmarTeam, and the rest is history.
First, I spent a significant part of my school life there, and later, I became a physics teacher in Eindhoven. Then, I got infected by CAD and data management, discovering SmarTeam, and the rest is history.
As I wrote in my last year’s post, the 3DEXPERIENCE conference always feels like a reunion, as I have worked most of my time in the SmarTeam, ENOVIA, and 3DEXPERIENCE Eco-system.
Innovation Drivers in the Generative Economy
Stephane Declee and Morgan Zimmerman kicked off the conference with their keynote, talking about the business theme for 2024: the Generative Economy. Where the initial focus was on the Experience Economy and emotion, the Generative Economy includes Sustainability. It is a clever move as the word Sustainability, like Digital Transformation, has become such a generic term. The Generative Economy clearly explains that the aim is to be sustainable for the planet.
Stephane and Morgan talked about the importance of the virtual twin, which is different from digital twins. A virtual twin typically refers to a broader concept that encompasses not only the physical characteristics and behavior of an object or system but also its environment, interactions, and context within a virtual or simulated world. Virtual Twins are crucial to developing sustainable solutions.
Morgan concluded the session by describing the characteristics of the data-driven 3DEXPERIENCE platform and its AI fundamentals, illustrating all the facets of the mix of a System of Record (traditional PLM) and Systems of Record (MODSIM).
3DEXPERIENCE for All at automation.eXpress
Daniel Schöpf, CEO and founder of automation.eXpress GmbH, gave a passionate story about why, for his business, the 3DEXPERIENCE platform is the only environment for product development, collaboration and sales.
 Automation.eXpress is a young but typical Engineering To Order company building special machinery and services in dedicated projects, which means that every project, from sales to delivery, requires a lot of communication.
Automation.eXpress is a young but typical Engineering To Order company building special machinery and services in dedicated projects, which means that every project, from sales to delivery, requires a lot of communication.
For that reason, Daniel insisted all employees to communicate using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform on the cloud. So, there are no separate emails, chats, or other siloed systems.
Everyone should work connected to the project and the product as they need to deliver projects as efficiently and fast as possible.
Daniel made this decision based on his 20 years of experience in traditional ways of working—the coordinated approach. Now, starting from scratch in a new company without a legacy, Daniel chose the connected approach, an ideal fit for his organization, and using the cloud solution as a scalable solution, an essential criterium for a startup company.
 My conclusion is that this example shows the unique situation of an inspired leader with 20 years of experience in this business who does not choose ways of working from the past but starts a new company in the same industry, but now based on a modern platform approach instead of individual traditional tools.
My conclusion is that this example shows the unique situation of an inspired leader with 20 years of experience in this business who does not choose ways of working from the past but starts a new company in the same industry, but now based on a modern platform approach instead of individual traditional tools.
Augment Me Through Innovative Technology
 Dr. Cara Antoine gave an inspiring keynote based on her own life experience and lessons learned from working in various industries, a major oil & gas company and major high-tech hardware and software brands. Currently, she is an EVP and the Chief Technology, Innovation & Portfolio Officer at Capgemini.
Dr. Cara Antoine gave an inspiring keynote based on her own life experience and lessons learned from working in various industries, a major oil & gas company and major high-tech hardware and software brands. Currently, she is an EVP and the Chief Technology, Innovation & Portfolio Officer at Capgemini.
She explained how a life-threatening infection that caused blindness in one of her eyes inspired her to find ways to augment herself to keep on functioning.
 With that, she drew a parallel with humanity, who continuously have been augmenting themselves from the prehistoric day to now at an ever-increasing speed of change.
With that, she drew a parallel with humanity, who continuously have been augmenting themselves from the prehistoric day to now at an ever-increasing speed of change.
The current augmentation is the digital revolution. Digital technology is coming, and you need to be prepared to survive – it is Innovate of Abdicate.
Dr. Cara continued expressing the need to invest in innovation (me: it was not better in the past 😉 ) – and, of course, with an economic purpose; however, it should go hand in hand with social progress (gender diversity) and creating a sustainable planet (innovation is needed here).
 Besides the focus on innovation drivers, Dr. Cara always connected her message to personal interaction. Her recently published book Make it Personal describes the importance of personal interaction, even if the topics can be very technical or complex.
Besides the focus on innovation drivers, Dr. Cara always connected her message to personal interaction. Her recently published book Make it Personal describes the importance of personal interaction, even if the topics can be very technical or complex.
I read the book with great pleasure, and it was one of the cornerstones of the panel discussion next.
It is all about people…
It might be strange to have a session like this in an ENOVIA/NETVIBES User Conference; however, it is another illustration that we are not just talking about technology and tools.
 I was happy to introduce and moderate this panel discussion,also using the iconic Share PLM image, which is close to my heart.
I was happy to introduce and moderate this panel discussion,also using the iconic Share PLM image, which is close to my heart.
The panelists, Dr. Cara Antoine, Daniel Schöpf, and Florens Wolters, each actively led transformational initiatives with their companies.
We discussed questions related to culture, personal leadership and involvement and concluded with many insights, including “Create chemistry, identify a passion, empower diversity, and make a connection as it could make/break your relationship, were discussed.
And it is about processes.
 Another trend I discovered is that cloud-based business platforms, like the 3DEXERIENCE platform, switch the focus from discussing functions and features in tools to establishing platform-based environments, where the focus is more on data-driven and connected processes.
Another trend I discovered is that cloud-based business platforms, like the 3DEXERIENCE platform, switch the focus from discussing functions and features in tools to establishing platform-based environments, where the focus is more on data-driven and connected processes.
Some examples:
Data Driven Quality at Suzlon Energy Ltd.
 Florens Wolters, who also participated in the panel discussion “It is all about people ..” explained how he took the lead to reimagine the Sulon Energy Quality Management System using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform and ENOVIA from a disconnected, fragmented, document-driven Quality Management System with many findings in 2020 to a fully integrated data-driven management system with zero findings in 2023.
Florens Wolters, who also participated in the panel discussion “It is all about people ..” explained how he took the lead to reimagine the Sulon Energy Quality Management System using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform and ENOVIA from a disconnected, fragmented, document-driven Quality Management System with many findings in 2020 to a fully integrated data-driven management system with zero findings in 2023.
 It is an illustration that a modern data-driven approach in a connected environment brings higher value to the organization as all stakeholders in the addressed solution work within an integrated, real-time environment. No time is wasted to search for related information.
It is an illustration that a modern data-driven approach in a connected environment brings higher value to the organization as all stakeholders in the addressed solution work within an integrated, real-time environment. No time is wasted to search for related information.
 Of course, there is the organizational change management needed to convince people not to work in their favorite siloes system, which might be dedicated to the job, but not designed for a connected future.
Of course, there is the organizational change management needed to convince people not to work in their favorite siloes system, which might be dedicated to the job, but not designed for a connected future.
The image to the left was also a part of the “It is all about people”- session.
Enterprise Virtual Twin at Renault Group
 The presentation of Renault was also an exciting surprise. Last year, they shared the scope of the Renaulution project at the conference (see also my post: The week after the 3DEXPERIENCE conference 2023).
The presentation of Renault was also an exciting surprise. Last year, they shared the scope of the Renaulution project at the conference (see also my post: The week after the 3DEXPERIENCE conference 2023).
Here, Renault mentioned that they would start using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform as an enterprise business platform instead of a traditional engineering tool.
Their presentation today, which was related to their Engineering Virtual Twin, was an example of that. Instead of using their document-based SCR (Système de Conception Renault – the Renault Design System) with over 1000 documents describing processes connected to over a hundred KPI, they have been modeling their whole business architecture and processes in UAF using a Systems of System Approach.
The image above shows Franck Gana, Renault’s engineering – transformation chief officer, explaining the approach. We could write an entire article about the details of how, again, the 3DEXPERIENCE platform can be used to provide a real-time virtual twin of the actual business processes, ensuring everyone is working on the same referential.
Bringing Business Collaboration to the Next Level with Business Experiences
To conclude this section about the shifting focus toward people and processes instead of system features, Alizée Meissonnier Aubin and Antoine Gravot introduced a new offering from 3DS, the marketplace for Business Experiences.

According to the HBR article, workers switch an average of 1200 times per day between applications, leading to 9 % of their time reorienting themselves after toggling.
1200 is a high number and a plea for working in a collaboration platform instead of siloed systems (the Systems of Engagement, in my terminology – data-driven, real-time connected). The story has been told before by Daniel Schöpf, Florens Wolters and Franck Gana, who shared the benefits of working in a connected collaboration environment.
The announced marketplace will be a place where customers can download Business Experiences.
There is was more ….
There were several engaging presentations and workshops during the conference. But, as we reach 1500 words, I will mention just two of them, which I hope to come back to in a later post with more detail.
- Delivering Sustainable & Eco Design with the 3DS LCA Solution
 Valentin Tofana from Comau, an Italian multinational company in the automation and committed to more sustainable products. In the last context Valentin shared his experiences and lessons learned starting to use the 3DS LifeCycle Assessment tools on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
Valentin Tofana from Comau, an Italian multinational company in the automation and committed to more sustainable products. In the last context Valentin shared his experiences and lessons learned starting to use the 3DS LifeCycle Assessment tools on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
This session gave such a clear overview that we will come back with the PLM Green Global Alliance in a separate interview. - Beyond PLM. Productivity is the Key to Sustainable Business
 Neerav MEHTA from L&T Energy Hydrocarbon demonstrated how they currently have implemented a virtual twin of the plant, allowing everyone to navigate, collaborate and explore all activities related to the plant.I was promoting this concept in 2013 also for Oil & Gas EPC companies, at that time, an immense performance and integration challenge. (PLM for all industries) Now, ten years later, thanks to the capabilities of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, it has become a workable reality. Impressive.
Neerav MEHTA from L&T Energy Hydrocarbon demonstrated how they currently have implemented a virtual twin of the plant, allowing everyone to navigate, collaborate and explore all activities related to the plant.I was promoting this concept in 2013 also for Oil & Gas EPC companies, at that time, an immense performance and integration challenge. (PLM for all industries) Now, ten years later, thanks to the capabilities of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, it has become a workable reality. Impressive.
Conclusion
Again, I learned a lot during these days, seeing the architecture of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform growing (image below). In addition, more and more companies are shifting their focus to real-time collaboration processes in the cloud on a connected platform. Their testimonies illustrate that to be sustainable in business, you have to augment yourself with digital.
Note: Dassault Systemes did not cover any of the cost for me attending this conference. I picked the topics close to my heart and got encouraged by all the conversations I had.
 We are happy to start the year with the next round of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability. This year, we will speak with some new companies, and we will also revisit some of our previous guests to learn about their progress.
We are happy to start the year with the next round of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability. This year, we will speak with some new companies, and we will also revisit some of our previous guests to learn about their progress.
Where we talked with Aras, Autodesk, CIMdata, Dassault Systèmes, PTC, SAP, Sustaira and Transition Technologies PSC, there are still a lot of software companies with an exciting portfolio related to sustainability.
Therefore, we are happy to talk this time with Makersite, a company whose AI-powered Product Lifecycle Intelligence software, according to their home page, brings together your cost, environment, compliance, and risk data in one place to make smarter, greener decisions powered by the deepest understanding of your supply chain. Let’s explore
Makersite
![]() We were lucky to have a stimulating discussion with Neil D’Souza, Makersite’s CEO and founder, who was active in the field of sustainability for almost twenty years, even before it became a cool (or disputed) profession.
We were lucky to have a stimulating discussion with Neil D’Souza, Makersite’s CEO and founder, who was active in the field of sustainability for almost twenty years, even before it became a cool (or disputed) profession.
It was an exciting dialogue where we enjoyed realistic answers without all the buzzwords and marketing terms often used in the new domain of sustainability. Enjoy the 39 minutes of interaction below:
Slides shown during the interview combined with additional company information can be found HERE.
What we have learned
- Makersite’s mission, to enable manufacturers to make better products, faster, initially applied to economic parameters, can be easily extended with sustainability parameters.The power of Makersite is that it connects to enterprise systems and sources using AI, Machine Learning and algorithms to support reporting views on compliance, sustainability, costs and risk.
- Compliance and sustainability are the areas where I see a significant need for companies to invest. It is not a revolutionary business change but an extension of scope.We discussed this in the context of the stage-gate process, where sustainability parameters should be added at each gate.
- Neil has an exciting podcast, Five Lifes to Fifty, where he discusses the path to sustainable products with co-hosts Shelley Metcalfe and Jim Fava, and recently, they discussed sustainability in the context of the stage-gate process.
- Again, to move forward with sustainability, it is about creating the base and caring about the data internally to understand what’s happening, and from there, enable value engineering, including your supplier where possible (IP protection remains a topic) – confirming digital transformation (the connected way of working) is needed for business and sustainability.
Want to learn more?
Here are some links to the topics discussed in our meeting:
- The Website – Makersite.io
- Makersite data foundation – makersite-data-foundation
- Makersite demo video – makersite-platform-demo
- Neil’s LinkedIn – neilsaviodsouza
Conclusions
With Makersite, we discovered an experienced company that used its experience in cost, compliance and risk analysis, including supply chains, to extend it to the domain of sustainability. As their technology partners page shows, they can be complementary in many industries and enterprises.
We will see another complementary solution soon in our following interview. Stay tuned.
 It might have been silent in the series of PLM and Sustainability … interviews where we as PLM Green Global Alliance core team members, talk with software vendors, implementers and consultants and their relation to PLM and sustainability. The interviews are still in a stage of exploring what is happening at this moment. More details per vendor or service provider next year.
It might have been silent in the series of PLM and Sustainability … interviews where we as PLM Green Global Alliance core team members, talk with software vendors, implementers and consultants and their relation to PLM and sustainability. The interviews are still in a stage of exploring what is happening at this moment. More details per vendor or service provider next year.
Our last interview was in April this year when we spoke with Mark Reisig, Green Energy Practice Director & Executive Consultant at CIMdata. You can find the interview here, and at that time, I mentioned the good news is that sustainability is no longer a software discussion.
As companies are planning or pushed by regulations to implement sustainable strategies, it becomes clear that education and guidance are needed beyond the tools.
This trend is also noticeable in our PLM Green Global Alliance community, which has grown significantly in the past half year. While writing this post, we have 862 members, not all as active as we hoped. Still, there is more good news related to dedicated contributors and more to come in the next PGGA update.
 This time, we want to share the interview with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services.
This time, we want to share the interview with Erik Rieger and Rafał Witkowski, both working for Transition Technologies PSC, a global IT solution integrator in the PLM world known for their PTC implementation services.
I met them during the LiveWorx conference in Boston in May – you can read more about the conference in my post: The weekend after LiveWorx 2023. Here we decided to follow-up on GreenPLM/
GreenPLM
![]() The label “GreenPLM” is always challenging as it could be considered green-washing. However, in this case, GreenPLM is an additional software offering that can be implemented on top of a PLM system, enabling people to make scientifically informed decisions for a more sustainable, greener product.
The label “GreenPLM” is always challenging as it could be considered green-washing. However, in this case, GreenPLM is an additional software offering that can be implemented on top of a PLM system, enabling people to make scientifically informed decisions for a more sustainable, greener product.
For GreenPLM, Rafal’s and Erik’s experiences are based on implementing GreenPLM on top of the PTC Windchill suite. Listen for the next 34 minutes to an educative session and learn.
You can download the slides shown in the recording here.
What I learned
- It was more a general educative session related to the relation PLM and Sustainability, focusing on the importance of design decisions – the 80 % impact number.
- Erik considers sustainability not a disruption for designers; they already work within cost, quality and time parameters. Now, sustainability is the fourth dimension to consider.
- Erik’s opinion is also reflected in the pragmatic approach of GreenPLM as an additional extension of Windchill using PTC Navigate and OSLC standards.
- GreenPLM is more design-oriented than Mendix-based Sustaira, a sustainability platform we discussed in this series – you can find the recording here.
Want to learn more?
Here are some links related to the topics discussed in our meeting:
Conclusions
With GreenPLM, it is clear that the focus of design for sustainability is changing from a vision (led by software vendors and environmental regulations) towards implementations in the field. Pragmatic and an extension of the current PLM infrastructure. System integrators like Transition Technologies are the required bridge between vision and realization. We are looking for more examples from the field.
Two more weeks to go – don’t miss this opportunity when you are in Europe
Click on the image to see the full and interesting agenda/
 During May and June, I wrote a guest chapter for the next edition of John Stark’s book Product Lifecycle Management (Volume 2): The Devil is in the Details.
During May and June, I wrote a guest chapter for the next edition of John Stark’s book Product Lifecycle Management (Volume 2): The Devil is in the Details.
The book is considered a standard in the academic world when studying aspects of PLM.
Looking into the table of contents through the above link, it shows that understanding PLM in its full scope is broad. I wrote about it recently: PLM is Complex (and we have to accept it?), and Roger Tempest and others are still fighting to get the job as PLM Professional recognized Associate Yourself With Professional PLM.
 To make the scope broader, John invited me to write a chapter about PLM and Sustainability, which is an actual topic in many organizations. As sustainability is my dedicated topic in the PLM Global Green Alliance (PGGA) core team, I was happy to accept this challenge.
To make the scope broader, John invited me to write a chapter about PLM and Sustainability, which is an actual topic in many organizations. As sustainability is my dedicated topic in the PLM Global Green Alliance (PGGA) core team, I was happy to accept this challenge.
This activity is challenging because writing a chapter on a current topic might make it outdated soon. For the same reason, I never wanted to write a PLM book as I wrote in my 2014 post: Did you notice PLM is changing?
 The book, with the additional chapter, will be available later this year. I want to share with you in this post the topics I addressed in this chapter. Perhaps relevant for your organization or personal interests. Also, I am looking forward to learning if I missed any topics.
The book, with the additional chapter, will be available later this year. I want to share with you in this post the topics I addressed in this chapter. Perhaps relevant for your organization or personal interests. Also, I am looking forward to learning if I missed any topics.
Introduction
The chapter starts with defining the context. PLM is considered a strategy supported by a connected IT infrastructure, and for the definition of sustainability, I refer to the relevant SDGs as described on our PGGA theme page: PLM and Sustainability

Next, I discuss two major concepts indissoluble connected with sustainability.
The Circular Economy
On a planet with limited resources and still a growing consumption of raw materials, we need to follow the concepts of the circular economy in our businesses and lives. The circular economy section addresses mainly the hardware side of the butterfly as, here, PLM practices have the most significant impact.
The circular economy requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including businesses, governments and consumers. It involves rethinking production processes and establishing new consumption patterns. Policies and regulations will push for circular economy patterns, as seen in the following paragraphs.
Systems Thinking
A significant change in bringing products to the market will be the need to change how we look at our development processes. Historically, many of these processes were linear and only focused on time to market, cost and quality. Now, we have to look into other dimensions, like environmental impact, usage and impact on the planet. As I wrote in the past Systems Thinking – a must-have skill in the 21st century?
Systems Thinking is a cognitive approach that emphasizes understanding complex problems by considering interconnections, feedback loops, and emergent properties. It provides a holistic perspective and explores multiple viewpoints.
Systems Thinking guides problem-solving and decision-making and requires you to treat a solution with a mindset of a system interacting with other systems.
Regulations
More sustainable products and services will be driven primarily by existing and upcoming regulations. In this section, I refer to the success of the CFC (ChloroFluorCarbon) emission reduction, leading to slowly fixing the hole in the Ozon layer. Current regulations like WEEE, RoHS and REACH are already relevant for many companies, and compliance with these regulations is a good exercise for more stringent regulations related to Carbon emissions and upcoming related to the Digital Product Passport.

Making regulatory compliance a part of the concept phase ensures no late changes are needed to become compliant, saving time and costs. In addition, making regulatory compliance as much as possible with a data-driven approach reduces the overhead required to prove regulatory compliance. Both topics are part of a PLM strategy.
![]() In this context, see Lionel Grealou’s article 5 Brand Value Benefits at the Intersection of Sustainability and Product Compliance. The article has also been shared in our PGGA LinkedIn group.
In this context, see Lionel Grealou’s article 5 Brand Value Benefits at the Intersection of Sustainability and Product Compliance. The article has also been shared in our PGGA LinkedIn group.
Business
On the business side, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol is explained. How companies will have to report their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions and, ultimately, Scope 3 – see the image below for the details.
GHG reporting will support companies, investors and consumers to decide where to prioritize and put their money.
Ultimately, companies have to be profitable to survive in their business. The ESG framework is relevant in this context as it will allow investors to put their money not only based on short-term gains (as expected) but also on Environmental or Social parameters. There are a lot of discussions related to the ESG framework, as you might have read in Vincent de la Mar’s monthly newsletter, Sustainability & ESG Insights, which is also published in our PGGA group – a link below..
Besides ESG guidelines, there is also the drive by governments and consumers to push for a Product as a Service economy. Instead of owning products, consumers would pay for the usage of these products.
The concept is not new when considering lease cars, EV scooters, or streaming services like Spotify and Netflix. In the CIMdata PLM Roadmap/PDT Fall 2021 conference, we heard Kenn Webster explaining: In the future, you will own nothing & you will be happy.
Changing the business to a Product as a Service is not something done overnight. It requires repairable, upgradeable products. And business related, it requires a connected ecosystem of all stakeholders – the manufacturer, the finance company, and the operating entities.
Digital Transformation
All the subjects discussed before require real-time reporting and analysis combined with data access to compliance-related databases. More in the section related to Life Cycle Assessment. As I discussed last year in several conferences, a sustainability initiative starts with data-driven and model-based approaches during the concept phase, but when manufacturing and operating (connected) products in the field. You can read the entire story here: Sustainability and Data-Driven PLM – the Perfect Storm.

Life Cycle Analysis
Special attention is given in this chapter to Life Cycle Analysis, which seems to be a popular topic among PLM vendors. Here, they can provide tools to make a lifecycle assessment, and you can read an impression of these tools in a guest blog from Roger L. Franz titled PLM Tools to Design for Sustainability – PLM Green Global Alliance.
However, Lifecycle Analysis is not as simple. Looking at the ISO 14040 framework, which describes – having the right goals and scope in mind, allows you to do an LCA where the Product Category Rules (PCS) will enable companies to compare their products with others.
PCRs include the description of the product category, the goal of the LCA, functional units, system boundaries, cut-off criteria, allocation rules, impact categories, information on the use phase, units, calculation procedures, requirements for data quality, and other information on the lifecycle Inventory Phase.
So be aware there is more to do than installing a tool.
Digital Twin
 This section describes the importance of implementing a digital twin for the design phase, allowing companies to develop, test and analyze their products and services first virtually. Trade-off studies on virtual products are much cheaper, and when they are done in a data-driven, model-based environment, it will be the most efficient environment. In my terminology, setting up such a collaboration environment might be considered a System of Engagement.
This section describes the importance of implementing a digital twin for the design phase, allowing companies to develop, test and analyze their products and services first virtually. Trade-off studies on virtual products are much cheaper, and when they are done in a data-driven, model-based environment, it will be the most efficient environment. In my terminology, setting up such a collaboration environment might be considered a System of Engagement.
The second crucial digital twin mentioned is the digital twin from a product in operation where performance can be monitored and usage can be optimized for a minimal environmental impact. Suppose a company is able to create a feedback loop between its products in the field and its product innovation platform. In that case, it can benchmark its design models and update the product behavior for better performance.

The manufacturing digital twin is also discussed in the context of environmental impact, as choosing the right processes and resources can significantly affect scope 3 emissions.
The chapter finishes with the story of a fictive company, WePack, where we can follow the impact and implementations of the topics described in this chapter.
Conclusion
As I described in the introduction, the topic of PLM and Sustainability is relatively new and constantly evolving. What do you think? Did I miss any dimensions?
Feel free to contribute to our PLM Global Green Alliance LinkedIn group.
 Last week I enjoyed visiting LiveWorx 2023 on behalf of the PLM Global Green Alliance. PTC had invited us to understand their sustainability ambitions and meet with the relevant people from PTC, partners, customers and several of my analyst friends. It felt like a reunion.
Last week I enjoyed visiting LiveWorx 2023 on behalf of the PLM Global Green Alliance. PTC had invited us to understand their sustainability ambitions and meet with the relevant people from PTC, partners, customers and several of my analyst friends. It felt like a reunion.
In addition, I used the opportunity to understand better their Velocity SaaS offering with OnShape and Arena. The almost 4-days event, with approximately 5000 attendees, was massive and well-organized.
So many people were excited that this was again an in-person event after four years.

With PTC’s broad product portfolio, you could easily have a full agenda for the whole event, depending on your interests.
I was personally motivated that I had a relatively full schedule focusing purely on Sustainability, leaving all these other beautiful end-to-end concepts for another time.
Here are some of my observations
Jim Heppelman’s keynote
The primary presentation of such an event is the keynote from PTC’s CEO. This session allows you to understand the company’s key focus areas.
My takeaways:
- Need for Speed: Software-driven innovation, or as Jim said, Software is eating the BOM, reminding me of my recent blog post: The Rise and Fall of the BOM. Here Jim was referring to the integration with ALM (CodeBeamer) and IoT to have full traceability of products. However, including Software also requires agile ways of working.
- Need for Speed: Agile ways of working – the OnShape and Arena offerings are examples of agile working methods. A SaaS solution is easy to extend with suppliers or other stakeholders. PTC calls this their Velocity offering, typical Systems of Engagement, and I spoke later with people working on this topic. More in the future.
- Need for Speed: Model-based digital continuity – a theme I have discussed in my blog post too. Here Jim explains the interaction between Windchill and ServiceMax, both Systems of Record for product definition and Operation.

- Environmental Sustainability: introducing Catherine Kniker, PTC’s Chief Strategy and Sustainability Officer, announcing that PTC has committed to Science Based Targets, pledging near-term emissions reductions and long-term net-zero targets – see image below and more on Sustainability in the next section.

- A further investment in a SaaS architecture, announcing CREO+ as a SaaS solution supporting dynamic multi-user collaboration (a System of Engagement)
- A further investment in the partnership with Ansys fits the needs of a model-based future where modeling and simulation go hand in hand.
You can watch the full session Path to the Future: Products in the Age of Transformation here.
Sustainability
 The PGGA spoke with Dave Duncan and James Norman last year about PTC’s sustainability initiatives. Remember: PLM and Sustainability: talking with PTC. Therefore, Klaus Brettschneider and I were happy to meet Dave and James in person just before the event and align on understanding what’s coming at PTC.
The PGGA spoke with Dave Duncan and James Norman last year about PTC’s sustainability initiatives. Remember: PLM and Sustainability: talking with PTC. Therefore, Klaus Brettschneider and I were happy to meet Dave and James in person just before the event and align on understanding what’s coming at PTC.
We agreed there is no “sustainability super app”; it is more about providing an open, digital infrastructure to connect data sources at any time of the product lifecycle, supporting decision-making and analysis. It is all about reliable data.
Product Sustainability 101
On Tuesday, Dave Duncan gave a great introductory session, Product Sustainability 101, addressing Business Drivers and Technical Opportunities. Dave started by explaining the business context aiming at greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction based on science-based targets, describing the content of Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 emissions.
The image above, which came back in several presentations later that week, nicely describes the mapping of lifecycle decisions and operations in the context of the GHG protocol.
Design for Sustainability (DfS)
On Wednesday, I started with a session moderated by James Norman titled Design for Sustainability: Harnessing Innovation for a Resilient Future. The panel consisted of Neil D’Souza (CEO Makersite), Tim Greiner (MD Pure Strategies), Francois Lamy (SVP Product Management PTC) and Asheen Phansey (Director ESG & Sustainability at PagerDuty). You can find the topic discussed below:
Some of the notes I took:
- No specific PLM modules are needed, LCA needs to become an additional practice for companies, and they rely on a connected infrastructure.
- Where to start? First, understand the current baseline based on data collection – what is your environmental impact? Next, decide where to start
- The importance of Design for Service – many companies design products for easy delivery, not for service. Being able to service products better will extend their lifetime, therefore reducing their environmental impact (manufacturing/decommissioning)
- There Is a value chain for carbon data. In addition, suppliers significantly impact reaching net zero, as many OEMs have an Assembly To Order process, and most of the emissions are done during part manufacturing.
DfS: an example from Cummins
 Next, on Wednesday, I attended the session from David Genter from Cummins, who presented their Design for Sustainability (DfS) project.
Next, on Wednesday, I attended the session from David Genter from Cummins, who presented their Design for Sustainability (DfS) project.
Dave started by sharing their 2030 sustainability goals:
- On Facilities and Operations: A reduction of 50 % of GHG emissions, reducing water usage by 30 %, reducing waste by 25 % and reducing organic compound emissions by 50%
- Reducing Scope 3 emissions for new products by 25%
- In general, reducing Scope 3 emissions by 55M metric tons.
The benefits for products were documented using a standardized scorecard (example below) to ensure the benefits are real and not based on wishful thinking.
Many motivated people wanted to participate in the project, and the ultimate result demonstrated that DfS has both business value for Cummins and the environment.
The project has been very well described in this whitepaper: How Cummins Made Changes to Optimize Product Designs for the Environment – a recommended case study to read.
Tangible Strategies for Improving Product Sustainability
The session was a dialogue between Catherine Kniker and Dave Duncan, discussing the strategies to move forward with Sustainability.
They reiterated the three areas where we as a PLM community can improve: Material choice and usage, Addressing Energy Emissions and Reducing Waste. And it is worth addressing them all, as you can see below – it is not only about carbon reduction.
It was an informative dialogue going through the different aspects of where we, as an engineering/ PLM community, can contribute. You can watch their full dialog here: Tangible Strategies for Improving Product Sustainability.
Conclusion
It was encouraging to see that at such an event as LiveWorx, you could learn about Sustainability and discuss Sustainability with the audience and PTC partners. And as I mentioned before, we need to learn to measure (data-driven / reliable data), and we need to be able to work in a connected infrastructure (digital thread) to allow design, simulation, validation and feedback to go hand in hand. It requires adapting a business strategy, not just a tactical solution. With the PLM Global Green Alliance, we are looking forward to following up on these.
NOTE: PTC covered the expenses associated with my participation in this event but did not in any way influence the content of this post – I made my tour fully independent through the conference and got encouraged by all the conversations I had.
We are happy to start the year with the next PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series round: PLM and Sustainability.
Last year we spoke mainly with the prominent PLM software editors (Aras, Autodesk, Dassault Systèmes, PTC, SAP) and Sustaira (Sustainability platform – Siemens partner).
 This time we talked with Mark Reisig, Sustainability and Green Energy Practice Director & Executive Consultant from CIMdata. The good news is that discussing a PLM strategy and Sustainability is no longer a software discussion.
This time we talked with Mark Reisig, Sustainability and Green Energy Practice Director & Executive Consultant from CIMdata. The good news is that discussing a PLM strategy and Sustainability is no longer a software discussion.
With CIMdata’s sustainability offering introduced last year, it becomes clear that the topic of sustainability reached a broader level than the tools.
CIMdata
 CIMdata is well known in the PLM domain, focusing on Market Analysis, Education, Research & Strategic Management Consulting, all related to PLM.
CIMdata is well known in the PLM domain, focusing on Market Analysis, Education, Research & Strategic Management Consulting, all related to PLM.
Last year, Mark joined CIMdata as Green Energy Practice Director & Executive Consultant. Listening to Mark, you will discover he has an exciting background, starting with the “Keeling Curve”, his early interest in oceanography and wind turbines, working with GE later in his career and many years active in the PLM domain.
Learn more from the 40 minutes discussion with Mark below.
You can download the slides shown during the recording HERE
What we have learned
 CIMdata has been discussing and promoting a circular economy already for a long time. A sustainable future and a circular economy have been a theme in many of the PLM Roadmap & PDT conferences. It is a logical relation as implementing a circular strategy depends significantly on the product design approach.
CIMdata has been discussing and promoting a circular economy already for a long time. A sustainable future and a circular economy have been a theme in many of the PLM Roadmap & PDT conferences. It is a logical relation as implementing a circular strategy depends significantly on the product design approach. CIMdata also combines Sustainability with the need to digitize the processes and data handled. A data-driven approach will allow companies to measure (and estimate) better their environmental impact.
CIMdata also combines Sustainability with the need to digitize the processes and data handled. A data-driven approach will allow companies to measure (and estimate) better their environmental impact.- CIMdata believes sustainability must be embedded in PLM for companies to reduce their product carbon footprint, and they must have greater visibility into their supply chain.
 Mark mentions that focusing on a sustainable business model (product & business) is crucial for survival in the upcoming years, and this has increasingly landed at the board level of companies.
Mark mentions that focusing on a sustainable business model (product & business) is crucial for survival in the upcoming years, and this has increasingly landed at the board level of companies.- The major change has to be driven by the business. PLM vendors will not drive the change; they will align their portfolio offerings based on the market needs.
- It was clear Mark has a lot of experience in wind energy throughout his whole lifecycle 😊
Want to learn more
Mark already pointed to several valuable resources in our discussion to learn more. Here are the most important links related to CIMdata
- Sustainability and Green Energy Consulting Practice
 Recent webinar: The Green Energy Transition and Sustainability from January 23, 2023
Recent webinar: The Green Energy Transition and Sustainability from January 23, 2023- Upcoming webinar: Meeting Sustainability and Green Energy Transition Objectives: The Industrial Perspective, April 27, 2023, 11:00 AM EDT
Conclusions
Last year we discussed sustainability with the software vendors and their product offerings. They all mentioned the importance of a data-driven approach and education. CIMdata has broadened the available sustainability offering for companies by providing additional education and strategy support.
Education at all levels is essential to make sustainable decisions. Sustainable for the company’s business and, above all, sustainable for the planet.
I will be @Livework in Boston, aiming to discuss PLM and Sustainability on behalf of the PGGA with PTC thought leaders. Will you be there too?
![]() In this post, I want to explain why Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) and Sustainability are closely connected. I would claim sustainability in our PLM domain will depend on MBSE.
In this post, I want to explain why Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) and Sustainability are closely connected. I would claim sustainability in our PLM domain will depend on MBSE.
Can we achieve Sustainability without MBSE? Yes, but it will be costly and slow. And as all businesses want to be efficient and agile, they should consider MBSE.
What is MBSE?
The abbreviation MBSE stands for Model-Based Systems Engineering, a specialized manner to perform Systems Engineering. Look at the Wikipedia definition in short:
MBSE is a technical approach to systems engineering that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models as the primary means of information exchange rather than on document-based information exchange.
Model-Based fits in the digital transformation scope of PLM – from a document-based approach to a data-driven, model-based one. In 2018, I focused on facets of the model-based enterprise and related to MBSE in this post: Model-Based: System Engineering (MBSE).
My conclusion in that post was:
Model-Based Systems Engineering might have been considered as a discipline for the automotive and aerospace industry only. As products become more and more complex, thanks to IoT-based applications and software, companies should consider evaluating the value of model-based systems engineering for their products/systems.
I drew this conclusion before I focused on sustainability and systems thinking. Implementing sustainability concepts, like the Circular Economy, require more complex engineering efforts, justifying a Model-Based Systems Engineering approach. Let’s have a look.
If you want to learn more about why we need MBSE, look at this excellent keynote speech lecture from Zhang Xin Guo at the Incose 2018 conference below:
The Mission / the stakeholders
A company might deliver products to the market with the best price/quality ratio and regulatory compliance, perceived and checked by the market. This approach is purely focusing on economic parameters.
There is no need for a system engineering approach as the complexity is manageable. The mission is more linear, a “job to do,” and a limited number of stakeholders are involved in this process.

… with sustainability
 Once we start to include sustainability in our product’s mission, we need a systems engineering approach, as several factors will push for different considerations. The most obvious considerations are the choice of materials and the optimizing the production process (reducing carbon emissions).
Once we start to include sustainability in our product’s mission, we need a systems engineering approach, as several factors will push for different considerations. The most obvious considerations are the choice of materials and the optimizing the production process (reducing carbon emissions).
However, the repairability/serviceability of the product should be considered with a more extended lifetime vision.
What about upgradeability and reusing components? Will the customer pay for these extra sustainable benefits?
 Probably Yes, when your customer has a long-term vision, as the overall lifecycle costs of the product will be lower.
Probably Yes, when your customer has a long-term vision, as the overall lifecycle costs of the product will be lower.
Probably No if none of your competitors delivers non-sustainable products much cheaper.
As long as regulations will not hurt traditional business models, there might be no significant change.
 However, the change has already started. Higher energy prices will impact the production of specific resources and raise costs. In addition, energy-intensive manufacturing processes will lead to more expensive materials. Combined with raising carbon taxes, this will be a significant driver for companies to reconsider their product offering and manufacturing processes.
However, the change has already started. Higher energy prices will impact the production of specific resources and raise costs. In addition, energy-intensive manufacturing processes will lead to more expensive materials. Combined with raising carbon taxes, this will be a significant driver for companies to reconsider their product offering and manufacturing processes.
The more expensive it becomes to create new products, the more attractive repairable and upgradable products will become. And this brings us to the concept of the circular economy, which is one of the pillars of sustainability.
 In short, looking at the diagram – the vertical flow from renewables and finite materials from part to product to product in service leads ultimately to wasted resources if there are no feedback loops. This is the traditional product delivery process that most companies are using.
In short, looking at the diagram – the vertical flow from renewables and finite materials from part to product to product in service leads ultimately to wasted resources if there are no feedback loops. This is the traditional product delivery process that most companies are using.
You can click on the image to the left to zoom in on the details.
 The renewable loop on the left side of the diagram is the usage of renewables during production and the use of the product. The more we use renewables instead of fossil fuels, the more sustainable this loop will be. This is the area where engineers should use simulations to find the optimal manufacturing processes and product behavior. Again click on the image to zoom in on the details.
The renewable loop on the left side of the diagram is the usage of renewables during production and the use of the product. The more we use renewables instead of fossil fuels, the more sustainable this loop will be. This is the area where engineers should use simulations to find the optimal manufacturing processes and product behavior. Again click on the image to zoom in on the details.
 The right side of the loop, related to the materials, is where we see the options for repairable, serviceable, upgradeable, and even further refurbishment and recycling to avoid leakage of precious materials. This is where mechanical engineers should dominate the activities. Focussing on each of the loops and how to enable them in the product. Click on the image to see the relevant loops.
The right side of the loop, related to the materials, is where we see the options for repairable, serviceable, upgradeable, and even further refurbishment and recycling to avoid leakage of precious materials. This is where mechanical engineers should dominate the activities. Focussing on each of the loops and how to enable them in the product. Click on the image to see the relevant loops.
Looking at the circular economy diagram, it is clear that we are no longer talking about a linear process – it has become the implementation of a system. Systems Engineering or MBSE?
The benefits of MBSE
Developing products with the circular economy in mind is no longer a “job to do,” a simple linear exercise. Instead, if we walk down the systems engineering V-shape, there are a lot of modeling exercises to perform before we reach the final solution.
To illustrate the benefits of MBSE, let’s walk through the following scenario.
 A well-known company sells lighting projects for stadiums and public infrastructure. Their current business model is based on reliable lighting equipment with a competitive price and range of products.
A well-known company sells lighting projects for stadiums and public infrastructure. Their current business model is based on reliable lighting equipment with a competitive price and range of products.
Most of the time, their contracts have clauses about performance/cost and maintenance. The company sells the products when they win the deal and deliver spare parts when needed.
Their current product design is quite linear – without systems engineering.
Now this company has decided to change its business model towards Product As A Service, or in their terminology LaaS (Lightening as a Service). For a certain amount per month, they will provide lighting to their customers, a stadium, a city, and a road infrastructure.
To implement this business model, this is how they used a Model-Based Systems Engineering approach.
Modeling the Mission
Before even delivering any products, the process starts with describing and analyzing the business model needed for Lightening as a Service.
Then, with modeling estimates about the material costs, there are exercises about the resources required to maintain the service, the potential market, and the possible price range.
It is the first step of using a model to define the mission of the service. After that, the model can be updated, adjusted, and used for a better go-to-market approach when the solution becomes more mature.
Part of the business modeling is also the intention to deliver serviceable and upgradeable products. As the company now owns the entire lifecycle, this is the cheapest way to guarantee a continuous or improved service over time.
Modeling the Functions
Providing Lighting as a Service also means you must be in touch with your installations in real time. Power consumption needs to be measured and analyzed in real-time for (predictive) maintenance, and the light-providing service should be as cheap as possible during operation.
Therefore LED technology is the most reliable, and connectivity functions need to be implemented in the solution. The functional design ensures installation, maintenance and service can be done in a connected manner (cheapest in operation – beneficial for the business).
Modeling the Logical components
As an owner of the solution, the design of the logical components of the lighting solution is also crucial. How to address various lighting demands efficiently? Modularity is one of the first topics to address. With modular components, it is possible to build customer-specific solutions with a reduced engineering effort. However, the work needs to be done by generically designing the solutions and focusing on the interfaces.
Such a design starts with a logical process and flow diagrams combined with behavior modeling. Without already having a physical definition, we can analyze the components’ behavior within an electrical scheme. Decisions on whether specific scenarios will be covered by hardware or software can be analyzed here. The company can define the lower-level requirements for the physical component by using virtual trade-offs on the logical models.
At this stage, we have used business modeling, functional modeling and logical modeling to understand our solution’s behavior.
Modeling the Physical product
The final stage of the solution design is to implement the logical components into a physical solution. The placement of components and interfaces between the components becomes essential. For the physical design, there are still a lot of sustainability requirements to verify:
- Repairability and serviceability – are the components reachable and replaceable? Reducing the lifecycle costs of the solution
- Upgradeability – are there components that can behave differently due to software choices, or are there components that can be replaced with improved functionality. Reducing the cost of creating entirely new solutions.
- Reuse & recyclable – are the materials used in the solution recyclable or reusable, reducing the cost of new materials or reducing the cost of dumping waste.
- RoHS/ REACH compliance
The image below from Zhang Xin Guo’s presentation nicely demonstrates the iterative steps before reaching a physical product
 Before committing to a hardware implementation, the virtual product can be analyzed, behavior can be simulated, and it carbon impact can be calculated for the various potential variants.
Before committing to a hardware implementation, the virtual product can be analyzed, behavior can be simulated, and it carbon impact can be calculated for the various potential variants.
The manufacturing process and energy usage during operation are also a part of the carbon impact calculation. The best performing virtual solution, including its simulations models, can be chosen for the realization to ensure the most environmentally friendly solution.
The digital twin for follow-up
Once the solution has been realized, the company still has a virtual model of the solution. By connecting the physical product’s observed and measured behavior, the virtual side’s modeling can be improved or used to identify improvement candidates – maintenance or upgrades. At this stage, the virtual twin is the actual twin of the physical solution. Without going deeper into the digital twin at this stage, I hope you also realize MBSE is a starting point for implementing digital twins serving sustainability outcomes.
The image below, published by Boeing, illustrates the power of the connected virtual and physical world and the various types of modeling that help to assess the optimal solution.
Conclusion
For sustainability, it all starts with the design. The design decisions for the product contribute for 80 % to the carbon footprint of the solution. Afterward, optimization is possible within smaller margins. MBSE is the recommended approach to get a trustworthy understanding and follow-up of the product’s environmental impact.
What do you think can we create sustainable products without MBSE?
 We are happy to close the year with the first round of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability.
We are happy to close the year with the first round of the PLM Global Green Alliances (PGGA) series: PLM and Sustainability.
We interviewed PLM-related software vendors in this series, discussing their sustainability mission and offering.
We talked with SAP, Autodesk, Dassault Systèmes, Sustaira and Aras and now with PTC. It was an exciting discussion, looking back at their Lifecycle Analysis (LCA) history and ending with a cliffhanger about what’s coming next year.
PTC
 The discussion was with Dave Duncan, VP Sustainability at PTC, focusing on industrial Sustainability as well as PTC’s internal footprint reduction programs, joined by James Norman, who globally leads PTC’s Community of Practice for PLM and Design-for-Sustainability.
The discussion was with Dave Duncan, VP Sustainability at PTC, focusing on industrial Sustainability as well as PTC’s internal footprint reduction programs, joined by James Norman, who globally leads PTC’s Community of Practice for PLM and Design-for-Sustainability.
Interesting to notice from this discussion, listen to the introduction of Dave and James and their history with Sustainability long before it became a buzzword and then notice how long it takes till digital thread and digital twin are mentioned – enjoy the 38 minutes of interaction below
Slides shown during the interview combined with additional company information can be found HERE.
What we have learned
- It was interesting to learn that just before the financial crisis in 2008, PTC invested (together with James Norman) in lifecycle analysis. But, unfortunately, a focus on restoring the economy silenced this activity until (as Dave Duncan says) a little more than six months ago, when Sustainability is almost in the top 3 of every company’s agenda.
- Regulation and financial reporting are the current drivers for companies to act related to Sustainability.
- The digital thread combined with the notion of relying on data quality are transformational aspects.
- Another transformational aspect is connecting sustainability as an integrated part of product development instead of a separate marketing discipline.
- Early next year, we will learn more about the realization of the PTC Digital Twin.
Want to learn more
Here are some links to the topics discussed in our meeting:
- The Innovators Program
- The Cummins Case Study
- The PTC Digital Twin description
- The PTC ServiceMax announcement
Conclusions
It was great to conclude with PTC this year. I hope readers following this series: “The PLM Global Green Alliance meets …” has given a good first impression of where PLM-related vendors are heading regarding their support for a sustainable future.
We touched base with them, the leaders, and the experts in their organizations. We discussed the need for data-driven infrastructures, the relation with the circular economy and compliance.
Next year we plan to follow up with them, now looking more into the customer experiences, tools, and methodology used.


























Interesting reflection, Jos. In my experience, the situation you describe is very recognizable. At the company where I work, sustainability…
[…] (The following post from PLM Green Global Alliance cofounder Jos Voskuil first appeared in his European PLM-focused blog HERE.) […]
[…] recent discussions in the PLM ecosystem, including PSC Transition Technologies (EcoPLM), CIMPA PLM services (LCA), and the Design for…
Jos, all interesting and relevant. There are additional elements to be mentioned and Ontologies seem to be one of the…
Jos, as usual, you've provided a buffet of "food for thought". Where do you see AI being trained by a…